Kinetic Energy
Kinetic Energy
Transformation
Transfers
Review
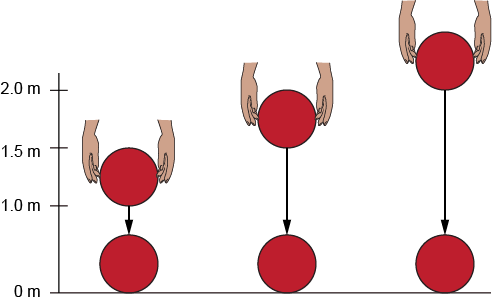
At which point does the rollercoaster car have the most potential energy?
Point B is the highest point so the rollercoaster car has the most gravitational potential energy.
Identify this type of energy:

Radiant or light energy
When you turn on a lamp, what energy transformation takes place?
Electrical energy → Light energy (and some heat energy)
Hot coffee is stirred with a spoon, the spoon gets hot due to _______________.

Conduction
Look at the liquids and their densities below, if all of these liquids were poured into a glass, which would float on top?
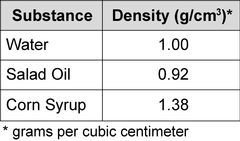
The salad oil because it is the least dense.
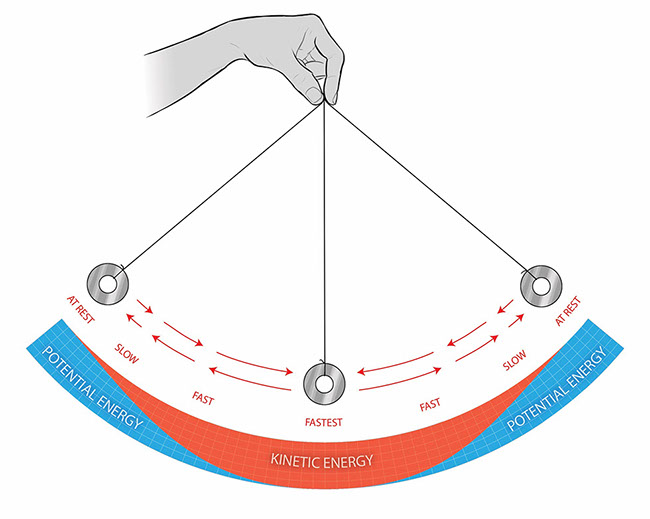
When a pendulum reaches its lowest point in the swing, which type of energy is greatest?
Kinetic energy is greatest at the bottom because the pendulum is moving its fastest.
What type energy is present in a stretched rubber band?

Elastic potential energy
When lighting a match, what is the main energy transformation?

Chemical energy → Heat and light energy
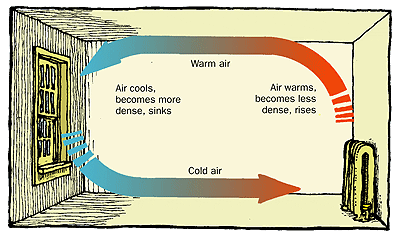
Near the ceiling of a room the air is warmer. The warm air rises because of _______________
Convection
How many atoms are in this compound?
CaCO3
Ca= 1
C= 1
O= 3
5 total atoms
Two grocery carts are rolling down a hill, which one has the greatest amount of kinetic energy? Why?

Cart 2 has the most kinetic energy because it has more mass.
What type of energy is stored in food before your body uses it?

Chemical energy
When a solar panel charges, what energy transformation occurs?
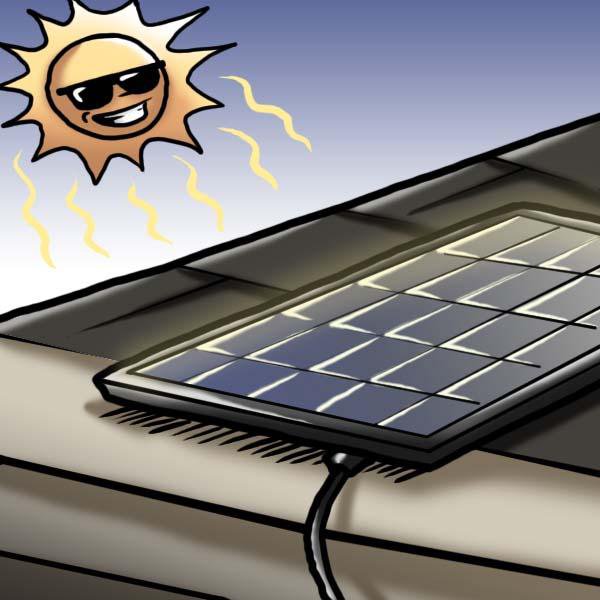

Light (or radiant) energy --> Electrical energy
A chair is placed several feet from a fire in a fireplace. The fireplace has a glass screen. The side of the chair facing the fireplace gets warm because of_______________.
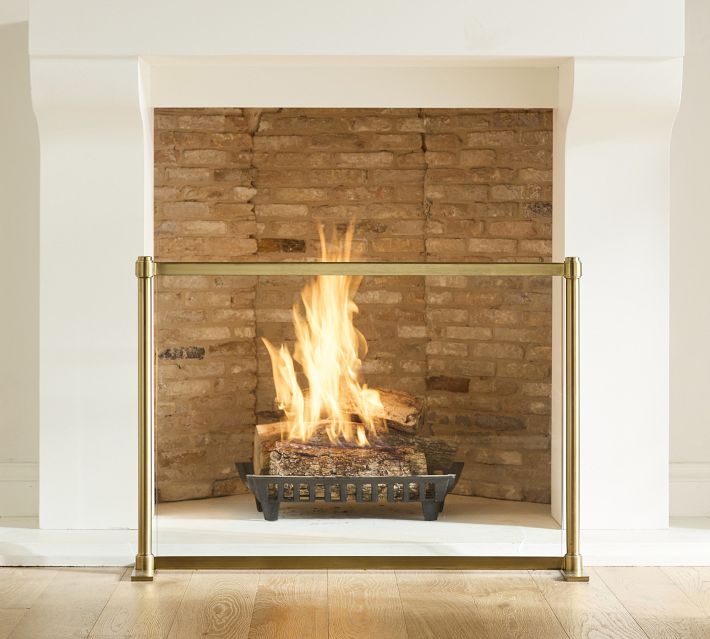

Radiation
Was thermal energy added or subtracted to this system?
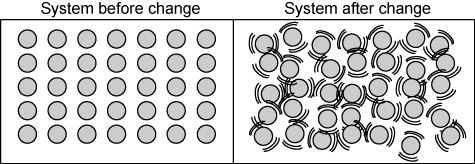
Thermal energy was added which increased particle motion.
A student is doing a ball-drop experiment. She notices that the higher she drops the ball, the higher it bounces. Why does this happen?
When the ball is dropped from a higher height, it has more potential energy. As it falls, that energy turns into kinetic energy. When the ball hits the ground, the law of conservation of energy says that energy is not lost, it changes form. So the more energy the ball starts with, the more energy it has to bounce back up, which makes it bounce higher.
Categorize a battery as either potential or kinetic:

Potential Energy (Chemical)
Describe the energy transformations that occur when a battery-powered flashlight is lit.

Chemical energy (battery) to electrical energy (wires) to radiant and thermal energy (light bulb).
It is a hot summer day, and Miguel wants to cool off. He decides to make a root beer float. He pours root beer into a mug and adds a scoop of vanilla ice cream. What thermal energy transfer occurs?

Thermal energy moves from the root beer to the ice cream by conduction.
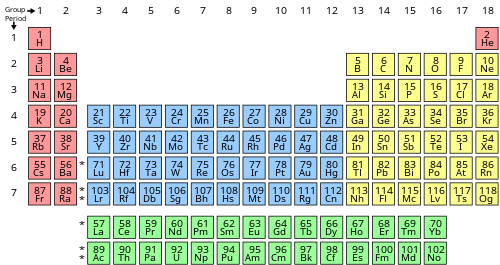
Name the element in group 7, period 4.

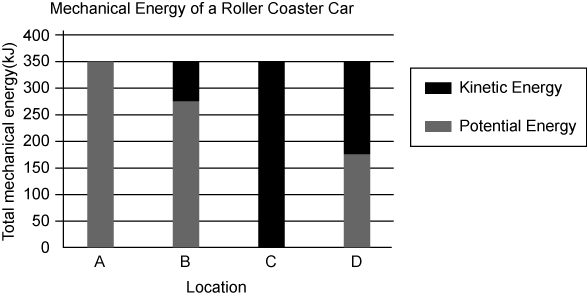
Take a look at the graph below, which represents the energy of a working rollercoaster. What happens to the potential & kinetic energy throughout the ride? what happens to the total amount of energy?
The potential and kinetic energy change but the total amount of energy stays the same.
Identify the types of energy below:


A student winds up a toy car, sets it down, and watches it speed across the floor.
Explain the energy transformations from winding the toy to its movement.
Mechanical energy--> potential energy--> kinetic energy
Winding the toy: Mechanical energy → Elastic potential energy (stored in spring)
When released: Elastic potential energy → Kinetic energy
A student is investigating thermal energy transfer. The student places two copper blocks, Block 1 at 40°C and Block 2 at 20°C, in contact with each other. They are allowed to sit until thermal energy transfer is complete.
Explain what will happen to the temperatures of the blocks and why.
When the two copper blocks are in contact, thermal energy will transfer from the hotter block (Block 1, 40°C) to the cooler block (Block 2, 20°C) through conduction. This transfer continues until both blocks reach thermal equilibrium, meaning they are at the same temperature.
What is the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures
Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout, while heterogeneous mixtures do not. Homogeneous mixtures appear as a single substance, like saltwater, where the components are evenly distributed and indistinguishable. Heterogeneous mixtures have visible, non-uniform parts, like sand in water, where you can see the individual components.