An object's tendency to resist a change in motion.
What is inertia?
What is the Law of Universal Gravitation?
This word describes the speed and direction of an object.
What is velocity?
The Law of Conservation of Energy
What is Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed?
This is something that we need to update, change, or accept new scientific knowledge.
What is evidence?
The formula used to describe Newton's 2nd Law of motion.
What is F=ma?
Forces that do not require direct contact between the two objects.
What are noncontact forces?
This word describes a change in speed or direction of an object (any change in motion).
This is an object's energy due to its position above the earth's surface.
What is Gravitational Potential Energy?
Jasper watches the birds in his yard for two weeks to determine which of the two bird feeders they like best. He tells his teacher that this is an experiment, but it is actually this.
What is an investigation?
This law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
This is the contact force that acts opposite to motion, slowing objects down, and generating heat.
Acceleration can only be caused by this kind of force.
What is an unbalanced force?
This is the type of energy stored in objects such as batteries, food, gasoline, charcoal, etc.
What is Chemical Energy?
Sal gives his each of his strawberry plants 500 mL of water daily. He makes sure they get the same amount of sunlight and fertilizer. Twenty plants are in pots with potting soil. The other twenty are in pots with a sand and clay mixture. This is the independent variable for Sal's experiment.
What is the type of soil?
This law of motion explains why a baseball thrown in outer space would fly infinitely.
The two factors that affect the strength of gravity.
What are distance and mass?
This describes the motion of the object in the graph from 5:00 to 5:15.
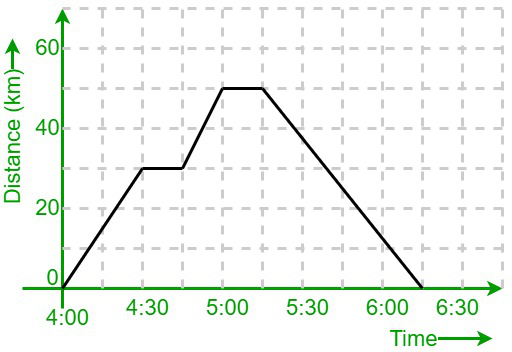
What is no motion?
What is transformation into thermal energy?
This is something that is held the same throughout an experiment to ensure it does not interfere with the variables we want to study.
What is a constant?
This law explains why swimmers can push themselves through the water from one side of the pool to another.
What is Newton's 3rd Law?
Calculate the net force on an airplane in which the plane is pushing up with 100N and gravity is pulling down with 75N.
What is 25N UP?
This describes the motion of the object from 4:00 to 4:30.

What is constant velocity?
 A pendulum swings back and forth. At what point in its swing does the pendulum have the most kinetic energy, and at what point does it have the most potential energy?
A pendulum swings back and forth. At what point in its swing does the pendulum have the most kinetic energy, and at what point does it have the most potential energy?
What are points 3 and 1 (or 5)?
Dylan finds two types of varnish that are supposed to help keep the wood on his deck from fading in the sun. He decides to test them. He paints 10 boards with Vivid Varnish, and 10 boards with Valiant Varnish. He leaves 10 boards with no varnish at all. He leaves them in the sun for 4 weeks, and makes notes on their daily appearance. The 10 boards with no varnish would be his ________________ ______________.
What is the control group?