The measure of angle 2. 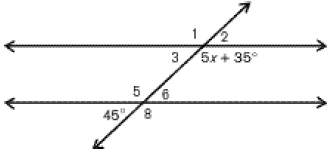
What is 45 degrees?
The slope of the line parallel to
y=-2x+4
What is -2?
The point of intersection
What is
(1,2)
The scale factor in the dilation shown 
The term describing congruent angles such as 3 and 6. 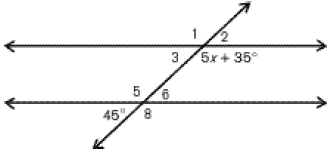
What are alternate interior angles?
The slope of the line perpendicular to
(y-3)=4/3(x+1)
What is
-3/4
The intersection between
y=1 and y=-2x+1
What is
(1,-1)
What is the image point of (4,−7) after a translation right 4 units and up 5 units?
(8, -2)
The value of x. 
What is 8?
The slope between the two points
(-2,1) and (3,-2)
What is
-3/5
The intersection between
y=x and y=3x-4
What is
(2,2)
An example of a non-rigid transformation.
The value of angle c.

What is 68?
The point slope equation passing through
(2,1) and (15,10).
What is
(y-1)=9/13(x-2) or (y-10)=9/13(x-15)
The intersection of
y=9x and y=3+12
What is
(2,18)
The function to describe the transformation from
B (0,4) to B' (0,-4) and G (1, -2) to G' (-1, 2)
What is
(-x,-y)
The value of x.
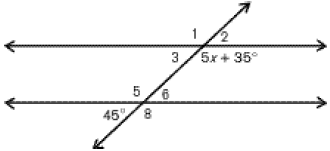
What is 20?
The standard form equation for
y = 1/2x - 3
What is
x-2y=6
The intersection of
4x−5y=46 and -4x-4y=8
What is
(4,-6)
The end coordinates of line segment undergoing a dilation (0.5x, 0.5y) starting at
A (2, 4) and B (6, -2)
What are
A' (1, 2) and B' (3, -1)
