Covered by a membrane and contains the genetic information for Eukaryotic cells.
What is the nucleus?
4 stages of nuclear division.
What is mitosis?
Transportation from high concentration to low concentration without the use of energy.
What is passive transportation?
Water property which maintains a stable temperature in living organisms.
What is high specific heat capacity?
Small simple cell with no membrane bound organelles.
Either free floating or attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum and synthesizes proteins.
What are ribosomes?
Phase in Interphase in which the DNA is synthesized.
What is the S Phase?
The diffusion of water.
What is osmosis?
The ability of water to stick to itself which allows it to bubble up.
What is cohesion?
Large and complex cell with nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
What are eukaryotes?
Double membraned powerhouse of the cell.
What is the mitochondria?
stage in which the DNA condenses, nuclear membrane dissolves, and spindle fibers form.
What is prophase?
Transportation from low concentration to high concentration with the use of energy.
What is active transportation?
Result of an unequal sharing of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen molecules of water.
What is polarity?
Cell which has chloroplasts, cell wall, and large central vacuole.
What are plant cells?
Made out of cellulose and gives structure to plants allowing for tall heights.
What is the cell wall?
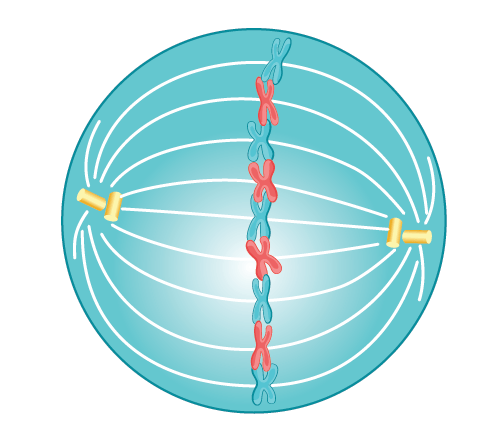
What is metaphase?
A type of active transportation in which the membrane fuses together to release content out of the cell.
What is exocytosis?
The ability to dissolve contents resulting in maintaining stable pH.
What is solubility?
What are eukaryotes?
Responsible for homeostasis of the cell by selective permeability.
What is the cell membrane?
Physical pinching of the cell which results in 2 daughter cells.
What is cytokinesis?
The result of a cell when placed in a hypotonic solution.
What is swell?
Water property that results from the accumulation of cohesion and adhesion which allows plants to absorb water in their roots and replace water in their leaves as it moves up the stem.
What is capillary action?
This cell type has two domains: Bacteria and Archaea.
What are prokaryotes?