Negatively charged particles that move around the nucleus of an atom are called
electrons
True or False: Due to biomagnification toxic compounds will build up in the cells of plants over time.
False, this is Bioaccumulation.
This term means "feeding level" and is a good estimate of how much energy from the sun is passed to each organism.
Trophic Level
What three elements make up most of the major macromolecules?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
A type of protein that speeds up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy.
What are Enzymes?
What three things do plants need to make food?
Energy from the sun, CO2 & Water
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy
A chemical reaction that STORES energy & heat in chemical bonds is called this...
Endothermic or Anabolic
What type of organism is responsible for the processes of nitrogen fixation that removes nitrogen from the atmosphere and denitrification that returns nitrogen to the atmosphere.
Bacteria / Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
What type of organism must make up the highest percentage of biomass in the environment?
Producers / Autotrophs
Glycogen in animals and Starch in plants are the stored forms of this macromolecule.
Carbohydrates
The primary functions of Carbohydrates
What is short term energy and cell wall?
What do plants combine to make sugars?
CO2 (by turning it into 3-Carbon molecules)
The overall equation of cellular respiration (include the energy)
O2 + Glucose -> CO2 + H2O + ATP
Carbon is important to our study of biological molecules because it:
Is the main element in all molecules of life
Why is nitrogen fixation such an important process to living things?
Nitrogen in the atmosphere is not useable by organisms and must first be converted into a useable form.
Approximately how much energy is transferred up each trophic level?
10%
These lipids are found in the cell membrane.
What are phosphlipids?
These are the three types of nucleic acids
DNA, RNA, ATP
What role does the Electron Transport Chain play in Photosynthesis?
Create ATP for the Calvin Cycle / Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reactions
What is anaerobic cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration without the presence of oxygen; fermentation
Unravel or unwind
List the four major nutrient cycles and one type of macromolecule or other chemical required for life by each.
Phosphorous -- Nucleic Acids
Nitrogen -- Proteins / Nucleic Acids
Carbon -- Lipids, Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acids, or Proteins
Water Cycle -- required for life no macromolecules
What process is responsible for creating all of the chemical energy used by life?
Photosynthesis / Chemosynthesis
Three components of a nucleotide.
What are phosphate group, 5 carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base?
The primary functions of Lipids
What are long term energy (stored energy), insulation of heat and to make cell membrane?
What happens to electrons as a result of sunlight during photosynthesis?
They get excited
What is the purpose of ATP?
ATP is a molecule that carries energy within cells
Name the 8 characteristics of a living thing
Grows & develops, reproduces, adapts or evolves, made of cells, requires energy, responds to the environment, displays organization, maintains homeostasis
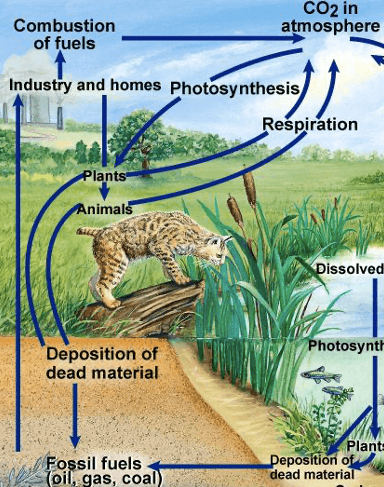
Diagram and label the Carbon Cycle. Include the role of fossil fuels, the form of carbon in the atmosphere, the chemical processes in animals, the chemical processes in plants.
Identify all Tertiary Consumers in the following food web: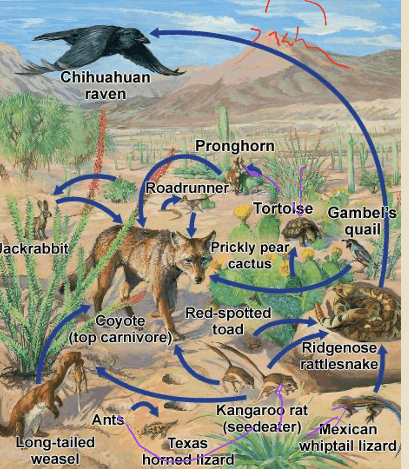
Chihuahuan raven, Coyote
The Four Categories of Macromolecules and their Monomers
Protein - Amino Acids
Nucleic Acids - Nucleotides
Carbohydrates - monosaccharides
Lipids - triglycerides
The functions of proteins (give me at least 4)
What are for Structural support, membranes, protection, catalysts (enzymes), transport, defense (anti-bodies), non-steriod hormones, regulation, movement (remember MEANS)
This type of photosynthesis is used in harsh environments and separates the timing of the Light-Dependent and Light-Independent reactions by time.
CAM plants / photosynthesis
Name & summarize the four major steps of cellular respiration.
1 - Glycolysis - convert sugar into Pyruvate & ATP
2 - Intermediate - turn Pyruvate into Acetyl CoA/citric acid
3 - Kreb cycle - turn citric acid into CO2, H+, electrons & ATP
4 - Electron Transport Chain - moves electrons and H+ to create ATP & Water
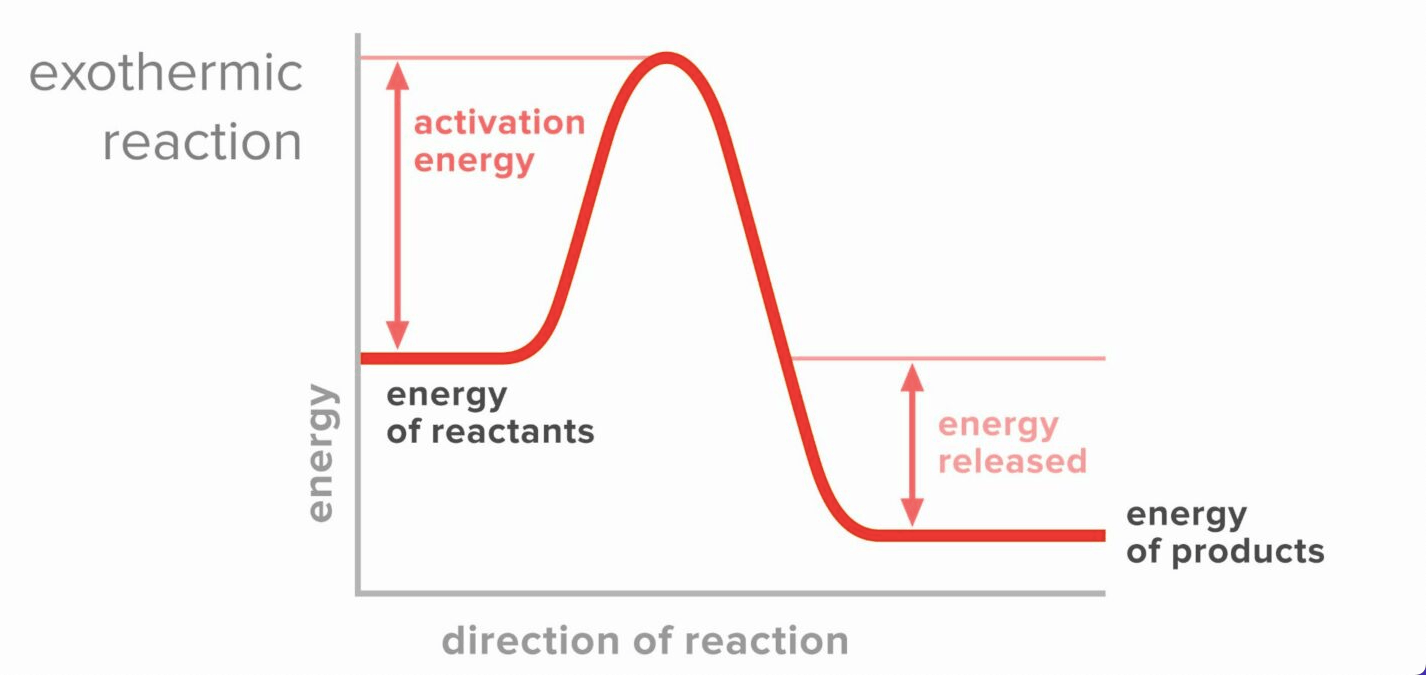
Draw and label the reactants, productsn and activation energy for the graph of an exothermic reaction