How do you calculate marginal benefit?
Change in total benefit
The opportunity cost of producing a unit of Toys in country A is: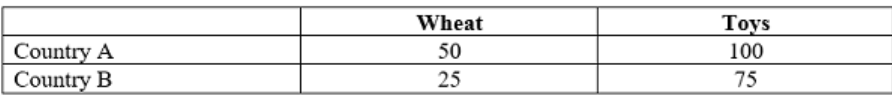
1/2 wheat
What will Country A specialize in?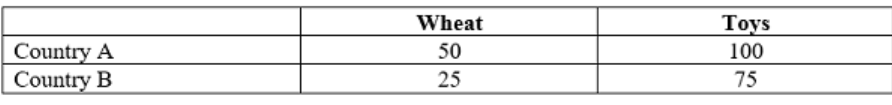
Wheat
Adam has $20 of daily income that can be spent on books (B) and pencils (P). The price of a book is $5 and the price of a pencil is $0.50. Which of the following bundles of books and pencils is currently affordable but does not use all of Adam's income?
a. 1 book and 30 pencils
b. zero books and 40 pencils
c. 2 books and 20 pencils
d. 1 book and 10 pencils
e. 4 books and 10 pencils
D
Draw a PPC curve with Consumer Goods on X axis and Capital Goods on Y axis.
On the PPC below, label a point where society decides to devote more resources toward producing items that help increase future production
Closer to capital versus consumer
Freddy has eaten three corn dogs at the county fair and knows that if he eats another, he will get sick on the roller coaster. Knowing this, and ignoring any impact that price might have on his decision, we can say that the marginal utility is
less than 0
What is the O.C of a Peach in Westland?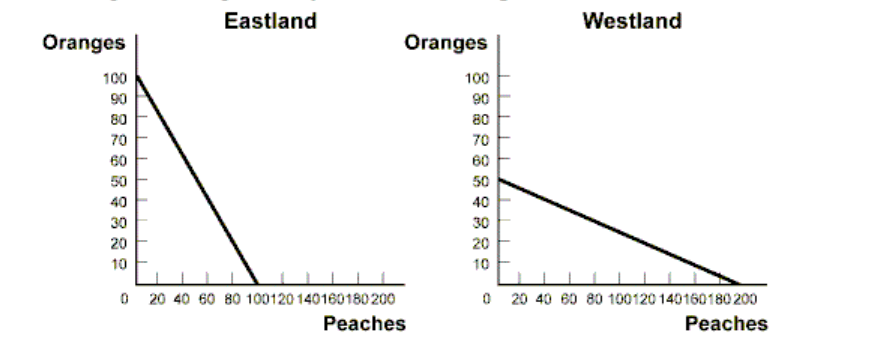
1/4 Orange
What would US specialize in?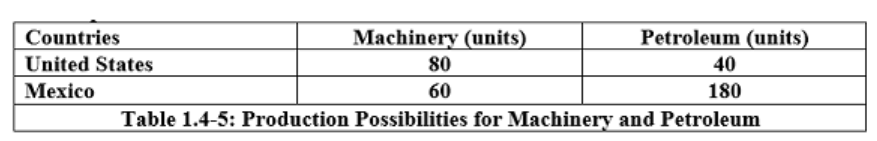
Machinery
Jie consumes 3 units of broccoli and 6 units of rice each week. The price of broccoli is $2 per unit and the price of rice is $4 per unit. Jie's marginal utility from the last unit of broccoli consumed is 4 utils while her marginal utility from her consumption of rice is 8 utils. If Jie wants to maximize her utility, Jie should:
a. increase her broccoli consumption and decrease her rice consumption.
b. increase her rice consumption and decrease her broccoli consumption.
c. continue to consume the amounts of broccoli and rice she is currently consuming.
d. stop consuming both goods.
e. increase her rice consumption and increase her broccoli consumption.
C
Suppose the economy is now producing only pears. The first piston, which is achieved at point T, would have an opportunity cost of ____ tons of pears.
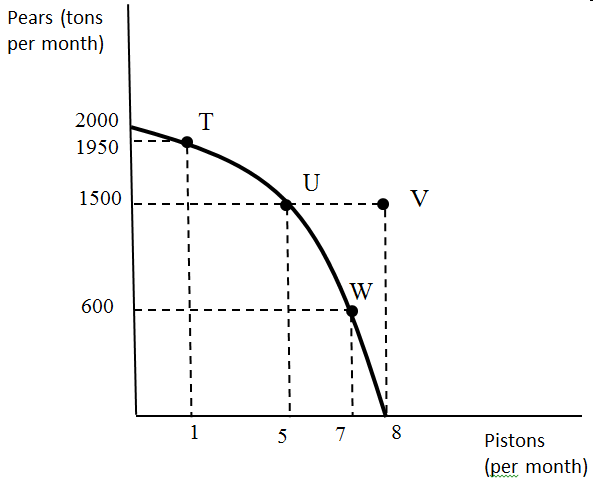
50
You should stop participating in an activity when
Marginal cost intersects (is equal to) marginal benefit
The opportunity cost of producing a unit of wheat in Country B is: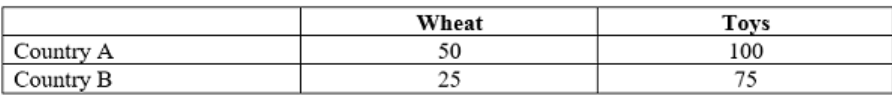
3 Toys
What will Eastland specialize in?
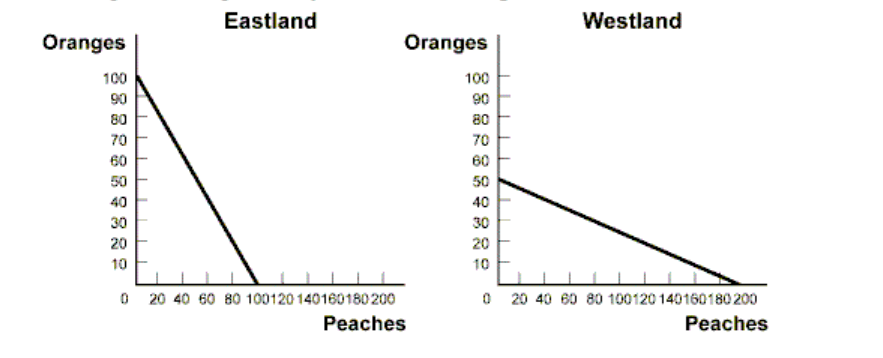
Orange production
Benny spends all his money buying wine and cheese. The marginal utility of the last bottle of wine is 60, and the marginal utility of the last block of cheese is 30. The price of wine is $3, and the price of cheese is $2. Benny:
a. is buying wine and cheese in the utility-maximizing amounts.
b. should buy more wine and less cheese.
c. should buy more cheese and less wine.
d. is spending too much money on wine and cheese.
e. should buy more cheese and more wine.
B
If the economy is operating at point A and its relevant PPF is Curve 2, this means that:
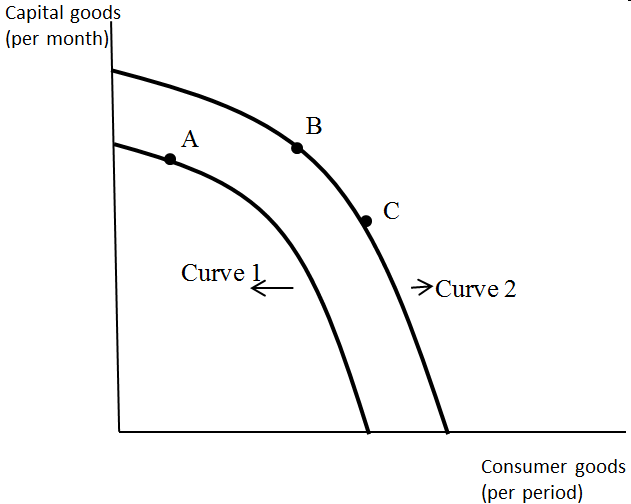
Inefficiencies
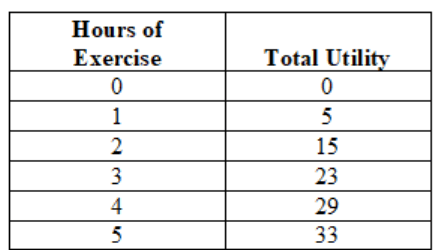
What is the marginal utility of the 3rd exercize
+8
What is the opportunity cost of an Orange in Westland?
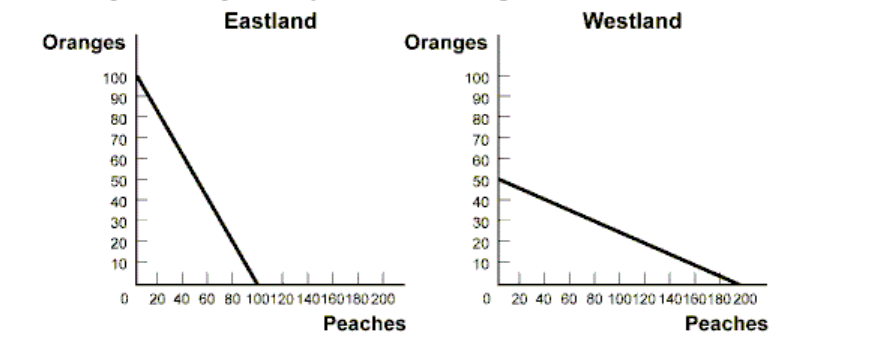
4 Peaches
What would Jackson specialize in?
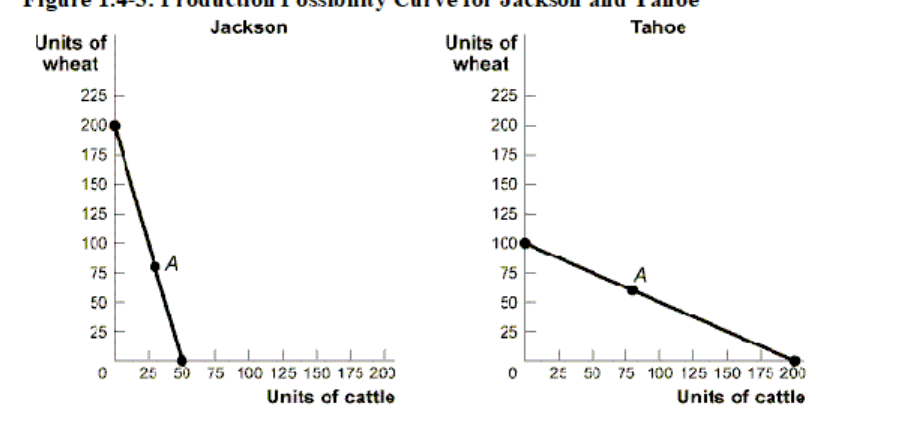
Wheat
Candy = $1 ... Soda = $2
IF you had $9, and you wanted to maximize utility... what/how much would you buy
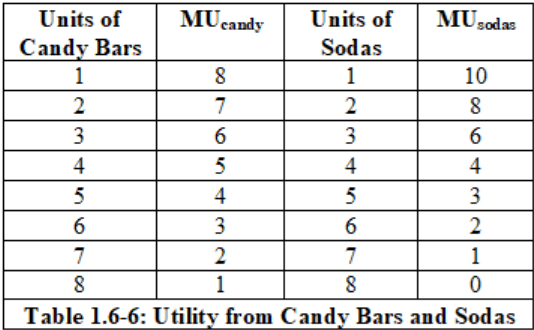
5 Candy Bars + 2 Sodas
If Largetown decides to devote half of its 80 hours of labor time toward the production of socks and half of the time to the production of shirts, what is the maximum number of socks and shirts it can produce?
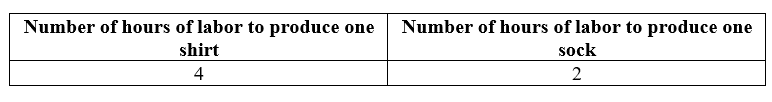
10 Shirts and 20 Socks
At what unit, do we experience diminishing marginal returns?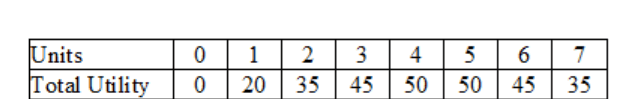
At unit 2
+20 then +15
An economy that has the lowest opportunity cost for producing a particular good is said to have a(n):
Comparative advantage
What will Finland specialize in: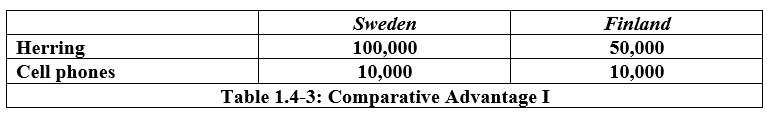
Cell Phones
If an economy has used up all opportunities to make someone better off (without making someone else worse off) then it has achieved ____.
Efficiency
If Farmer Sam MacDonald can produce 200 pounds of cabbages and 0 pounds of potatoes or 0 pounds of cabbages and 100 pounds of potatoes and faces a linear production possibility curve for his farm, the opportunity cost of producing an additional pound of cabbage is ____ pound(s) of potatoes.
1/2
If Urbanville is currently producing at Combination C and moves to Combination D, what is its opportunity cost of this move?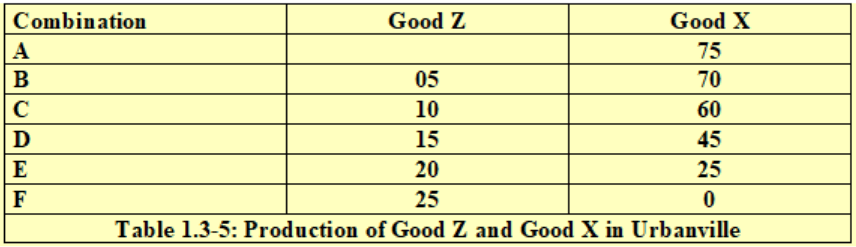
15 X
The opportunity cost of 1 cell phone for finland is: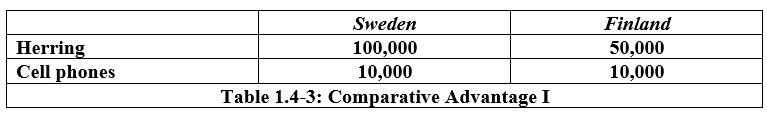
5 Herring
When consumers and producers are behaving rationally and making decisions that are optimal, they are acting as ____.
Rational agents
The opportunity cost of 1 Herring for Sweden is: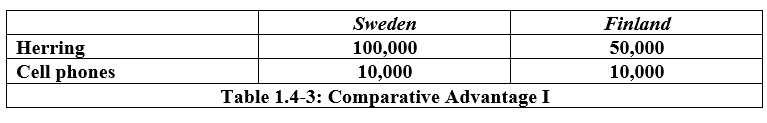
1/10 cell phone