A -12 N force acts on a 3 kg cart at rest. What is the acceleration of the cart?
-4 m/s2
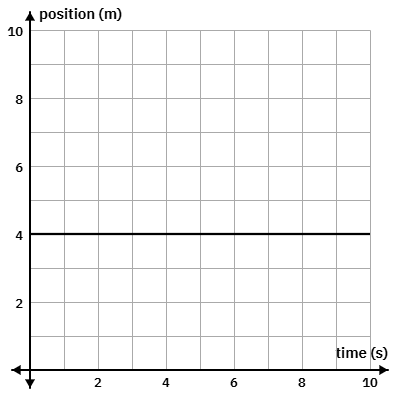
The object is
* not moving
* moving right at a constant velocity
* moving left at a constant velocity
* accelerating right
* accelerating left
What is its velocity?
Not moving
Velocity = 0 m/s
Two students push on opposite sides of a door with equal forces at the same time. What happens to the motion of the door? Why?
The forces are balanced so the door does not move.
You apply a force of 20 N over 2 m to push a box forward. How much work do you do? Include units.
W = Fd
= 20*2
= 40 J
Two cars of identical mass are parked on two different hills. Hill A has an angle of 25 degrees with the street while hill B has an angle of 45 degrees with the street. Which car is in more danger of sliding down the hill? Explain with a model.
Car B.
Greater component of weight along the hill. (parallel) (Fwx)
A 4 kg block accelerates at +2.5 m/s². What is the net force on the block?
+10 N
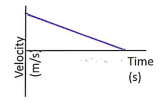
The object is
* not moving
* moving right at a constant velocity
* moving left at a constant velocity
* moving right and speeding up
* moving right and slowing down
* moving left and speeding up
* moving left and slowing down
Is the acceleration positive or negative?
Moving right (positive velocity)
Slowing down (velocity approaching zero)
acceleration is negative (slope is negative)
An astronaut pushes herself off from the spaceship and keeps moving without coming to a stop. Name and explain the physics concept that explains why this happens.
Bonus: Why would the same not happen on earth?
Inertia: an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by external force.
Bonus -- there is friction on earth which provides a stopping force.
A student applies 50 N of force on a 0.25 m² area. What pressure does the student apply? Include units.
P = F/a
= 50/0.25
= 200 Pa
Marshan who has a mass of 100 kg does a wall push-up so her body is at a 45 degree angle to the ground. Is more of her weight in her arms or her legs? Support with calculations.
Equal! Marshan cannot do this pushup :)
A 5 kg object is pulled right with 30 N and left with 20 N. Find the magnitude and direction of its acceleration.
+2 m/s2
Calculate this object's velocity. Include sign and units
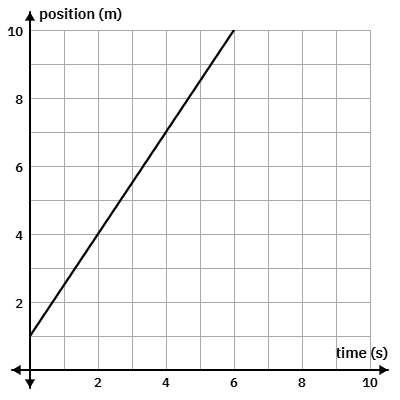
v = +1.5 m/s2
A factory worker pushes a cart with a force of 10N. What force does the cart exert on the factory worker? Why?
10N in the opposite direction. This is an action-reaction pair.
How much work is done pushing a 15 kg suitcase 2 m? Include units.
= 15 *9.8 * 2
= 294 J
A 5 kg block rests on a 30° incline. Calculate the weight component parallel to the ramp. Round to 2 decimal places. Include units
Fwx = 24.53 N
A 2 kg block on a table is pulled with 14 N to the right and experiences 6 N of friction. Draw an FBD and find the block’s acceleration.
Fnet = +8 N
a = +4 m/s2
Calculate this object's acceleration. Include a sign and units.
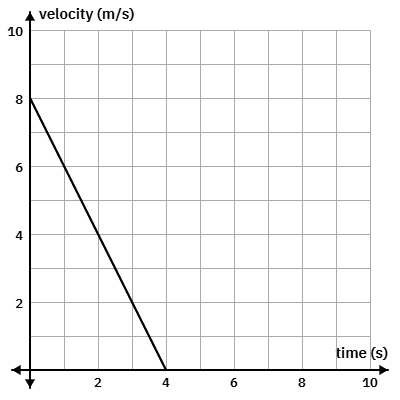
acceleration = -2 m/s2
The car suddenly brakes because the driver almost missed a red light. What happens to the people in the car? Why?
Bonus: What would prevent this from happening? Explain.
Their bodies lurch forward. Their body is an object in motion so it will stay in motion. The force of the brakes only applied to the car, not to the people.
Bonus: Seatbelt or hold on to something. That would provide an external force to slow the person down as well.
A student molding some clay doubles the applied force and also uses twice the surface area. What happens to the pressure?
pressure does not change. the two changes cancel each other out.
A 3 kg object sits on a 40° incline. Calculate the perpendicular component of its weight. Round to 2 decimal places and include units.
22.54 N
A 1.5 kg object is pulled horizontally with 4 N while friction is 10 N. Find acceleration.
-4 m/s2
Analyze the graph. Choose the right option, then sketch the velocity-time graph.
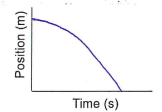
The object is:
a. moving forward and speeding up
b. moving forward and slowing down
c. moving backward and speeding up
d. Moving backward and slowing down
c. moving backward and speeding up.
The position starts away from the origin and slowly goes down to zero (origin).
The slope keeps increasing.
v-t graph:
A person on roller skates pushes on the wall. The person slides backwards but the wall remains standing. The two are an action-reaction pair -- why doesn't the wall move?
The wall has more mass than the person
The wall is stabilized by other forces (ceiling and floor hold it in place) while the person is free to move (no other forces holding the skater in place).
How much work is done lifting a 50 kg crate 1.2 m? Include units.
W = m*g*d
= 50 * 9.8 * 1.2
= 588 J
A 4 kg object on a 25° ramp slides down. Find its acceleration if there is no friction.
Fwx = 16.58 N
a = F/m
= 16.58/4
= 4.15 m/s2