What part of the DNA molecule is responsible for coding genetic information?
Nitrogen Base
In all plant and animal cells, the nucleus contains long molecules of DNA. Describe the function of DNA.
DNA contains the blueprint (genetic information).
State the phases of Interphase
G0, G1, S Phase, G2
Why are checkpoints important in the cell cycle?
They maintain accuracy and prevent damaged cells from dividing
What is uncontrolled cell division called?
Cancer
Solve the complementary strand to the DNA strand shown below.
AGGTCAGGT
TCCAGTCCA
Guanine is complementary to which nitrogen base?
Cytosine
In which phase does the amount of DNA duplicate?
S Phase
Apoptosis is known as...
Programmed cell death
What type of cell are the blue cells in this picture?

Tumor
What makes up the backbone of a DNA molecule?
Phosphate and Deoxyribose Sugar
Nitrogen bases are connected by which bond?
Hydrogen bond
Which phase is only focused on cell growth?
G1 Phase
List the name of 4 checkpoints.
G1 checkpoint, S Checkpoint, G2 checkpoint, M checkpoint
When a cell undergoes uncontrollable growth, what most likely will form...
A tumor
What are the building blocks of DNA called?
Nucleotide
In a molecule of double-stranded DNA, the amount of Adenine equals to 22%. What is the percentage of Thymine present in double-stranded DNA?
22%
In which phase does the cell start to prepare for cell division?
G2 Phase
What is a way the cell cycle could be disrupted?
If a mutation is found
If the DNA is damaged
Environmental stresses
What is a distinguishing feature of a cancer cell?
It grows uncontrollably
List all 4 Nitrogen bases.
1. Thymine 2. Adenine 3. Guanine 4. Cytosine
The method by which DNA replicates is called...
Semi-Conservative method
In which phase does the cell leave the cycle and no longer prepare to divide?
G0 Phase
What happens to a cell if it does not pass a checkpoint and cannot be repaired?
Apoptosis
When tumor does not spread, it is known as
benign tumor
What does anti-parallel mean?
DNA strands go in opposite direction
During DNA replication where does the DNA open up?
Between the Nitrogen base pairs
In which phase does the cytoplasm split, creating two new daughter cells?
Cytokinesis
Why is cancer considered a disease of the cell cycle?
Because it bypasses checkpoints
What causes cancer cells to form instead of normal healthy cells?
Mutations in DNA
Describe the base-pair ruel
A=T
C=G
What does facilitate DNA replication in a cell?
Enzymes
In which phase does the nucleus divide to make two identical sets of chromosomes?
M Phase
What does the S-phase checkpoint monitor?
DNA replication accuracy
When tumor spreads, it is known as
malignant tumor
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
1. Phosphate 2. Deoxyribose sugar 3. Nitrogen Base
DNA's backbone is connected by which bond?
Covalent bond
At what numbers on the graph is the DNA replicating?
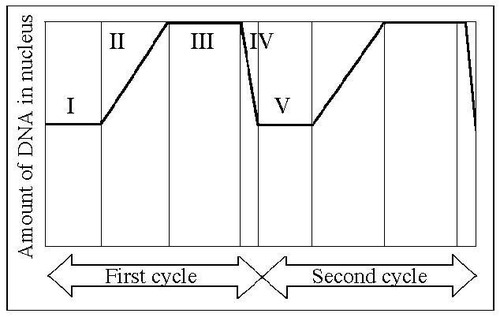
II
What normally controls the cell cycle but can become damaged, leading to cancer?
Cell cycle checkpoints
What is metastasis?
The spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body
Albumin is a protein that is secreted by liver cells and transported to the bloodstream. What factor most directly determines the amino acids that are combined to create albumin?
The sequence of nitrogen bases.
Which phase of the cell cycle is the longest?
Interphase
Which checkpoint helps prevent uncontrolled cell growth, like cancer?
G1
What is one environmental factor that can increase the risk of cancer?
UV radiation, smoking, pollution, etc.
What is a theory explaining the origin of DNA?
It evolved out of RNA
Lightning created a chemical reaction
Hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor
What happens during the M phase (mitosis)?
The nucleus divides to make two identical sets of chromosomes
How do cancer cells affect normal cells around them?
They take nutrients and space, harming healthy cells