Ecology is the study of ____________________________________ ?
Is the study of relationships between two organisms
Is the study of relationships between an organism and its environment
What is is one biotic or abiotic factor that affects the size of a population in an ecosystem?
ex:
# of predators - biotic
food supply - abiotic
births - biotic
deaths - abiotic
space - abiotic
water - abiotic
climate - abiotic
In a span of 50 years, the number of fur seals have been steadily increasing before it began to level off. What is this graph an example of?
Logistic Growth
What is happening in nitrification?
Bacteria convert nitrogen in ammonia into nitrates and nitrites to be absorbed by plants in their roots.
What are 2 of the 4 limiting factors affecting the Population Density of a given space?
1. birth
2. immigration
3. death
4. emigration
What does biotic and abiotic mean?
Biotic = living
Abiotic = nonliving
Describe the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process in which a plant/tree/flower uses sunlight to help turn the carbon dioxide from the air and the water from the soil/rain to make sugar and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the air, which is good for other living organisms that take in oxygen to breathe.
When we have 20 knights in a 10 x 2 space and there are 40 knights in another 20 x 1 space. Which one of these spaces has a greater population density?
the space with 40 knights in a 20 x 1 space.
How is nitrogen different from the other geochemical cycles?
The Nitrogen Cycle is different from the other geochemical cycles in that no step is completed without the help of living organisms.
Bacteria is the most important living organism in converting nitrogen to different forms.
Fungi and other decomposers breakdown nitrogen-rich waste and put it in the soil
Give an example of a stimulus and a response.
Responses may vary.
ex: Sunflowers tend to grow facing east (response), towards sunrise (stimulus)
ex: You are hungry (stimulus), so you eat some food (response)
ex: You are cold (stimulus), so you put on a jacket (response)
ex: A dog is hot (stimulus), so it lies in the shade (response)
ex: It starts raining (stimulus), so you pull out an umbrella (response)
Identify the fith rock sample.
Conglomerate
What would happen to the nitrogen cycle if decomposers were not present?
If decomposers were not present, nitrogen would not be able to be put into the soil by dead matter/organisms. No nitrogen would be put in soil by waste either.
What type of survivorship curve is the image displaying? Explain why.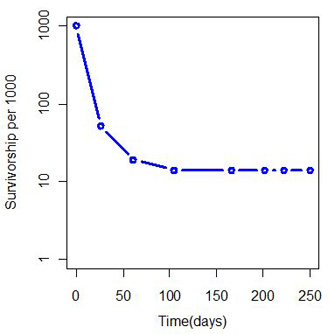
The image displays a Type III Survivorship Curve because it is displaying an early loss as time passes. (250 days is less than a year, so those organisms did not make it past their 1st birthday.)
What are some examples of density-dependent limiting factors?
- competition for food, water, shelter, mates, light (biotic)
- predation (biotic)
- parasitism (biotic)
- disease that results in death (biotic)
- waste accumulation
What are some examples of density-independent limiting factors?
- weather changes (abiotic)
- pollution in environment (abiotic)
- natural disasters such as fires, earthquakes, tsunamis, hurricanes, tornadoes, etc. (abiotic)
- food (abiotic)
What are the 6 levels of Ecological Organization?
1. Organism
2. Population
3. Community
4. Ecosystem
5. Biome
6. Biosphere
If water rose from a lake, formed clouds and then fell from the sky to move down an incline, what step would be next in the water cycle if that water was to be absorbed by the underground?
Infiltration
State the difference between immigration and emigration using geese as an example.
 Geese leaving their home is called emigration.
Geese leaving their home is called emigration.
Geese arriving to a new home/place is called immigration.
State one negative impact for the water cycle, the carbon cycle and the nitrogen cycle)
Carbon Cycle:
Combustion: when wood or fossil fuels, which contain carbon, are burned
Don't use your notes. Challenge yourself. Can you name all the steps of the nitrogen cycle? There are five.
Also, what does the first step do?
1. Nitrogen fixation - Bacteria in the soil or water converts nitrogen into forms that plants can use.
2. Decomposition
3. Ammonification
4. Nitrification
5. Denitrification
How many criterias for Life are there for Living Organisms? What are they?
6 criterias
1. Be made up of one or more cells
2. Contains DNA or RNA
3. Can grow and reproduce
4. Responds to stimuli
5. Can adapt to environment
6. Has a metabolism (can consume energy and make waste)
Humans increase carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere, and contribute to the carbon cycle by doing what?
By
- giving birth to more babies each year
- combustion from driving cars or burning fossil fuels
- cutting down forests/trees
- not planting more plants
What is the difference between a Density-Dependent Limiting Factor AND a Density-Indepedent Limiting Factor
Density-dependent limiting factors operate more strongly on large, dense populations than on smaller ones
These are factors that can be triggered by an increase in population size, and thus crowding.
Density-independent limiting factors regulate population growth regardless of its size or density.
Nearly all species in an ecosystem are affected equally by density-independent limiting factors.
Why can disease be spread more easily in a larger, more dense population? What type of limiting factor does this make disease?
Because it is density-dependent limiting factor ( a biotic one because a living organism is effecting another living organism) therefore it has a bigger effect on a more dense population.
Sing the Living Things Characteristics Song for 500 points
Grow and Reproduce!
Use energy,
Have DNA,
Adaptive Living Dudes!