Nucleic Acids
Nucleic Acids
What is the main function of carbohydrates in humans?
What is first energy source?
Protein tertiary structure is held together by what?
What is R-group interactions?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic acids are known as what?
What are macromolecules?
Strong cohesion along the air-water interface of a body of water creates what property of water?
What is surface tension?
Amino Acids in their primary structure are held together by what type of bond?
What is a peptide bond?
The 4 nitrogenous bases of a DNA molecule include...
What is Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine
This is the site of protein synthesis, it builds the primary structure
What is the ribosome?
DAILY DOUBLE
When error bars do NOT overlap, data is known to be what?
What is data is significant?
What type of bond is shown below between the Hydrogen and Oxygen?
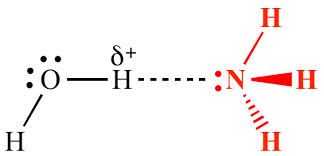
What is a Covalent Bond
What type of charge would a positively charged molecule be attracted to?
What is a negative charge?
What is the elemental composition & structure of Carbohydrates?
What is Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen in a hexamer ring structure?
What two types of fats make up fatty acids?
What are saturated and unsaturated fats?
Name the macromolecule used for first energy as well as the macromolecule used for second energy in a food crisis.
What is Carbohydrates & Lipids?
Oxygen's larger electronegativity allows it to pull hydrogen's electrons towards itself. This gives it a slight negative charge while hydrogen gains a slight positive charge. This property is known as what?
What is Polarity?
What type of bond is shown below between the Hydrogen and Nitrogen?
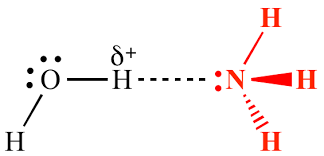
What is a Hydrogen Bond
DAILY DOUBLE
List 3 differences between a DNA & RNA molecule
DNA is double stranded; RNA is single stranded
Nitrogenous Bases for DNA: A, C, G, T; RNA: A, U, C, G
DNA has a deoxyribose sugar; RNA: ribose sugar
DNA has the genetic code; RNA is a small copy of the genetic code.
DNA can't leave the nucleus; RNA has to leave the nucleus
What is the difference between Tertiary and Quaternary Protein Folding?
Tertiary - Proteins collapse & are functional. All proteins have this structure.
Quaternary - Proteins are attached to other proteins to make them larger. NOT all proteins are built to this structure!
What is the difference between an independent and dependent variable?
Independent = What the scientist changes/experiments on
Dependent = What the scientist measures/looks at for change
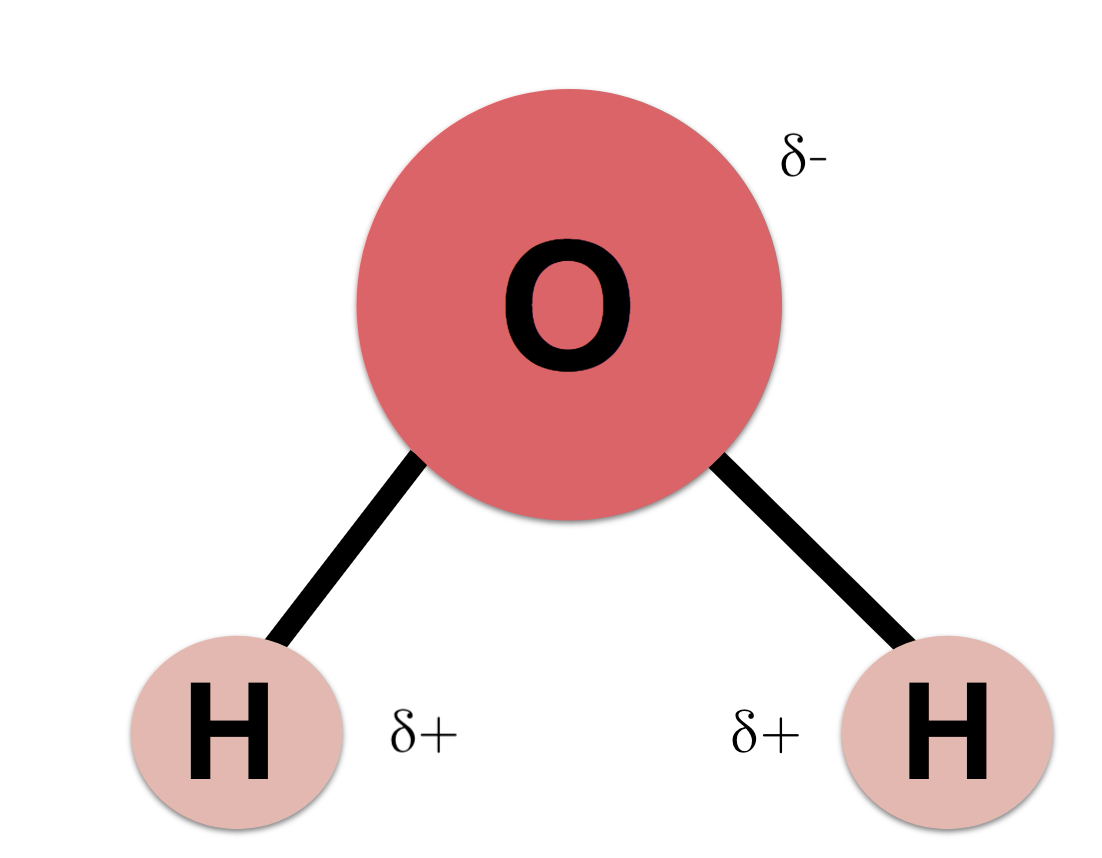
Draw a water molecule.
What is:
Why do hydrophobic molecules position themselves on the inside of their structure?
What is to avoid the hydrogen bonds with water?
Sucrose is a dimer made up of one glucose molecule and one fructose molecule. If Sucrose goes through dehydration synthesis, its becoming what type of "-mer" molecule?
It is becoming a polymer - 3 or more?
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats contain only single bonds.
Unsaturated fats contain double bonds.
DAILY TRIPLE
Explain how an Ant and it's Colony is similar to a monomer of a macromolecule.
An Ant has a specific job. It works with other ants that have the same job to accomplish a task to benefit the Queen and thus the future generations of the colony.
Monomers have specific functions. They can be build into functional macromolecules that have a job to accomplish a task that will benefit the cell and thus future generations of cells.
Water moves up the roots & stalks/trunks of plants due to Capillary Action - the combination of these two types of water attractions.
What is cohesion and adhesion?
DAILY DOUBLE
List the monomer for each Macromolecule:
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
Lipids: Fatty Acids (Saturated or Unsaturated Fat)
Proteins: Amino Acids (Carboxyl, Amino, & R-group)
Nucleic Acids: Nucleotide (sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base)
Carbohydrates: Monosaccharide (Glucose, Fructose, or Galactose)