When energy is released, the value for heat will be this (positive/negative)
What is positive?
Letter B represents this on the phase diagram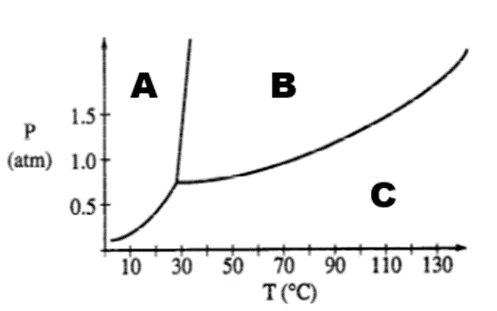
What is liquid?
Filtration would work to separate these states of matter.
What is liquid and solid?
Antimony is an example of this.
What is an element?
A metal has a mass of 23.5 g, a specific heat of 0.288 J/goC, and temperature went from 25.0oC to 55.0oC. This is the energy.
What is -203 J?
This is what the phase change from solid to gas is called.
What is sublimation?
This method of separation is based on boiling point
What is distillation?
A glue gun melting a stick of glue is an example of this.
What is a physical change?
49 J of energy is used to heat an object with a mass of 1.243 g from 15.3oC to 47.8oC. This is the specific heat.
What is 1.2 J/goC?

This is what is occurring at #4 on the graph
What is boiling?
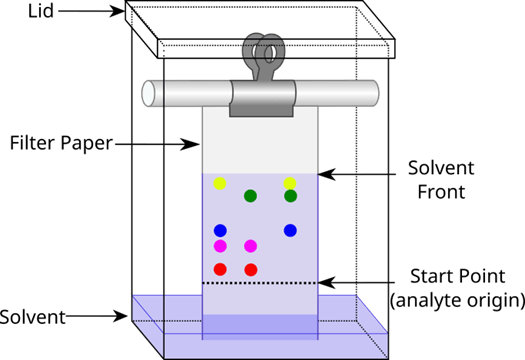
This image displays this method of separation.
What is chromatography?
Rust is an example of this.
What is a chemical change?
What temperature must a 50.0 g piece of glass start at if it absorbs 475 joules of heat and its specific heat capacity is 0.20 J/g°C? The final temperature of the glass is 70.5°C.
What is 23°C?
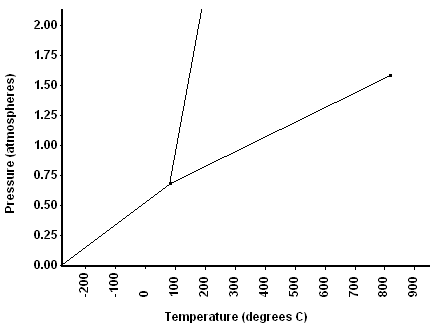
At 1.50 atm, this is the melting point.
What is ~150 oC
In the separation lab, filtration was NOT successful for this type of substance.
What is homogeneous mixture/two liquids
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid, C6H8O6) is an example of this.
What is a pure substance/compound?

If the substance is at 400oC and 0.75 atm, this is what must be done to have the substance condense.
What is increase pressure?
A student has a mixture of sand and salt dissolved in water. These are the methods of separation.
Filtration then evaporation/distillation
This is an example of a homogeneous mixture
(Answers may vary)