What is a theory?
Answers “How or why does that happen?”
Identify the key structure that distinguishes a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
What is a nucleus?
In prokaryotes, how is the DNA described and where is the DNA located?
What is Free-floating in the cytoplasm?
Identify the types of genetic material found in viruses.
What is DNA and RNA?
Identify the image. BE SPECIFIC.
What is a bacteria (Bacillus)?
What is the term for an organism that causes a disease?
Pathogen
Who is Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, or Virchow?
Give an example of a prokaryotic cell.
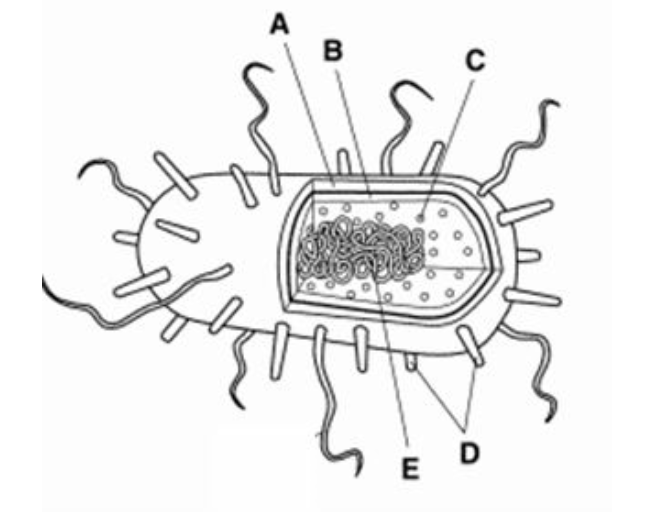 Letter C represents ________________.
Letter C represents ________________.
Describe the structure of a virus.
What is genetic material (DNA/RNA) surrounded by a protein coat (capsid)?
Identify the type of cell shown below and cite your evidence.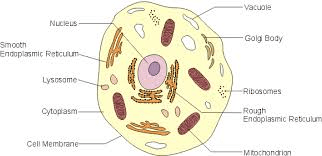
What is a eukaryotic animal cell? The cell does NOT have a cell wall, large central vacuole or chloroplasts.
Identify whether each of the following is caused by a bacteria or virus.
A. Common cold
B. Flu
C. Strep throat
D. Lyme Disease
A. Common cold - Virus
B. Flu - Virus
C. Strep Throat - Bacteria
D. Lyme Disease - Bacteria
Identify TWO characteristics of living things that are part of the Cell Theory
Cells
Reproduce
What are membrane-bound organelles?
Identify the two kingdoms that consist of prokaryotic cells.
What is Archaebacteria and Eubacteria?
Identify how bacterial and viral infections are treated/prevented.
Identify the image below.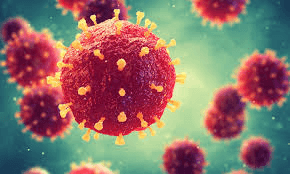
What is a virus?
How do bacteria cause disease?
Bacteria release toxin and damage nearby cells by reproducing and causing overcrowding.
How did the microscope contribute the cell theory?
The microscope allowed scientists to see cells which could not be seen with the human eye.
What is DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes and the cell membrane?
Give TWO examples of the roles bacteria play in an ecosystem.
What is decomposer and nitrogen fixer?
Viruses are considered host-specific because _____.
Viruses can only infect specific hosts. For example, the tobacco mosaic virus can only infect the tobacco plant.
Identify the type of cell shown below and cite your evidence.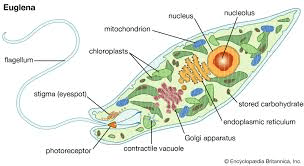
Describe how viruses cause disease.
Viruses inject the host cell with genetic material such as DNA or RNA that then takes over the cell. The virus can immediately takes over the cells and uses the cell machinery to make new copies of itself. Eventually, the new viruses are released when the cell breaks apart or lysis. In some cases, the viral DNA or RNA remains in the cell and is dormant for a while and then makes copies of itself.
Identify THREE parts of the cell theory.
What is :
1.) All living things are made of cells.
2.) Cells are the basic unit of structure & function.
3.) All cells come from preexisting cells.
Identify the 4 Kingdoms that contain eukaryotic cells.
What is Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia?
Give an example of TWO ways that bacteria are helpful to humans.
Bacteria can be used to:
1.) make cheese and yogurt
2.) clean up oil spills
3.) purify water
4.) make drugs
5.) extract needed nutrients and vitamins from food you eat
USING CR RED HOG, explain why viruses are considered nonliving. BE SPECIFIC.
Viruses are considered nonliving because viruses do NOT have all 8 characteristics of living things. Some but not all viruses contain DNA. All viruses evolve and reproduce, but only can reproduce inside a host cell. Viruses are not cells, do not respond to stimuli, undergo homeostasis, obtain or use energy or grow/develop.
This red structures in the diagram depict a _______________.
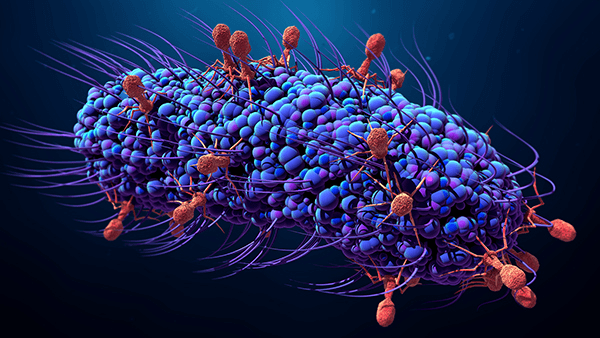
Desribe how both bacterial and viral infections can be treated and prevented.
Bacterial & Viral Prevention
Wash hands, store food in fridge, sterizilize with heat, cover mouth when cough
Vaccination
Bacterial Treatment - Antibiotics
Viral Treatment - Antiviral Drugs