YOU are an example of this type of cell:
a) Prokaryotes
b) Eukaryotes
c) Both
b
This person is attributed with naming cells
Robert Hooke
This is the site of protein production:
ribosomes/ rER
These cells can become any other cell except embryonic cells
Pluripotent stem cells
What is the name of this model?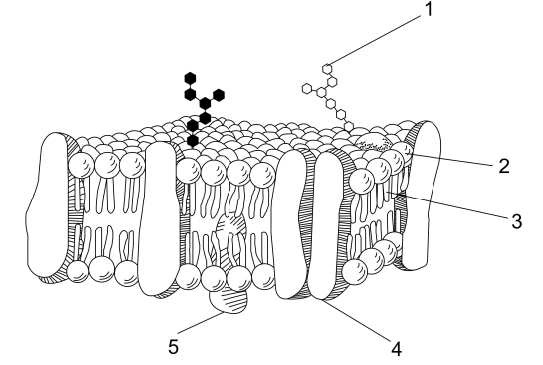
Fluid Mosaic Model
This cell type contains a cell membrane:
a) Prokaryotes
b) Eukaryotes
c) Both
c
This person looked at single celled organisms under a microscope while looking at pond water:
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
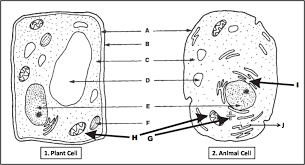
State both the name of the organelle and the letter of the diagram below.
This is where DNA lives:
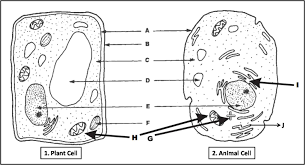
Nucleus, E
This is the process in which embryonic cells become specialized in structure and function.
Cell Differentiation
Which part is hydrophilic?
This cell type contains DNA:
a) Prokaryotes
b) Eukaryotes
c) Both
c
What is Number 1?
Body tube
State both the name of the organelle and the letter of the diagram below.
This is the site of ATP production:
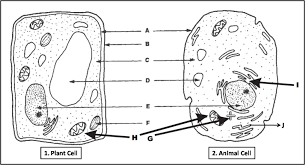
Mitochondria: H
This is a long, whiplike structure that allows for movement in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
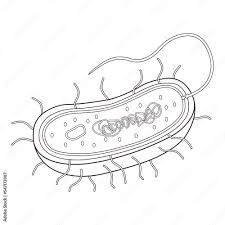
Flagellum
This part is hydrophobic:
3
This cell type does NOT contain membrane bound organelles:
a) Prokaryotes
b) Eukaryotes
c) Both
a
What is number 7?
Diaphragm
State both the name of the organelle and the letter of the diagram below.
This is the site of photosynthesis:

Chloroplast, F
These are short hairlike structures that are used for movement or attachment in prokaryotes and eukarotes.
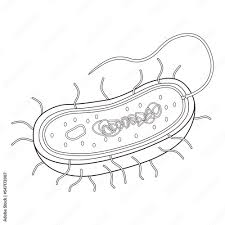
Cillia
This is a protein where substances pass through the membrane:
4
This cell type contains a nucleoid:
a) Prokaryotes
b) Eukaryotes
c) Both
If looking at a tissue slide with the 40x objective lens, what is the total magnification of the image?
400x
These 3 organelles are unique to plants:
Chloroplasts, cell wall and central vacuole
State the 3 parts of the cell theory.
2) Cells are the smallest unit that carries out life's functions
3) All cells come from pre-existing cells
Describe the function of the membrane, using the term semi-permeable.
The membrane is semi-permeable, acting as a bouncer, only letting certain substances in and out of the cell.