Name the figure pictured on this section of the Catalan Atlas:
Mansa Musa
This network involved a diverse group of individuals, including white abolitionists, free Blacks, Native Americans, and even sympathetic farmers, who risked their lives to provide shelter, guidance, and resources to those seeking freedom.
The Underground Railroad
This image depicts which conquistador of African descent who participated in Spanish expeditions in the early 1500s, including the conquest of Mexico with Hernán Cortés.
Juan Garrido
This 1787 agreement was intended to be a way to balance the political power between Northern and Southern states, giving Southern states more representation while still acknowledging the enslaved population without granting them full rights.
The 3/5ths Compromise (only 3/5ths of the slave population would be credited to southern states in determining the amount of federal representation they would receive).
This 1850 law required that slaves be returned to their owners, even if they were in a free state.
The Fugitive Slave Act
(Note: The second Fugitive Slave Act was part of the Compromise of 1850 and was much stricter. It required citizens to assist in capturing escaped enslaved people and imposed harsher penalties for those who aided fugitives. It also denied fugitives the right to a jury trial, causing widespread controversy and resistance in the Northern states.)
This complex stone work can be found in what African country?
Zimbabwe
This term refers to a community formed by escaped enslaved Africans and their descendants in the Americas. These societies were established in remote areas such as forests, swamps, and mountains, where they could resist re-enslavement and maintain their independence.
Maroon
Freedom fighter depicted in this picture:
Harriet Tubman
The church was founded in 1816 by Bishop Richard Allen in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
The African Methodist Episcopal Church (AME)
This white abolitionist led a raid on Harpers Ferry (October 16–18, 1859) this was an armed effort to seize a federal arsenal in Harpers Ferry, Virginia, aiming to incite a slave uprising.
John Brown
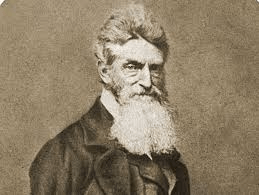
NOTE: The raid failed, and Brown was captured, tried for treason, and executed, becoming a polarizing figure in the lead-up to the Civil War.
These are court drawings of men who were part of what trial IN WHAT YEAR(S)??
Amistad Trial (1839-1841)
The term refers to the internal forced migration of enslaved Black people within the United States, primarily from the Upper South to the Deep South, driven by the expanding demand for labor in cotton, sugar, and tobacco plantations.
The Second Middle Passage
(NOTE: This often led to the brutal separation of families and increasingly brutal and inhumane slave auctions)
This picture depicts the Festival of Our Lady of the Rosary -- from what country?
Brazil
This former slave and abolitionist addressed the World Fair of Chicago in 1893 and was one of the most photographed men of the 19th century.
Frederick Douglass
This executive order issued by President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, declared freedom for enslaved people in Confederate states still in rebellion against the Union. While it did not immediately free all enslaved individuals, it reframed the Civil War as a fight against slavery and paved the way for eventual abolition through the 13th Amendment.
The Emancipation Proclamation
This object was used to help sift what crop?
Rice
This term refers to the period after the Civil War (1865-1877) when the U.S. government worked to rebuild the South, integrate formerly enslaved people into society, and redefine the nation’s laws and policies regarding race and civil rights.
Reconstruction
One of the first African American units in the Union Army during the Civil War, formed in 1863 and led by Colonel Robert Gould Shaw. Their bravery, particularly in the assault on Fort Wagner, demonstrated the valor of Black soldiers and helped pave the way for broader inclusion/acceptance of African Americans in the military.

The 54th Massachusetts Regiment
The invention of this item in 1793 led to an increased demand for slave labor in southern states.
The cotton gin
This landmark 1893 U.S. Supreme Court case upheld the constitutionality of racial segregation under the "separate but equal" doctrine.
Plessy v Ferguson
Name the ARTIST who created this portrait of Toussaint L'Ouverture:
Jacob Lawrence
The term used to collectively refer to laws passed in Southern states after the Civil War aimed at restricting the freedoms of African Americans, particularly in relation to labor, mobility, and civil rights, and often used to enforce racial segregation.
Deep cut -- Who is the artist who created this intricate quilt depicting Harriet Tubman:

Bisa Butler
This person was an enslaved African American preacher who led a violent rebellion in 1831 in Southampton County, Virginia. It resulted in the deaths of around 60 white people and was one of the most significant slave revolts in U.S. history, leading to harsher laws and increased fear of slave uprisings in the South.
Nat Turner
The ratification of this amendment on December 6, 1865, abolished slavery and involuntary servitude in the United States, except as punishment for a crime. This loophole allowed systems like convict leasing to exploit incarcerated individuals for free labor, perpetuating racial inequities and economic exploitation.
The 13th Amendment