Name the structure that surrounds the cell and sparates it from the external environment.
Cell membrane
What are "tissues"?
Tissues are groups of cells that specialize in performing the same function in a coordinated way.
Which system is composed by the heart and blood vessels?
The cardiovascular system
Describe conjunctive tissue
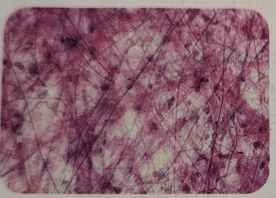
It provides continuity and support to the epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues.
It is also present in ligaments and tendons.
Name the gelatinous fluid that occupies the inside part of the cell.
Cytoplasm
What are the 4 types of tissues in the human body?
Epithelial
Nervous
Connective
Muscle tissues
What are Ribosomes?
What are they responsible for?

They are organelles without membranes formed by two subunits of RNA and proteins.
They are in the cytoplasm and remain free in it or associate to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
They are responsible for protein synthesis.
Which tissue is formed by chondocytes, which are cells that secrete a durable and elastic substance?
(It is found at body joints and between the vertebrae)
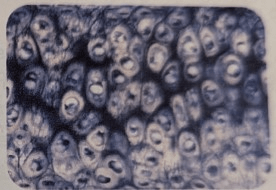
Cartilaginous tissue
What is the name of the vesicles that store reserve substances?
(In plant cells there is usually only one; in animal cells they are smaller and numerous)
Vacuoles
Nervous tissue is mainly made up of which two cell types?
Neurons and Glial cells
What is the name of the vesicles with enzymes that digest waste substances?
Lysosomes
Which type of muscle tissue is made up of involuntary contraction fibres and is located in the heart?
Cardiac muscle tissue
Name and describe the two types of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER).
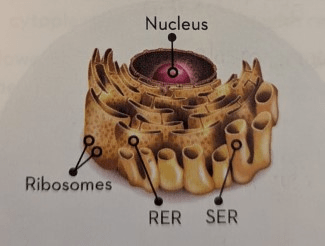
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER), the closest to the nucleus, which is associated with ribosomes and is responsible for protein storage and transport;
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER), which is responsible for lipid synthesis, storage and transport.
What is the function of connective tissue?
What are the types of connective tissue
The function of connective tissue is to provide support, binding, and protection to the rest of the body tissues.
The types of connective tissue are:
Conjunctive tissue
Cartilaginous tissue
Adipose tissue
Bone tissue
Indicate five areas of your body that are covered by mucous membranes.
The
-mouth,
-tongue,
-esophagus,
-stomach,
-and intestines are all lined with mucous membranes.
These membranes are referred to as the oral mucosa, esophageal mucosa, gastric mucosa, and intestinal mucosa.
Describe what Bone tissue is composed of?
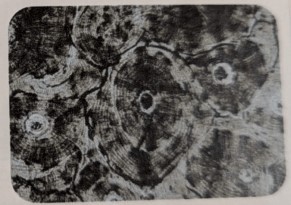
It is composed of osteocytes, the cells that secrete a rigid substance that makes up bones.
Name the double-membrane organelles that have their own DNA.
How do they obtain energy for the cell?
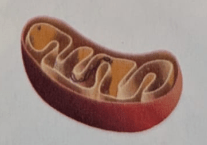
Mitochondria
They obtain energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
What is epithelial tissue responsible for?
What are the two types of Epithelial tissue?
It is responsible for covering and protecting the internal and external body surfaces.
The two types are "epithelial lining" and "glandular epithelium"
Where do Endocrine glands release hormones and proteins?
They release hormones and proteins into the bloodstream.
What is Smooth muscle tissue made up of?
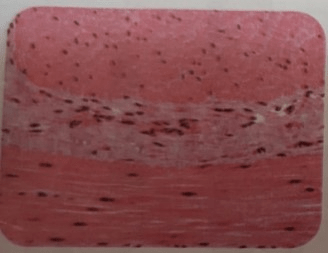
It is made up of involuntary contraction fibres and it is located, for example, in the digestive tract.
Describe Golgi apparatus (GA)
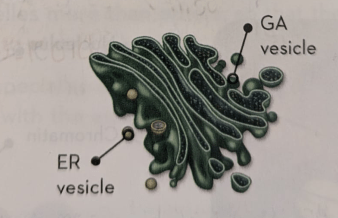
Set of flattened membrane-enclosed discs known as cisternae; it is located next to the ER, so it receives the molecules coming from this organelle and packs them into vesicles to facilitate their transport.
In addition, it is involved in the formation of membranous structures such as lysosomes and, in plant cells, also in the formation of the cell wall.
What is Muscle tissue made up of?
What are 3 types of Muscle fibers?
Muscle tissue is made up of muscle fibers, which are elongated cells that contain a series of proteins in their cytoplasm that allow muscle contraction and relaxation.
Types:
Smooth muscle tissue
Striated muscle tissue
Cardiac muscle tissue
What is the outermost layer of the skin?
Epidermis
Which muscle tissue is made up of voluntary contraction fibres and is located in skeletal muscles; for example, in the biceps?

Striated muscle tissue