A jungle, which is composed of different living organisms, is an example of what?
A. Biosphere
B. Ecosystem
C. Community
D. Population
C. Community
A molecule that contains all nonpolar covalent bonds can be considered:
A. Hydrophilic
B. Hydrophobic
C. Amphiphilic
B. Hydrophobic
Water (H2O) is a(n):
A. Nonpolar molecule
B. Element
C. Compound
D. None of these
C. Compound
[OH-] = 1 x 10-8
Find:
[H+] =
pH =
A. [H+] = 6 pH = 6
B. [H+] = -Log[10-6] pH = 8
C. [H+] = -Log[10-42] pH =8
D. [H+] = -Log[10-6] pH = 6
D. [H+] =-Log[10-6] pH = 6
A mega Chad scientist is studying this organism that appears to be passing exact copies of its genes to its offspring. The organism is most likely performing what:
A. Meiosis
B. Asexual reproduction
C. Sexual reproduction
D. Hydrophilic
B. Asexual reproduction
Which of the following is the least inclusive in the classification of living organisms
A. Kingdom
B. Class
C. Domain
D. Species
D. Species
These elements make up 98% of the human body except for:
A. Iron
B. Carbon
C. Phosphorus
D. Oxygen
E. Hydrogen
A. Iron
What is responsible for water's life sustaining properties?
A. Hydrogen bonds
B. Molecular shape
C. Versatile Solvent
D. Cohesion & Adhesion
A. Hydrogen bonds
Soda (pH 3) is how many times more acidic than milk (pH 6)?
A. 1
B. 10
C. 100
D. 1000
D. 1000
Match the terms:
A.
I. Sugar - Nucleic acids
II. Fatty acids - Fats, lipids, membranes
III. Amino Acids - Proteins
IV. Nucleotides - Polysaccharides
B.
I. Sugar - Polysaccharides
II. Fatty acids - Nucleic acids
III. Amino Acids - Fats, lipids, membranes
IV. Nucleotides - Proteins
C.
I. Sugar - Proteins
II. Fatty acids - Fats, lipids, membranes
III. Amino Acids - Polysaccharides
IV. Nucleotides - Nucleic acids
D.
I. Sugar - Polysaccharides
II. Fatty acids - Fats, lipids, membranes
III. Amino Acids- Proteins
IV. Nucleotides - Nucleic acids
D.
I. Sugar - Polysaccharides
II. Fatty acids - Fats, lipids, membranes
III. Amino Acids- Proteins
IV. Nucleotides - Nucleic acids
You are walking down the street & you pass by a trashcan. The trash smells horrible so you cover your nose.
What is the stimulus & what is the response?
A. Walking is the stimulus & the smell is the response
B. Covering your nose is the stimulus & the smell is the response
C. The smell is the stimulus & covering your nose is the response
D. The smell is the stimulus but there is no response
C. The smell is the stimulus & covering your nose is the response
What is the polarity of the following molecule:
A. Polar
B. Nonpolar
C. Amphipathic
D. Polar covalent
C. Amphipathic
What is the reason for why ice is less dense than water?
A. The nonpolar covalent bonds cause the water molecules to spread
B. The hydrogen bonds cause the water molecules clump together
C. The hydrogen bonds cause water molecules spread
D. Idk
C. The hydrogen bonds cause water molecules spread
You drink a bunch of orange juice because oranges = helth, which lowers the pH of your body. Your body will compensate for that change in pH by:
A. Increasing the amount of [OH-]
B. Decreasing the amount of [OH-]
C. Increasing the amount of [H+]
D. Decreasing the amount of [H+]
A. Increasing the amount of [OH-]
Name the functional group:
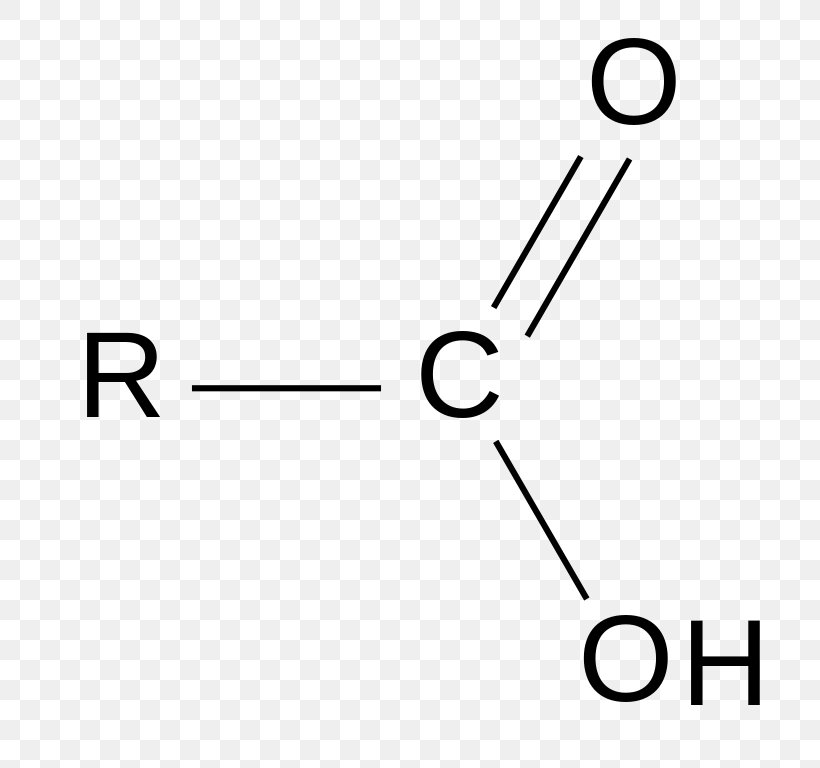
A. Methyl
B. Carbonyl
C. Carboxyl
D. Hydroxyl
C. Carboxyl
A chad microbiologist uses a microscope to look through a slide containing single celled organisms that whose walls are made up of chitin. It appears that the organism is a heterotroph. What organism is the chad microbiologist most likely looking at?
A. Bacteria
B. Fungi
C. Plant cell
D. An animal cell
E. Protist
B. Fungi
Lithium (Li) has one valence electron and Chloride (Cl) has seven valence electrons.
What type of bond would they form?
Who would be the cation?
A. Bond: Covalent Cation: Cl
B. Bond: Covalent Cation: Li
C. Bond: Ionic Cation: Cl
D. Bond: Ionic Cation: Li

![]()
D. Bond: Ionic Cation: Li
What going up a straw tube needs which two forces?
A. Cohesion & Hydrogen bonds
B. Cohesion & Adhesion
C. Adhesion & being a universal solvent
D. Adhesion & Covalent bonds
B. Cohesion & Adhesion
1. In a neutral solution, I increase the number of hydroxide ions. The pH would
2. In a neutral solution, I decrease the number of hydrogen ions. The pH would
A. 1. Increase, 2. Decrease
B. 1. Decrease, 2. Increase
C. 1. Increase, 2. Increase
D. 1. Decrease, 2. Decrease
C. 1. Increase, 2. Increase
Name the three domains of life & all the kingdoms that correspond to their domain of life.
Domains: Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Kingdoms in Bacteria: Bacteria
Kingdoms in Archaea: Archeae
Kingdoms in Eukarya: Protists, Animalia, Plantae, Fungi
Name the 7 properties of life & give a brief overview of each.
Order - Organized. Nothing is randomly assorted.
Regulation - Maintain balance like homeostasis
Reproduction - Making offspring by a sexual or asexual process
Energy processing - Consuming "food" from the environment & converting it into energy
Growth & development - Being able to grow and mature
Response to the environment - Feeling hot or feeling cold
Evolutionary adaptation - Adapt to the environment; takes many generations
Name all the chemical bonds & briefly describe each one
Covalent - Share electrons & can have polar covalent or nonpolar covalent bonds
Ionic - Transfer electrons & opposite charges attract
Hydrogen - The partial positive hydrogen from a polar molecule attracts to the partial negative atom of another polar molecule
Name the four properties of water & give a brief explanation of each
Cohesion & Adhesion - Water can stick to itself (cohesion) and water can stick to anything else (adhesion)
Moderation of temperature - Water can resist temperature changes. Water has high heat capacity.
Expansion upon freezing - Molecules are more spread when water is in ice form
Versatility as a solvent - A lot of substances can dissolve in water
Human blood has a pH of ~7.4 you take a bunch of tums (pH 10) because you feel acid reflux. This makes your blood go to ~7.8. To make your pH less basic you chug some soda (pH 2)
I. Which condition did you have when your blood was ~7.8 pH?
II. Are the tums releasing or accepting H+?
III. How would your body get rid of those H+ ions from the soda? (What would it release & why?)
I. Alkalosis
II. Accepting H+
III. It would release OH- to accept the H+
Li+ & Cl- are put in a container in which water is the solvent. What happened to the Li+ & Cl- after I stirred them?
A. The partial positives and negatives formed hydrogen bonds
B. The partial positives of hydrogen surrounded Li
C. The partial negatives of oxygen surrounded Li
D. The partial positives of hydrogen surrounded Oxygen
C. The partial negatives of oxygen surrounded Li