Giant molecules that are important building blocks for life
What are macromolecules?
Parts of molecules that tell how a larger molecule will work
What is a functional group?
What is polarity?

What is a construction worker?
Why DNA dissolves in water
What is "because water and DNA are both polar"?
This functional group and its characteristics
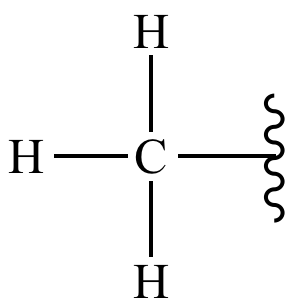
What is methyl (non-polar and stores energy)?
The two factors that affect polarity
What are electronegativity and molecular geometry?
What is hydrolysis?
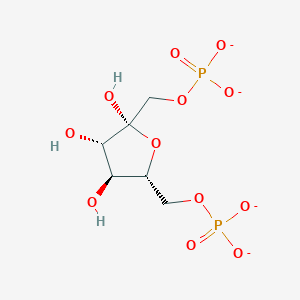
This molecule is a building block for this macromolecule

What is a nucleic acid?
The functional groups present and the properties of each functional group
What are phosphate (polar and acidic) and hydroxyl (polar)?
A special type of dipole-dipole IMF that includes a hydrogen bonded to Nitrogen, Oxygen, or Fluorine
What is a hydrogen bond?
Two monomers are chemically bonded together and produce a water molecule
What is dehydration synthesis?
The 4 macromolecules along with their corresponding elements
What are:
1. Carbohydrates (CHO)
2. Lipids (CHO)
3. Proteins (CHON)
4. Nucleic Acids (CHONP)
The common name for molecules that contain hydroxyl groups
What is an alcohol?
This molecule

What is soap?
What is hydrolysis?
The 4 macromolecules along with their corresponding monomers
What are:
1. Carbohydrates (monosaccharides)
2. Lipids (glycerol and fatty acids)
3. Proteins (amino acids)
4. Nucleic Acids (nucleotides)
Molecules that release hydrogen ions into solution
What are acids?
How this molecule reacts with water

What is "it would dissolve"?
DAILY DOUBLE!
What happens to a solution when this molecule is heated in water
What is "hydrolysis would break down the molecule and cause the solution to thicken"?