What is a constant in an experiment?
Something that must stay the same between all trials for an accurate experiment
What are the monomers of fats?
glycerol and fatty acid tails
What are the monomers for nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What does the term "macromolecule" mean?
"Large molecule," usually found in living things
A patient is diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes. His pancreas does not produce enough insulin, which is a hormone that allows sugar to enter the body's cells. What kind of Macromolecule is insulin?
protein
What's the difference between an independent and dependent variable?
Independent-- what I change / what is changed intentionally by the scientist
Dependent-- what is measured or observed
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharide
What are the monomers of proteins?
amino acids
Which macromolecule is nonpolar and hydrophobic?
lipids / fats
A patient experiences constant stomach pains for the past month. Eventually, doctors decide his gallbladder needs to be removed. This organ normally breaks down fats. Name 3 foods this patient should avoid after surgery.
anything containing fat / lipids : butter, avocado, oil, fried foods like bacon, etc.
What is the dependent variable in this experiment:
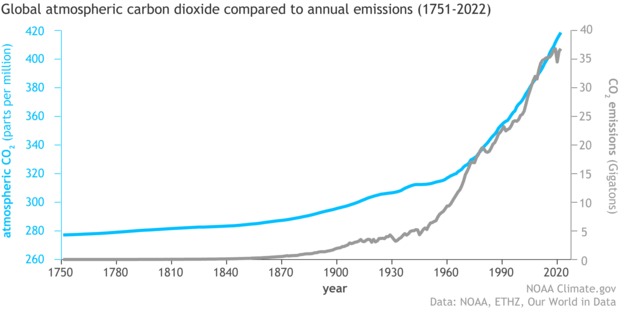
Atmospheric CO2 (because it is on the Y axis)
Name 2 functions of carbohydrates.
short-term energy and structure in plants
What is the main function of nucleic acids?
store the genetic information that is used to build all proteins in the cell
The area that a substrate binds to on an enzyme is called the ___________
active site
What is the process call where you break a molecule into 2 parts using water?
A patient has a genetic condition called sickle-cell anemia. This causes red blood cells to curve into a sickle shape, blocking small blood vessels from getting oxygen and other nutrients. What macromolecule is responsible for this disease? 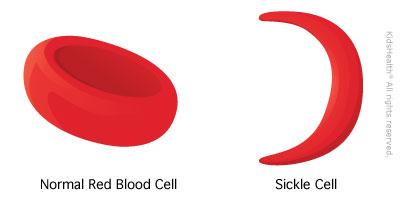
nucleic acids / DNA since this is a genetic condition
What words describe molecules that like water?
hydrophilic
Name 3 functions of fats.
insulates our bodies and nerve cells, cushions, act as steroids, chlorophyll in plants, phospholipids make up cell membrane, long-term energy storage
What are the 2 types of nucleic acid?
DNA and RNA
What happens to the enzymes from the stomach as they move from the stomach at pH 2 to intestines at pH 9? A. it becomes denatured B. it begins to replicate C. its shape changes to take in larger proteins D. its activity increases to digest more proteins
A. it becomes denatured
An enzyme called lipase binds to a substrate and catalyzes a reaction that breaks the substrate into a glycerol backbone and fatty acid tail. What was the substrate that the enzyme broke down?
a lipid/ fat
Tay-Sachs disease is caused by a faulty enzyme, hexosaminidase. It causes macrocephaly, or swelling in babies heads. What macromolecule is responsible for Tay-Sachs disease? 
an enzyme, which is a protein
Name the process that links monomers together to form a larger molecule, or polymer. (removes a molecule of water)
Dehydration synthesis
What are the 3 groups of carbohydrates and provide examples.
monosaccharide-- glucose, fructose
disaccharide-- sucrose, maltose, lactose
polysaccharide-- cellulose, starch, fiber
What is the relationship between proteins and nucleic acids? A. Nucleic acids use proteins for energy B. Nucleic acids are made of proteins C. Proteins are long chains of nucleic acids D. Nucleic acids contain the genetic info to make proteins
D. Nucleic acids contain the genetic info to make proteins
What 2 environmental conditions greatly affect the ability of enzymes to function?
pH and temperature
What macromolecule group do chitin and cellulose belong to?
carbohydrates
Albinism is a genetic condition where individuals do not produce melanin, a pigment normally in skin and hair. They will have very pale skin, white or very fair hair, and light colored eyes. What TWO macromolecules are involved in this condition?
nucleic acids because its a genetic condition
protein because melanin is a protein