What is the fundamental difference between covalent and ionic bonding?
Covalent involves shared electrons
Ionic involves transfer of electrons
An example of a monosaccharide is ________.
- fructose
- glucose
- galactose
True or False? All cells have a cell wall.
False
Are membrane phospholipids fluid or stationary?
Fluid.
Most of the functions of a cell membrane, including transport and enzymatic function, are performed by
proteins
Magnesium has an atomic number of 12. How many protons, neutrons and electrons does it have?
12 protons
12 neutrons
12 electrons
What feature of fats makes them hydrophobic?
Fats have nonpolar hydrocarbon chains.
The function of chloroplasts is
photosynthesis
Phospholipids are important components of
the plasma membrane of cells
How does water moves via osmosis?
from an area with a low concentration of solutes to an area with a higher concentration of solutes.
The figure below shows five water molecules. What atoms are involved in hydrogen bonding?
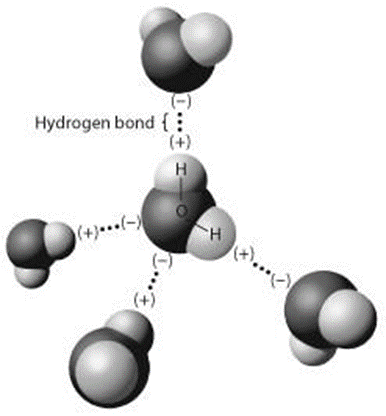
oxygen and hydrogen atoms of different water molecules.
Amino acids can be distinguished from one another by
the chemical properties of their R groups
Why is the membranous compartmentalization of a cell important?
Because it allows different chemical conditions to be maintained in different parts of the cell.
How are phospholipids different from triglygerides?
Phospholipids have a hydrophilic phosphate head group and hydrophobic fatty acid side chains.
The principal force driving movement in diffusion is __________.
the concentration gradient
What is a compound?
A substance that contains two or more elements in a fixed ratio.
How are genes used by cells to build proteins?
The genes in DNA direct the synthesis of an RNA molecule, which is used to build a protein.
Cyanide inhibits mitochondrial function; as a result, the rate of
ATP synthesis decreases.
How do phospholipids assemble to form a membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer. Polar head groups face the extracellular and cytoplasmic side of the membrane, hydrophobic fatty acid side chains orient towards the inside of the bilayer.
Facilitated diffusion across a biological membrane requires ________ and moves a substance ________ its concentration gradient.
transport proteins; down
A single water molecule (H—O—H) is held together by
two polar covalent bonds.
A diet high in animal products and hydrogenated vegetable margarine may increase the risk for heart disease. This is because:
most animal fats are saturated and many hydrogenated vegetable margarines contain high levels of trans fats.
Name the organelles that are not components of the endomembrane system.
Ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, cytoskeleton
The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as consisting of
a phospholipid bilayer with embedded carbohydrates and proteins.
Some protozoans have special organelles called contractile vacuoles that continually eliminate excess water from the cell. The presence of these organelles tells you that the environment:
is hypotonic to the protozoan.