Which of the following statements about levels of biodiversity is correct?
A.Genetic biodiversity is a measure of the total number of genes in a community.
B.A narrow distribution of habitats leads to an increase in species diversity.
C.Global hotspots are areas where species diversity is thriving due to habitat restoration.
D.A population with high genetic biodiversity is better able to respond to environmental stressors.
D.A population with high genetic biodiversity is better able to respond to environmental stressors.
How does the practice of overfishing disrupt the provisioning services that oceans provide, and what are the wider ecological and economic effects?
A) It leads to healthier fish populations.
B) It increases fish sales in the short term, but reduces future population levels and economic stability.
C) It reduces pollution in marine ecosystems.
D) It has no impact on fish populations.
B) It increases fish sales in the short term, but reduces future population levels and economic stability.
Why are species with high genetic diversity more likely to survive changes in environmental conditions?
A) They have fewer offspring.
B) They are more susceptible to disease.
C) They have a greater variety of traits that increase the likelihood that some individuals will survive new conditions.
D) They reproduce slower than low-diversity species
C) They have a greater variety of traits that increase the likelihood that some individuals will survive new conditions.
How do species adapt to environmental changes over time, and why is genetic variation important in this process?
A) Species adapt by acquiring traits through mutation, and genetic variation increases the chances of beneficial traits emerging.
B) Species adapt by becoming smaller, and genetic variation reduces adaptability.
C) Species do not need genetic variation to adapt.
D) Genetic variation slows down the adaptation process.
A) Species adapt by acquiring traits through mutation, and genetic variation increases the chances of beneficial traits emerging.
What is the primary difference between primary succession and secondary succession?
A) Primary succession occurs in areas with existing soil, while secondary succession begins on bare rock.
B) Primary succession occurs after a disturbance that leaves soil intact, while secondary succession starts with no soil.
C) Primary succession starts on bare rock without any pre-existing soil, while secondary succession starts with established soil after a disturbance.
D) Secondary succession occurs after volcanic eruptions, while primary succession occurs after human disturbances.
C) Primary succession starts on bare rock without any pre-existing soil, while secondary succession starts with established soil after a disturbance.
Which of the following best explains how environmental stressors, such as wildfires, can affect biodiversity in an ecosystem?
A.After an environmental stress, a genetic bottleneck may occur, which will increase genetic diversity.
B.Habitat diversity will increase the available niches if the landscape becomes more uniform after a disturbance.
C.Ecosystems with more species diversity are more likely to recover after a disturbance than ecosystems with low species diversity.
D.Small populations are less likely to go extinct than larger populations, so the species diversity will remain constant.
C.Ecosystems with more species diversity are more likely to recover after a disturbance than ecosystems with low species diversity.
Which of the following would be categorized as a cultural ecosystem service of forests?
A.Recreation and scenic areas for tourism
B.Timber and landscape materials
C.Mushroom and plant harvests
D.Soil stabilization and air purification
A.Recreation and scenic areas for tourism
How do rising ocean temperatures due to climate change affect the ecological tolerance of marine species?
A) Marine species become more adaptable to changing conditions.
B) Warmer temperatures push marine species outside their range of tolerance, potentially causing population declines or migration.
C) Warmer temperatures have no impact on marine species.
D) Marine species thrive in warmer temperatures.
B) Warmer temperatures push marine species outside their range of tolerance, potentially causing population declines or migration.
Which best describes GPP in an ecosystem?
A. The amount of cellular respiration occurring over a given time.
B. GPP is the total amount of energy lost as energy moves between trophic levels.
C. GPP is the total amount of energy captured by producers minus the energy energy that producers respire.
D. GPP Is the total amount of solar energy captured by producers over a period of time.
D. GPP Is the total amount of solar energy captured by producers over a period of time.
Which of the following best describes the role of a keystone species in an ecosystem?
A) A keystone species is always the most abundant species in an ecosystem.
B) A keystone species is critical to maintaining the structure and function of an ecosystem, even if its population size is small.
C) A keystone species is a plant species that provides food for most herbivores in the ecosystem.
D) A keystone species is the largest predator in an ecosystem, and its removal only affects prey populations.
B) A keystone species is critical to maintaining the structure and function of an ecosystem, even if its population size is small.
Based on the theory of island biogeography, which of the following is the most likely reason that an island in the ocean that is 5 kilometers from a continent would have a higher number of species that one that is 15 kilometers from a continent?
A.There are more species that have the ability to travel 5 kilometers than can travel 15 kilometers.
B.Islands that are closer to continents always have a wider range of habitats than more distant islands do.
C.There are smaller populations of each species on islands that are at greater distances from continents.
D.Islands that are closer to continents always have more ecological niches than more distant islands do.
A.There are more species that have the ability to travel 5 kilometers than can travel 15 kilometers.
In what ways does deforestation impact both the regulating and supporting services that forests provide?
A) It increases air quality and soil fertility.
B) It has no significant effect on regulating services.
C) It reduces CO2 storage and disrupts water filtration processes, leading to negative ecological consequences.
D) It increases timber production
C) It reduces CO2 storage and disrupts water filtration processes, leading to negative ecological consequences.
Consider a species that migrates seasonally: how might changing climate patterns affect its migration routes or breeding behavior?
A) Climate changes can shift migration patterns by altering food availability and timing, leading to stress on the population.
B) Climate changes will improve migration routes, increasing population sizes.
C) Migration routes will remain unaffected by climate change.
D) Breeding will occur more frequently due to climate changes.
A) Climate changes can shift migration patterns by altering food availability and timing, leading to stress on the population.
Which statement is true about both the Phosphorus and Nitrogen Cycle?
A. Bacteria play a crucial role in converting the nutrients to an atmospheric form.
B. Volcanic eruptions are major sources.
C. Both Nitrogen and Phosphorus are required for plant growth.
D. Both processes depend on weathering and erosion.
C. Both Nitrogen and Phosphorus are required for plant growth.
In a forest undergoing secondary succession after a fire, which sequence of plant species would you expect to see over time?
A) Large trees → grasses → shrubs → mosses and lichens
B) Mosses and lichens → small shrubs → grasses → large trees
C) Grasses and wildflowers → shrubs and small trees → large trees
D) Large trees → small shrubs → grasses → mosses and lichens
C) Grasses and wildflowers → shrubs and small trees → large trees
Why do small isolated islands have higher extinction rates then larger islands that are less isolated?
A. Small islands have less available resources.
B. Small islands accumulate more species.
C. Small islands have more species available.
D. There are less available niches in small islands.
A. Small islands have less available resources.
Which of the following correctly describes the disruption of an ecosystem service by an anthropogenic activity?
A.Provisioning services are disrupted by increased combustion of fossil fuels, which leads to an increase in air pollution
B.Regulating services are disrupted by flash flooding from a hurricane, which decreases available food sources
C.Supporting services are disrupted by an earthquake that causes habitat destruction, which displaces plants and animals.
D.Cultural services are disrupted by a tornado that causes the loss of acres of forest, which reduces the amount of harvestable timber.
A.Provisioning services are disrupted by increased combustion of fossil fuels, which leads to an increase in air pollution
How could rising sea levels, due to climate change, lead to the displacement or extinction of coastal species?
A) Coastal species will adapt quickly to rising sea levels.
B) Rising sea levels can flood habitats, forcing species to migrate or face extinction due to loss of resources.
C) Rising sea levels provide new habitats for coastal species.
D) Coastal species will not be affected by sea level rise.
B) Rising sea levels can flood habitats, forcing species to migrate or face extinction due to loss of resources.
Scientists calculated the NPP at 2 different forest sites. Both forests have the same GPP.
Forest A has a NPP of 600 and Forest B has a NPP of378. Why?
A.Forest A has higher soil nutrients.
B.Forest B has has less biodiversity.
C.Forest A plants have lower rates of cellular respiration.
D.Forest A plants have higher biomass.
C.Forest A plants have lower rates of cellular respiration.
In a coastal ecosystem, sea otters are considered a keystone species because they prey on sea urchins, which feed on kelp. If the sea otter population significantly decreases due to human activity, what is the most likely long-term ecological effect?
A) The sea urchin population will increase, leading to a decline in kelp forests, which will disrupt habitat for many marine species.
B) The sea urchin population will decrease, causing kelp forests to grow uncontrollably and outcompete other plant species.
C) The sea otter population will quickly rebound, and the ecosystem will return to its original state without any major changes.
D) The loss of sea otters will have no significant impact, as other predators will take over their role in controlling the sea urchin population.
A) The sea urchin population will increase, leading to a decline in kelp forests, which will disrupt habitat for many marine species.
Why do islands present unique opportunities to observe evolutionary processes such as adaptive radiation?
A) Islands are shrubbier so species evolve faster.
B) Islands have limited resources and unique environmental pressures, leading to rapid speciation.
C) Islands do not experience natural selection.
D) Evolution does not occur on islands.
B) Islands have limited resources and unique environmental pressures, leading to rapid speciation.
Reflect on the ecosystem near where you live: which service provided by that ecosystem best support the health of the ecosystem, and why is it crucial to maintain?
A) Recreation because it’s a source of income.
B) Supporting services because they help maintain biodiversity and provide long-term stability.
C) Provisioning services because they directly provide goods like food and timber.
D) Cultural services because they generate tourism revenue.
B) Supporting services because they help maintain biodiversity and provide long-term stability.
Based on the data in the graph, which of the following events occurred after the glacial retreat?
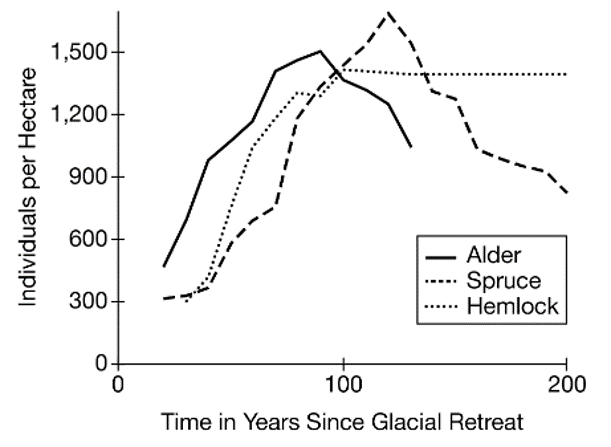
A.Primary succession
B.Flooding
C.Sea level rise
D.Global Climate Change
A.Primary succession
In a northern forest, a population of rabbits is exposed to increasingly colder winters due to climate change. Over several generations, researchers notice that more rabbits are born with thicker fur, which helps them survive the harsh winters better than those with thinner fur. As the winters become even colder, the proportion of thick-furred rabbits continues to increase.
Which of the following best explains the role of selective pressure in this scenario?
A) Thicker fur is a mutation that appears randomly, but it provides no advantage to the rabbits in colder climates.
B) Cold winters act as a selective pressure, favoring rabbits with thicker fur, leading to an increase in the trait over time.
C) Rabbits with thinner fur migrate to warmer climates, leaving only thick-furred rabbits in the population.
D) The rabbits with thinner fur actively grow thicker coats in response to the colder weather
B) Cold winters act as a selective pressure, favoring rabbits with thicker fur, leading to an increase in the trait over time.
Based on the data showing in the graph, which of the following best describes how ecologists could determine when this ecosystem is approaching climax community?
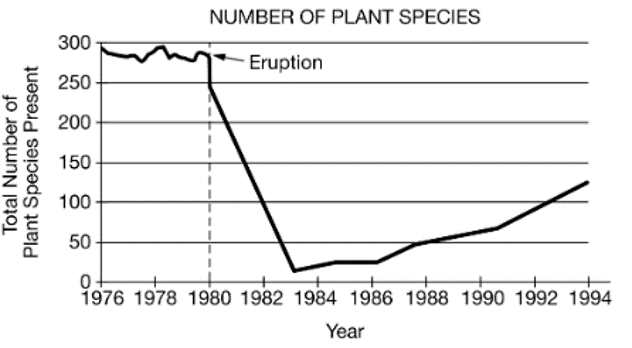
A.Determine if the keystone species in the ecosystem is present two years after the volcanic eruption.
B.Measure the biomass of pioneer species present before and after the volcanic eruption.
C.Record the number and type of producers present every year after the eruption.
D.Calculate the net primary productivity of a specific indicator species every year after the eruption
C.Record the number and type of producers present every year after the eruption.