What causes daytime and nighttime on Earth?
Earth’s rotation on its axis causes day/night.
What is weathering?
Weathering is breaking down rocks into smaller pieces
What is a sediment?
small pieces of rock
Name 1 renewable resource
Wind, plants, animals, sunshine etc.
Give one example of a rapid change to Earth’s surface (a sudden event)
Earthquake, Volcano, Landslide
What is evaporation? Where does the water go when it evaporates?
Evaporation = liquid water becomes water vapor and rises into air.
Describe why we have seasons on Earth.
Tilt of Earth’s axis and orbit around the Sun cause seasons (tilt makes sunlight more direct in one hemisphere at a time).
What is erosion?
Erosion is movement of weathered material by wind, water, ice, or gravity
What step is missing?
1. Sediments are deposited
2. Layers are built up
3.
4. Cementation sticks the sediments together
3. Compaction
coal, oil/petroleum, natural gas
What rapid change does this image show?
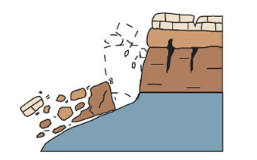
Landslide
Weather or Climate?
"The average yearly rainfall in San Antonio is 22 inches."
Climate because it is talking about the AVERAGE
What motion of earth causes a year (rotation or revolution) and approximately how long is one?
Revolution and about 365 days
Name two landforms created by deposition
River delta and a sand dune
What process squeezes layers of sediment together, helping form sedimentary rock and fossil fuels?
Compaction
Name one way people can conserve water at home or school
School: not leaving the sink running when you are done with it, not playing with the water fountains
Home: take shorter showers, turn the water off when you're not using it.
What is one way that Earthquakes change the Earth's surface?
they create cracks and openings in the Earth's surface
OR
they create mountains or mountain ranges.
What is the different between weather and climate?
Weather is short term air conditions and climate is long term, or the average weather conditions in an area.
Name two phases the Moon goes through?
new moon, full moon, crescent, quarter.
What causes the formation of a u shaped valley
Glaciers
What process sticks or "glues" sediment particles together to make hard rock?
Cementation
Explain why conserving fossil fuels is important for the future.
It is important to conserve fossil fuels because we will one day run out of fossil fuels.
What is one way landslides change the Earth's surface?
when land settles, new land is created at the base of the hill or mountain
land moves down slopes destroying hill and mountain sides in the process
True or False:
The interaction of the sun and the ocean can affect weather by increasing precipitation.
TRUE
What is a lunar phase?
Lunar phases are the changing appearance of the Moon as seen from Earth
How can water break a rock?
flowing water wearing away little bits at a time OR water getting into rock cracks and then freezing, thawing and freezing again
Name two differences between the formation of fossil fuels and sedimentary rocks.
What is an advantage of using renewable resources?
They are available in unlimited supply.
Volcanos can be destructive to Earth's surface but what is another way they affect Earth's surface?
They can create new rock/land.
True or False:
The interaction of the sun and the ocean can affect the weather by causing more frequent hurricanes.
TRUE