Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering this.
What is the activation energy?
In which organelle does cellular respiration take place?
What is the Mitochondria?
Photosynthesis occurs in this organelle in plant cells.
What is the chloroplast?
ATP is often referred to as the "currency" of this in the cell.
What is energy?
Enzyme activity is highly dependent on these two environmental factors.
What is PH and Temperature?
Label Y, is known as the ---.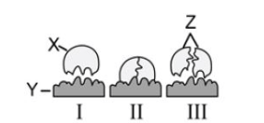
What is the Enzyme?
This first stage of cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into pyruvate.
What is Glycolysis?
The products of the light-dependent reactions are ATP, NADPH, and this gas.
What is oxygen?
ATP is produced in large quantities during this last stage of cellular respiration.
What is the electron transport chain?
This is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
What is photosynthesis?
This is the specific region of an enzyme where the substrate binds.
What is the active site?
This cycle produces electron carriers like NADH and FADH2 and takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
What is the Krebs cycle?
This molecule is the primary electron carrier produced in photosynthesis.
What is NADPH?
Enzyme names often end with this suffix.
What is -ase?
Carbon dioxide is used to facilitate the process.
What is photosynthesis?
This term describes the condition when an enzyme loses its shape due to extreme temperature or pH.
What is denaturation?
What molecule is the letter J representing? 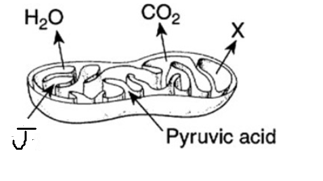
What is Oxygen?
This term refers to organisms that can produce their own food through photosynthesis.
What is autotrophs?
During cellular respiration, most ATP is generated in this stage where electrons are passed along a chain of proteins.
What is the electron transport chain?
This term describes how enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy.
What is catalysis?
Enzymes are made of this type of biological molecule.
What is proteins?
What molecule is the letter x representing? 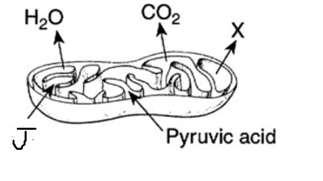
What is ATP?
This is the primary sugar produced during photosynthesis.
What is Glucose?
ATP stands for this.
What is adenosine triphosphate?
ATP is used to power this type of cell transport that moves molecules against their concentration gradient.
What is active transport?
This term refers to the reactants that fit into an enzyme's active site.
What is substrate?
The x represents the products of cellular respiration. What is X?
What is Carbon Dioxide and Water?
The rate of photosynthesis will increase if which factor increases?
What is light intensity?
Converts light energy into simple sugars.
What is photosynthesis?
Converts simple sugars into energy.
What is cellular respiration?
This is the part of the enzyme where catalysis occurs.
What is active site?
Why is cellular respiration important in the human body?
To remove carbon dioxide, and provide energy to fight off infections.
What is missing at letter Y?
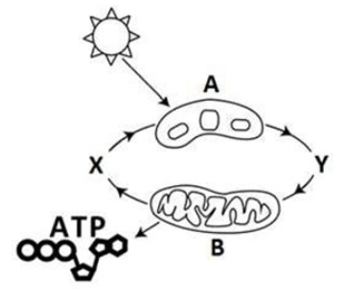
What is Glucose and Oxygen?
What cellular process is occurring at organelle B?
What is cellular Respiration?
Which letter on the graph indicates the energy of activation for the catalyze reaction? 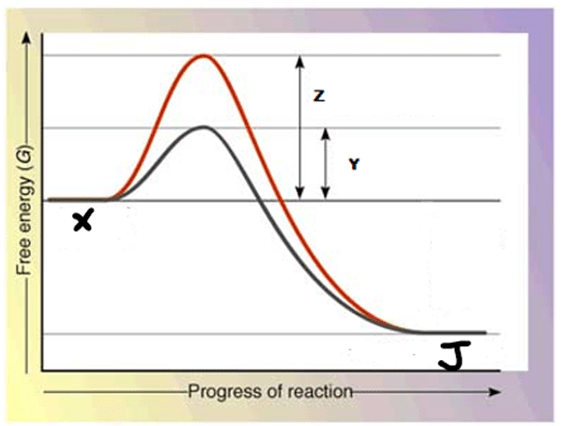
What is Y?