Hydrocarbon chains that consist of only single bonds are called _____.
Saturated.
This organelle is the site of protein synthesis.
Ribosomes
Free energy diagrams illustrate the energy profiles for a given reaction. These diagrams are displayed on a graph, with _____ on the x-axis and _____ on the y-axis.
The reaction progress is displayed on the x-axis, while Gibbs free energy is displayed on the y-axis.
The only step in cellular respiration that occurs in the cytoplasm.
Glycolysis
Name the three reactants required for photosynthesis to occur.
Carbon dioxide, water, and energy (sunlight)
Fats are nonpolar molecules composed of these two things.
Three fatty acids and a glycerol.
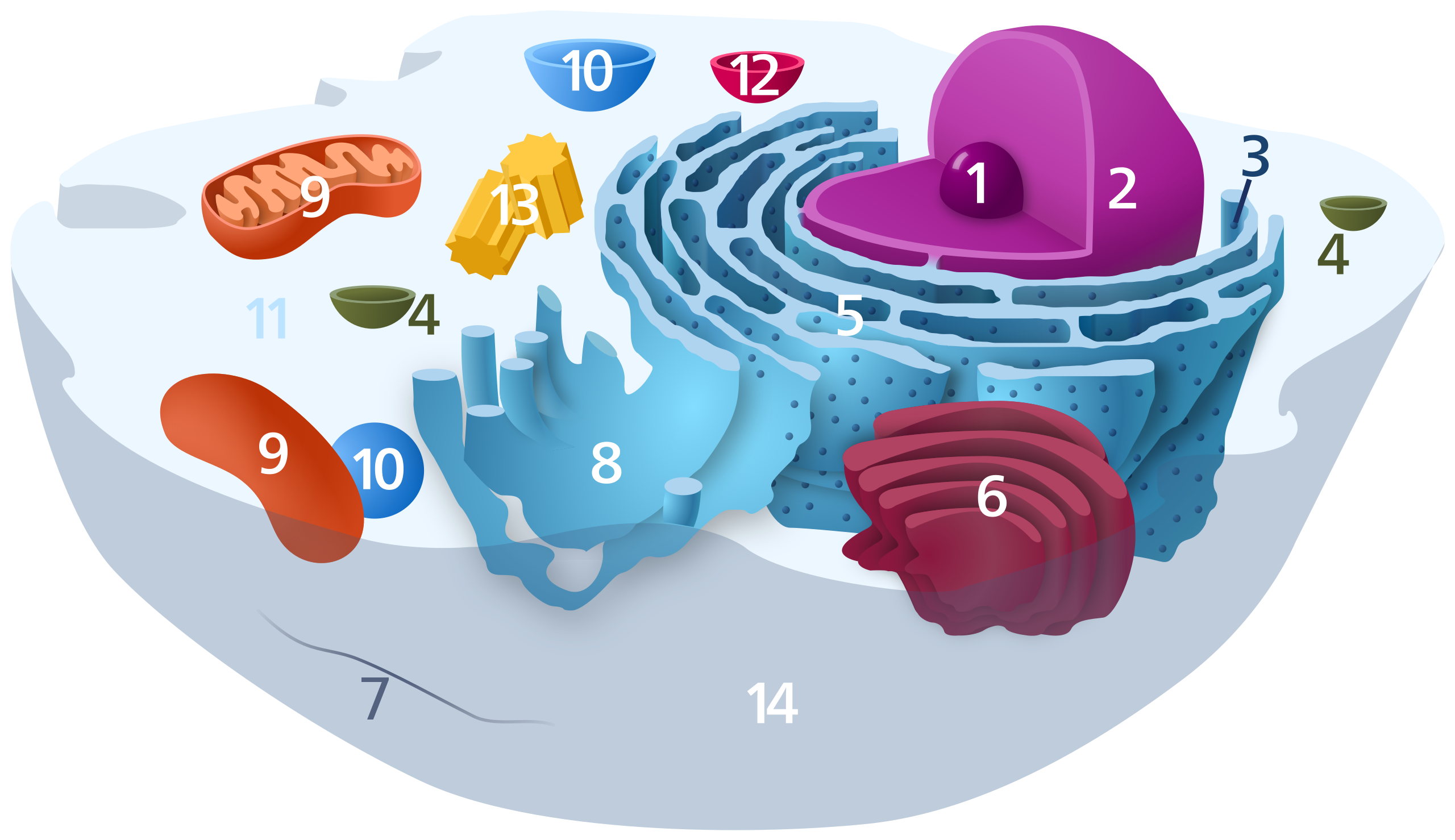 Name organelle #5.
Name organelle #5.
Rough ER
Exergonic and endergonic reactions can tell you whether energy was absorbed or released in a reaction. Which type of reaction results in a ΔG > 0?
Endergonic reactions have a ΔG > 0.
For each molecule of glucose that started cellular respiration, how many times will you go through the citric acid cycle?
2
Light reactions occur in what part of the chloroplasts.
Thylakoids.
This term means that some substances cross a membrane more readily than other substances do.
Selective permeability.
Name two similarities and two differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Reference figure
✩ DOUBLE JEOPARDY ✩
Describe energetic coupling
The mechanism by which energy released from an exergonic reaction is used to drive an endergonic reaction.
Name one product of glycolysis, pyruvate processing, and the citric acid cycle.
NADH
✩ DOUBLE JEOPARDY ✩
Name the three phases of the Calvin cycle, in the correct order.
1. Fixation phase
2. Reduction phase
3. Regeneration phase
✩ DOUBLE JEOPARDY ✩
Give one example of a substance that has high permeability and another that has low permeability.

✩ DOUBLE JEOPARDY ✩
Four organelles make up the endomembrane system. Name three of them.
ER; smooth and rough
Golgi
Lysosomes
During the redox reactions that occur in cells, electrons may be transferred from an atom in one molecule called the _____, to an atom in a different molecule called the _____.
Electron donor
Electron acceptor
In the citric acid cycle, _____ and _____ come together to form citrate.
Acetyl CoA and Oxaloacetate.
C3 – ‘normal’ photosynthesis
C4 – making a 4-carbon intermediate from initial CO2 fixation using an enzyme other than rubisco to reduce photorespiration
CAM – separating initial fixation from rest of Calvin Cycle by time of day to reduce photorespiration
Temperature, structure, etc. can affect membrane fluidity and/or permeability. Name two specific examples of how these factors can impact membrane characteristics.
↑ cholestrol → ↓ permeability (etc.)
↑ temp. → ↑ permeability (etc.)
↑ unsaturation → ↑ fluidity (etc.)
Describe the endosymbiosis theory.
The theory that mitochondria & chloroplasts evolved from prokaryotes that were engulfed by host cells and took up a symbiotic existence within those cells, a process termed primary endosymbiosis. In some eukaryotes, chloroplasts may have originated by secondary endosymbiosis -- when a cell engulfed a chloroplast-containing protist and retained its chloroplasts.
Some reactions are considered to be spontaneous or non-spontaneous. The following reaction is which of these options?
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Non-spontaneous
✩ DOUBLE JEOPARDY ✩
Write the chemical equation for cellular respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
 Label four of the five parts of the chloroplast.
Label four of the five parts of the chloroplast.
Bonus 50 points if you can name two more parts.
L to R:
Outer membrane
Inner membrane
Stroma
Thylakoid
Granum