What is Newton's 1st Law?
Inertia or An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion
Three things needed to calculate potential energy.
Mass, height, gravity
What two unknowns do you need to calculate kinetic energy
A vehicles capacity to gain speed within a short time.
Acceleration
What's the difference between mass and weight?
Mass measures the amount of matter, weight measures the force of gravity
Mass is always the same but weight can change
What is Newton's 2nd Law?
Force = Mass x Acceleration
F=MA
At what point on the roller coaster will potential and kinetic energy be equal?
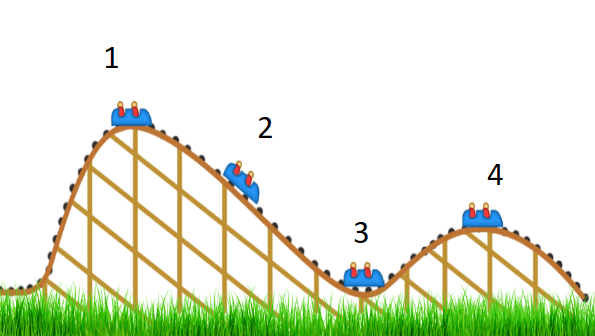
2
Which point would have the highest amount of kinetic energy?
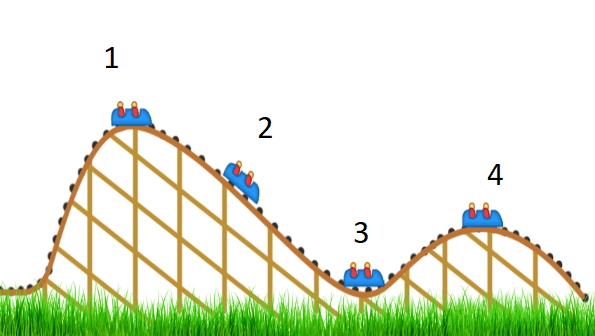
3
Something that moves an object.
Force
Determine the net force and give the direction.
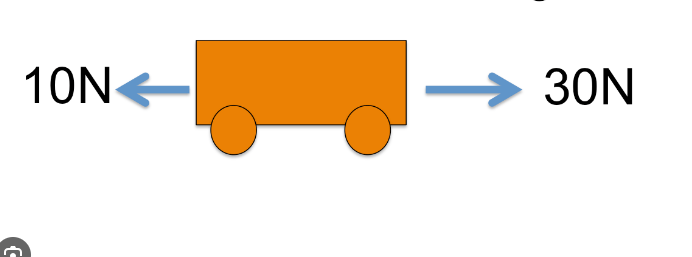
20N to the right
What's Newton's 3rd Law?
If placed at the same starting position on a ramp, which would have the least amount of potential energy? Why?
Golf ball, tennis ball, baseball, bowling ball
Golf ball because it has the smallest mass
What is the relationship between kinetic energy and speed?
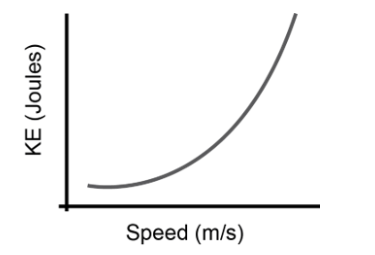
As speed increases, kinetic energy increases
Movement of energy from one system to another.
Energy transfer
Heating a substance will cause the particle motion to _____.
Increase
Calculate the Force for Newton’s Second Law of Motion, if a 125 kg sphere is accelerating at 5 m/s2 - NO CALCULATORS
625 N
At what point on the roller coaster will potential and be highest?

1
Energy at 2 m/s would have how much kinetic energy (Joules)?
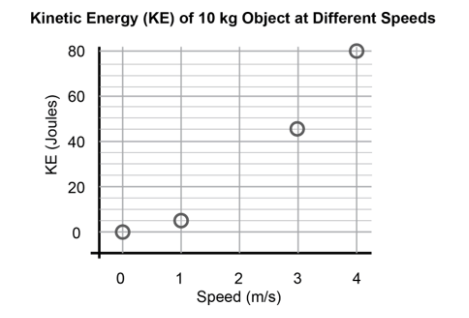
20 Joules
An object in motion stays in motion and an object at rest stays at rest unless application of force causes change in speed or direction.
Inertia
Energy transformation in the image below would include electromagnetic, chemical, and electrical. What order would the energy transformation occur?
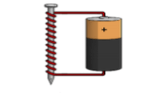
Chemical > electrical > electromagnetic
What's the difference between Balanced and Unbalanced Force?
Balanced Force = 0 N
Unbalanced Force = Everything else
Three types of potential energy we discussed and give an example for two
Elastic - rubber band, spring, bow and arrow
Chemical - battery, food, fuel
Gravitational - dropping an object
The acronym for types of kinetic energy is MELTS - what does each letter stand for and give an example for two.
Mechanical (movement) - scissors, pulleys, bike
Electrical - lamp, toaster, cell phone
Light - sun, flashlight, camera
Thermal - oven, fire, microwave
Sound - music, bells, talking
Define potential energy and kinetic energy and how they are related.
Potential energy is stored energy and kinetic energy is moving or in use. The amount of potential energy an object has determines the amount of kinetic energy an object has. Potential energy is converted to kinetic energy and back to potential energy.
Cooling a substance will cause a _____ in particle motion. The space between molecules will get _____.
Decreases; smaller