Problem
A general description of a task that can (or cannot) be solved with an algorithm
Efficiency
A measure of how many steps are needed to complete an algorithm
Reasonable Time
Algorithms with a polynomial efficiency or lower (constant, linear, square, cube, etc.) are said to run in a reasonable amount of time.
Decision Problems
a yes-or-no question on an infinite set of inputs
Sequential Computing
programs run in order, one command at a time
Algorithm
a finite set of instructions that accomplish a task
Linear Search
A search algorithm that checks each element of a list, in order, until the desired value is found or all elements in the list have been checked.
Unreasonable Time
Algorithms with exponential or factorial efficiencies are examples of algorithms that run in an unreasonable amount of time.
Optimization Problems
Parallel Computing
programs are broken into small pieces, some of which are run simultaneously
Sequencing
Putting steps in an order
Binary Search
A search algorithm starts in the middle of a sorted set of numbers and removes half of the data; this process repeats until the desired value is found or all elements have been eliminated
What line is considered unreasonable?
Orange
Heuristics
provide a "good enough" solution to a problem when an actual solution is impractical or impossible
Distributed Computing
programs are run by multiple devices
Selection
Deciding which steps to do next
When is binary search more efficient?
Binary Search is more optimized and efficient than Linear Search in many ways, especially when the elements are in sorted order and are large.
What lines are considered reasonable?
Undecidable Problem
a problem for which no algorithm can be constructed that is always capable of providing a correct yes-or-no answer
Speedup
the time used to complete a task sequentially divided by the time to complete a task in parallel
Iteration
Doing some steps over and over
When is linear search more efficient?
Linear search is more efficient when the numbers are not in a sorted list and are smaller.
Do unreasonable algorithms solve problems correctly?
It's important to recognize that an unreasonable algorithm still solves a problem correctly! It just takes an unreasonably long time.
How would you solve the traveling salesman problem?
Use a heuristic to provide a good enough answer.
What is this an example of? 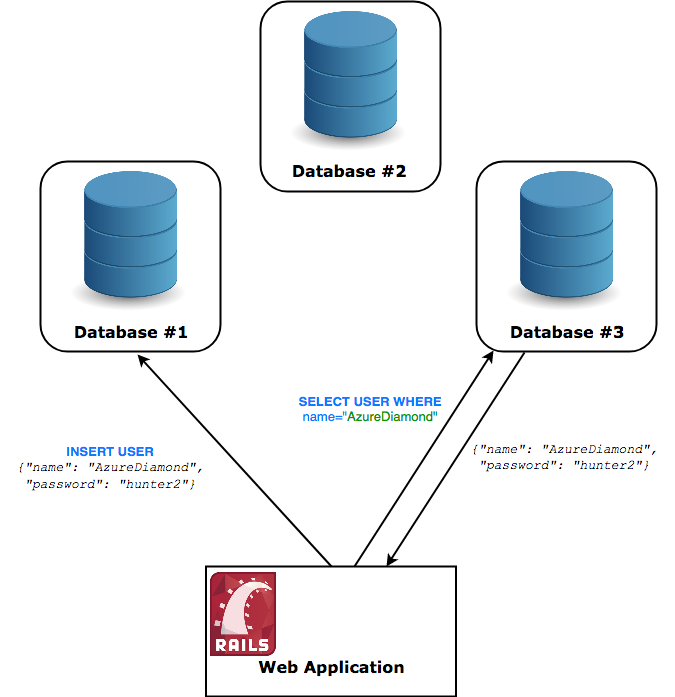
Distributed Computing
