Which organelle modifies, packs and ships proteins?
Golgi Bodies or Golgi Appuratus
What is the main component of the cell membrane?
phospholipids
Is this passive or active?
Active
Active moves from a _____ concentration gradient to ________ concentration gradient.
low, high
What is osmosis?
Movement of water through the cell membrane from high to low
What is the biggest difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
nucleus
The cell membrane is semi-permeable. What does semi-permeable mean?
It allows certain molecules to come in and out but not all.
What type of transport is used when a cell wants to remove a large amount of molecules to the outside of a cell?
Exocytosis

What type of transportation is happening?
Diffusion
What are the 3 types of solutions?
Hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic
What is the correct order of classification from general to more specific?
KFCOFGS
What is another name for cell membrane?
plasma membrane
Does way does passive move from the concentration gradient?
down
What kind of proteins does facilitated diffusion use?
Channel protein or carrier protein
What type of solution was this plant cell placed in?

Hypertonic
How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration connected?
reactants and products are opposite
Why is the cell membrane described as a bilayer?
It has 2 rows of phospholipids
Why does active transport require energy to move molecules of a substance across a cell membrane?
The substance moves from low to high concentration, against the concentration gradient.
The sodium-potassium pump functions to pump sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell. Which type of transport does this statement describe?
Active Transport
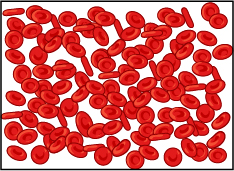
A sample of red blood cells are placed in an isotonic solution and viewed under a microscope.
Then, sugar is added to the solution to create a hypertonic solution. The sample is then looked at under a microscope again.
What happened to the red blood cells after the sugar was added to the solution?
The water came out of the cells
Which of the following is a lipid?
A
What is the fluid mosaic model and what does it mean?
Fluid- moves around
mosaic- many parts
The cell membrane is fluid and flexible and made out of lipids, carbs and proteins.
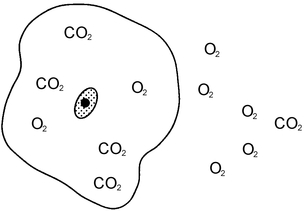
What would happen to the C02 that's inside the cell?
CO2 would move across the cell membrane to maintain homeostasis
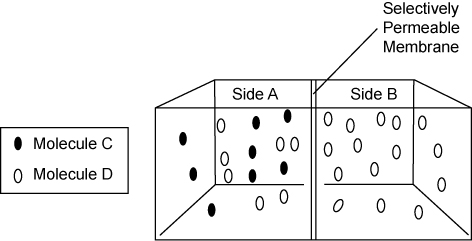
The membrane shown below is permeable to Molecule C, but not to Molecule D.
How will the molecules move to reach equilibrium?
Molecule C will move across the membrane to reach equilibrium but Molecule D can not move across the membrane.
Which cup has a hypertonic solution?

3