Mitochondria
Cellular Respiration
Passive does not require the input of energy while Active does.
Presence of a nucleus, membrane bound organelles, size, complexity
What are the two phases of photosynthesis and where do each take place?
light dependent: thylakoid
light independent: stroma
What is the overall equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light --> Oxygen + Sugar
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis
Differentiate between endocytosis and exocytosis. What type of transport are they?
Endocytosis: taking material into the cell
Exocytosis: releasing material from the cell
Active Transport
Give a real-world biological example of the levels of organization within and organism from simplest to most complex.
cell --> tissue --> organ --> organ system --> organism
What are electron carriers and what is the name of the most important electron carrier in photosynthesis?
Molecules that accept/transport high energy electrons; NADPH
Miss Regan placed four dialysis bags each filled with a solution with an unknown concentration of sucrose, into four beakers, each with a different concentration of sucrose. The initial mass of each bag was 20g. The final mass of each bag is shown below.
0.2M: 14g
0.4M: 16.7g
0.6M: 19g
0.8M: 23g
What is the most likely concentration of sucrose inside the dialysis bags? How do you know?
0.6M
It had the least change in mass.
breaks down large molecules into smaller usable ones, and breaks down non-functional organelles
The specialized protein channel that allows the passage of water is known as a(n)_______________.
Aquaporin
Plants have tiny openings in their leaves called stomata that let ______ in, but expose the plant to the loss of ______.
CO2... water
Define pigment and state the most important pigment in photosynthesis.
A light absorbing molecule; chlorophyll
Below is a major theme in the study of biology:
________ = _________
Structure = Function
Smooth ER
makes membrane lipids and gets rid of toxins
Phagocytosis is a specific form of ________ which involves engulfing food particles and forming a _______ to store them.
HINT: We watched a video of this in real life involving an amoeba and paramecium.
Endocytosis .... Vacuole
The contraction of many heart muscles as a single unit is possible because of __________.
Cellular junctions
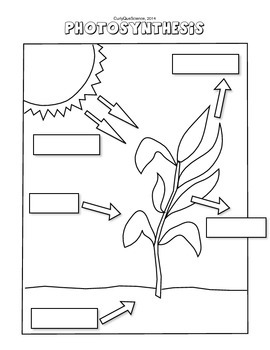
Fill in the diagram of photosynthesis.
From start to finish, describe the pathway of a newly synthesize secretory protein (a protein that leaves the cell)
Ribosome --> Rough ER --> Smooth ER --> Golgi Apparatus --> Cell Membrane --> Out of cell
Vesicle
small membrane sac that store and transport material from one organelle to another or outside of the cell
Passive: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
Active: protein pump, endocytosis, exocytosis
Cell membranes are otherwise known as a ___________. They are composed of specialized lipids called _________. These lipids have two parts: a _______ head and a _______ tail. Cell membranes are _________________, meaning that they allow passage of certain materials, but not others.
lipid bilayers...phospholipids...hydrophobic head...hydrophilic tail....selectively permeable
ATP synthase in an enzyme that functions to convert _____ to ____. In order to accomplish this, it uses the build up of _______. This process specifically occurs in the ____________ phase of photosynthesis, which takes place in the __________ of the chloroplasts.
ADP to ATP.
H+ ions.
light-dependent...thylakoids
What is a CAM Plant? Give one example in your definition.
Takes in carbon dioxide only at night to prevent water loss. Plants in dry climates (cacti, succulents, etc.)