What is the primary source of energy that drives Earth's weather and climate systems?
The Sun
What is albedo?
the fraction of light that a surface reflects.
What is the primary greenhouse gas released when fossil fuels are burned?
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
41,000 years
What is the name of these imaginary horizontal lines that help you identify locations on Earth North and South of the equator?
Lines of Latitude
As ice melts and more dark land is exposed, air temperature ___________
Increases
What is a greenhouse gas?
Gases (like CO2 and Methane) that trap heat in the atmosphere and keep the Earth warm.
Provide two pieces of evidence to support the claim that the climate stability of the Holocene Optimum made agriculture possible.
- Higher temperatures released more CO2 into the atmosphere which allowed plants to absorb more CO2. This meant they could be more productive.
- Temperatures were higher and more stable after the Holocene warming, allowing longer growing seasons and better conditions for plants to grow.
The three cyclical changes in the Earth's position that affect the amount of sunlight the Earth receives are together referred to as...
Milankovitch Cycles
What is the name and temperature of the ocean current which circulates water off the West coast of South America?
Peru Current, Cold
What is the relationship between CO2 and temperature?
As one increases, the other increases. This is called a positive feedback loop.
Describe how CO2 concentrations in plants change as temperatures increase.
Higher temperatures allow plants to trap more CO2.
However, if the temperature levels increase too much it will kill the plants and CO2 will be released back into the atmosphere.
What angle of insolation hits location X on the December solstice?
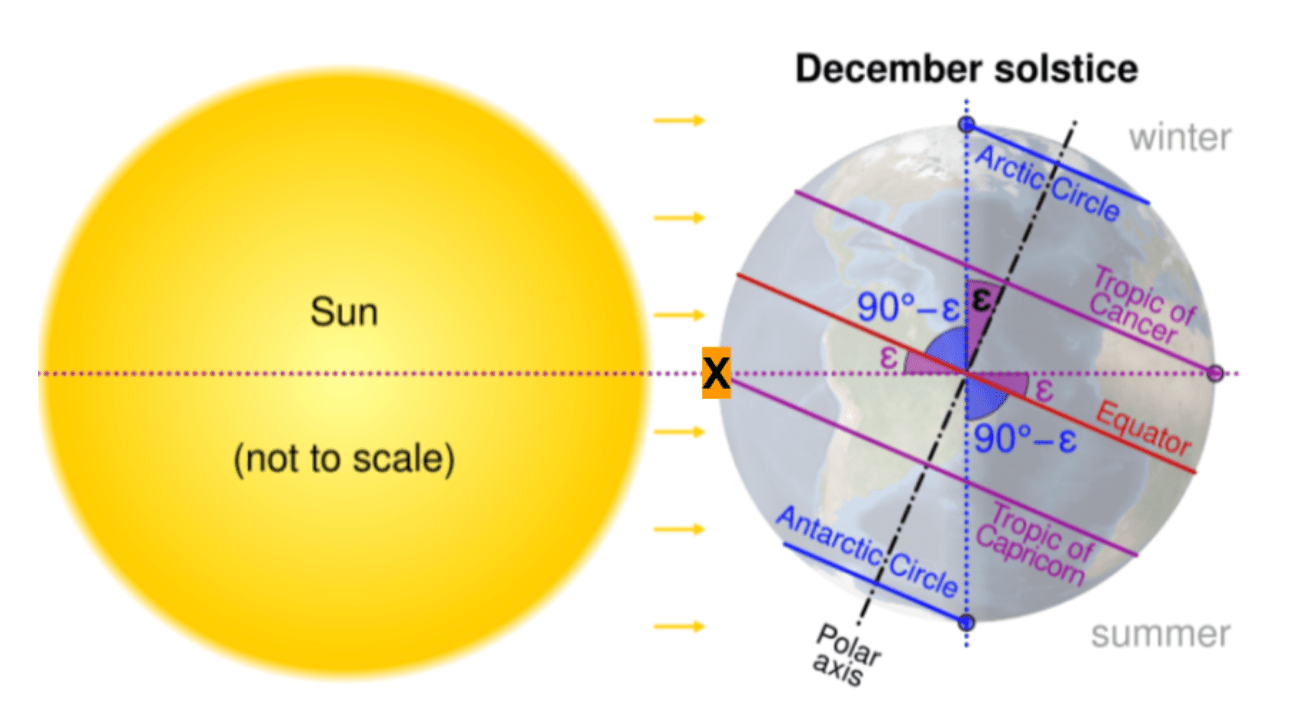
90 degrees
In which example is the air temperature above the surface warmer, and WHY?
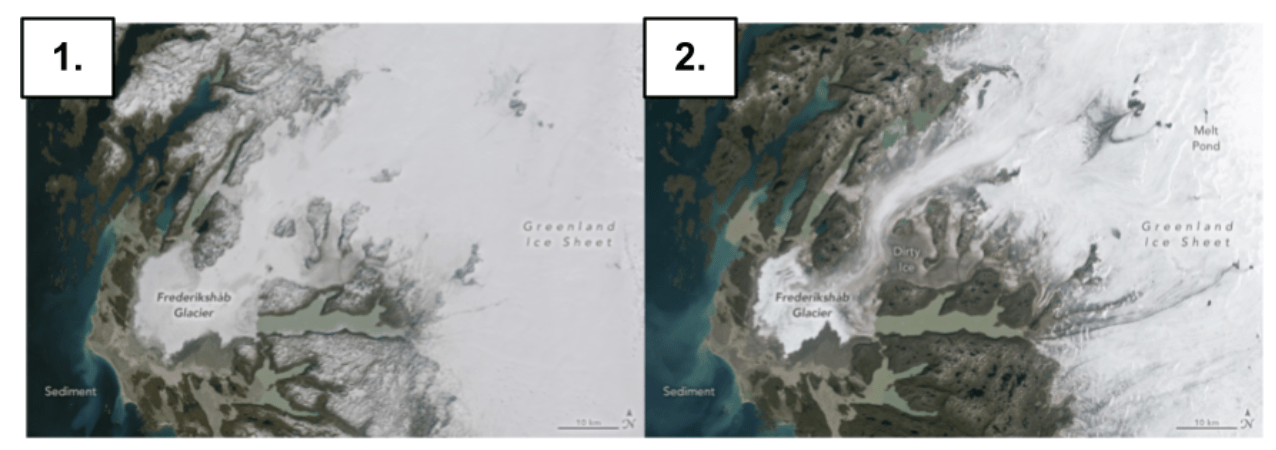
Picture 2 because more dark land is exposed. This means albedo is low so heat is absorbed by the land and transferred to the air above it.
Which carbon reservoir holds the most amount of carbon?
The Ocean
Explain, step by step, why the climate warmed rapidly after the Younger Dryas.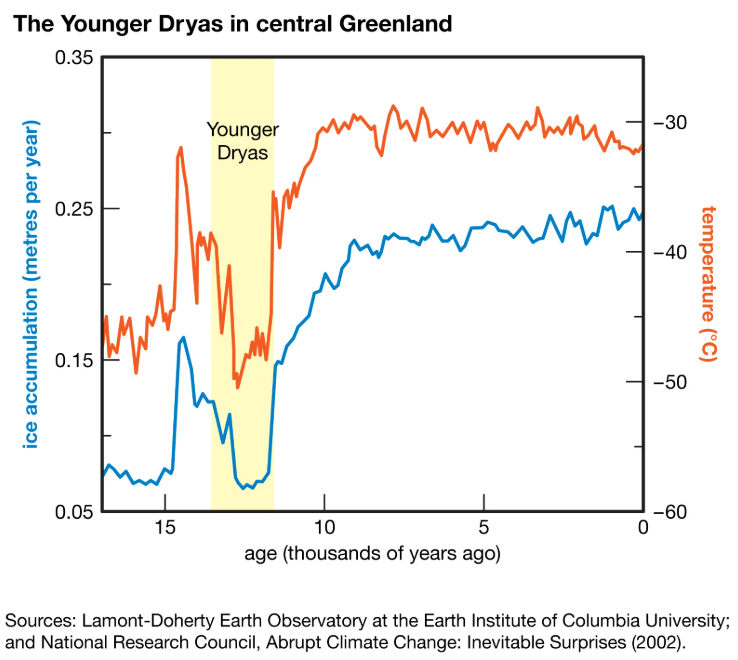
1. Since ocean currents were no longer taking warmer equatorial waters toward the Arctic, warm water accumulated at the equator and spread south to Antarctica.
2. Warming oceans in the south released CO2 into the atmosphere.
3. Warming temperatures caused permafrost in Antarctica to melt and release more CO2 and methane which spread around the globe.
4. Global temperatures spiked.
How does the angle of insolation affect heating at Earth's surface?
Higher angle of insolation = warmer surface temperature
Lower angle of insolation = cooler surface temperature
Why does the Arctic warm 4 times more quickly than other places in the world?
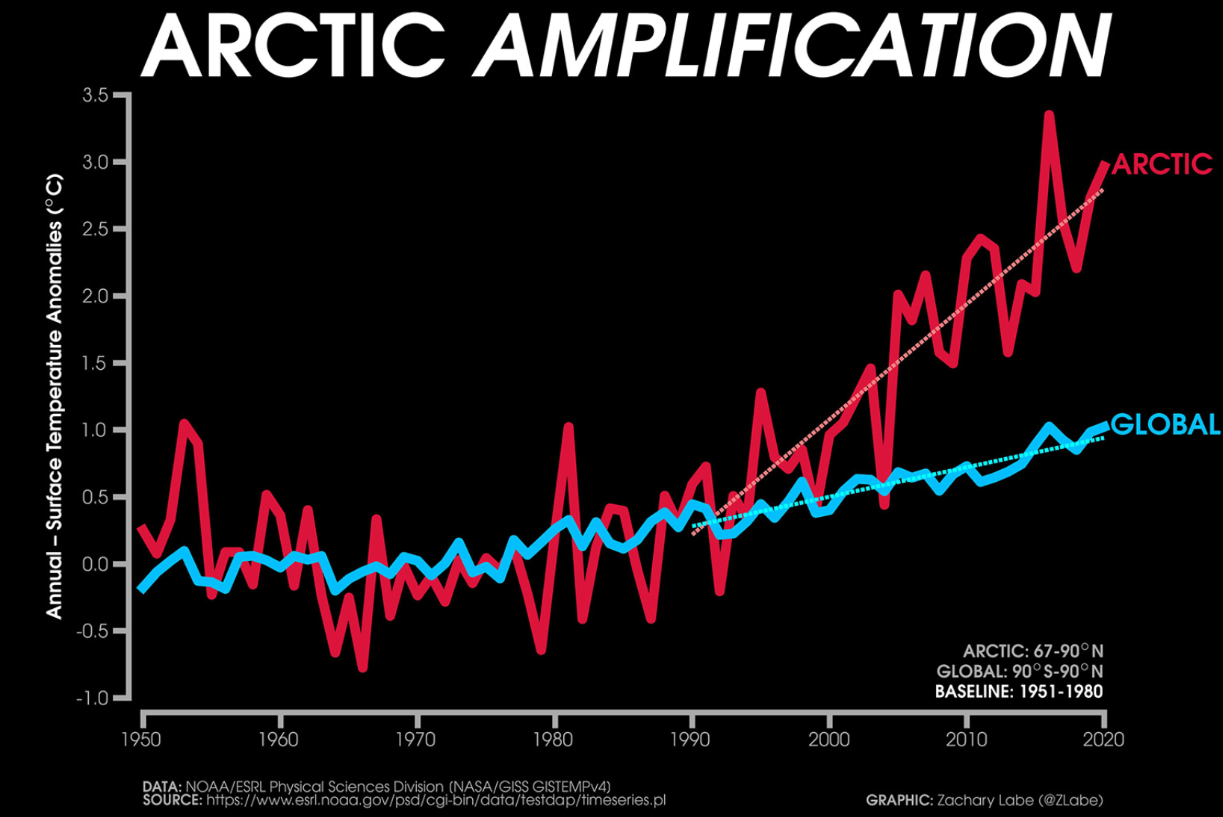
When ice melts, it exposes the darker ocean, which absorbs more heat from the sun than ice. This reduces the Earth's albedo, which is the amount of heat a surface absorbs from sunlight.
Other places on Earth do not have this same change in Albedo so do not have the same positive feedback loop.
Which three reservoirs exchange carbon with the atmosphere?
1. ocean
2. terrestrial biosphere
3. permafrost
(I will also accept ice sheets/glaciers if that was one of your three).
Explain, step by step, why the climate cooled rapidly during the Younger Dryas.
1. Temperatures rose and caused freshwater to melt into the Atlantic Ocean.
2. Density difference was disrupted.
3. Ocean currents slowed/stopped, ceasing the movement of warm water to the north pole.
4. When warm water stopped circulating, so did warm air.
5. Temperatures cooled.