a finite set of instructions that accomplish a task
What is - Algorithms
a measure of how many steps are needed to complete an algorithm
What is - Efficiency
a problem for which no algorithm can be constructed that is always capable of providing a correct yes-or-no answer
What is - Undecidable Problem
a model in which programs are run by multiple devices
What is - Distributed Computing
Algorithms with a polynomial efficiency or lower (constant, linear, square, cube, etc.) are said to run in a reasonable amount of time
What is - Reasonable Time
a repetitive portion of an algorithm which repeats a specified number of times or until a given condition is met
What is - Iteration
this algorithmic efficiencies would be considered LEAST efficient 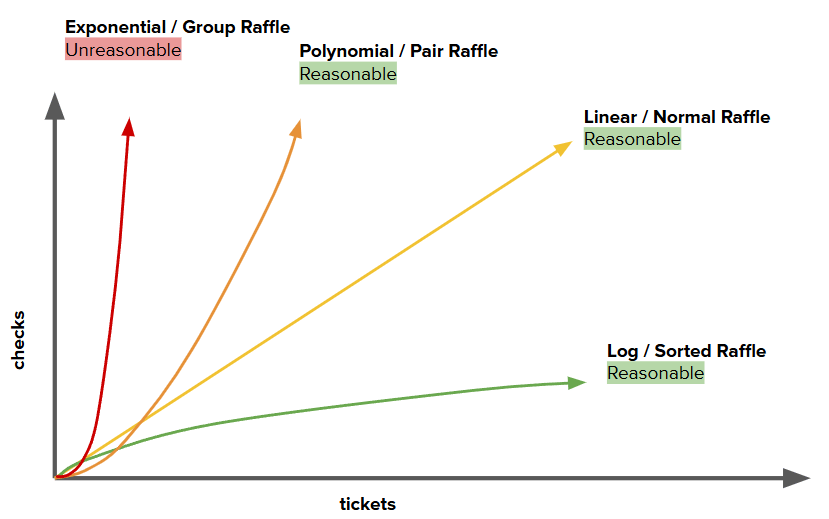
What is - Exponential
a problem with the goal of finding the "best" solution among many (e.g., what is the shortest path from A to B?)
What is - Optimization Problem
a model in which programs run in order, one command at a time
What is - Sequential Computing
Algorithms with exponential or factorial efficiencies are examples of algorithms that run in an unreasonable amount of time
What is - Unreasonable Time
a general description of a task that can (or cannot) be solved with an algorithm
What is - problem
a search algorithm that starts at the middle of a sorted set of numbers and removes half of the data; this process repeats until the desired value is found or all elements have been eliminated
What is - Binary Search
provides a "good enough" solution to a problem when an actual solution is impractical or impossible
What is - Heuristic
the time used to complete a task sequentially divided by the time to complete a task in parallel
What is - Speedup
If the data is not sorted, this is the only search you can use
What is - linear search
deciding which steps to do next
What is - selection
a search algorithm which checks each element of a list, in order, until the desired value is found or all elements in the list have been checked
What is - Linear Search
a problem with a yes/no answer (e.g., is there a path from A to B?)
What is - Decision Problem
a model in which programs are broken into small pieces, some of which are run simultaneously
What is - Parallel Computing
Lists or Arrays often allow their size to be easily updated to hold as many data values as needed. This is an example of _______________
What is - abstraction
putting steps in an order
What is - Sequencing
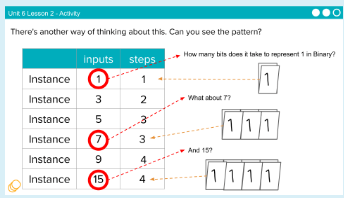
A graphic artist uses a program to draw geometric shapes in a given pattern. The program uses an algorithm that draws the shapes based on input from the artist. The table shows the approximate number of steps the algorithm takes to draw different numbers of shapes.
When an algorithm runs in a reasonable amount of time because it uses approximately n2 steps to draw n shapes, this is known as a _________
What is - polynomial
Finding the fastest route that visits every location among n locations, which requires n! possible routes be examined. To find the most reasonable amount of time a person would use a _____________ algorithm.
What is - heuristic
A sequential algorithm is broken into three stages with the following set of times:
Sequential Algorithm Time
- Download stage: 1 minute
- Sorting stage: 6 minutes
- Upload stage: 1 minute
A parallel version of the algorithm completes the sorting stage in parallel, leading to a new set of times:
Parallel Algorithm Time
- Download stage: 1 minute
- Sorting stage: 2 minutes
- Upload stage: 1 minute
The speedup of the parallel solution's total algorithm time is...
What is 2
A computer is performing a binary search on the sorted list of 13 numbers below.
the maximum number of iterations needed to find the item is...
What is 4