What happens during the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
The cell grows, makes organelles except chromosomes
To produce Gametes
If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes, how many are in a gamete?
23
How many divisions occur in mitosis vs. meiosis?
Mitosis = one division; Meiosis = two divisions
What happens when cell cycle control fails?
Cells divide uncontrollably, forming tumors (cancer).
Which phase does DNA Replicate in?
S
Look at this image. What is occuring and during what phase does this happen?
Crossing over, Prophase I
Define diploid and haploid
Diploid (2n) = full set of chromosomes; Haploid (n) = half set.
How do their genetic results differ?
Mitosis makes identical cells; Meiosis makes genetically unique cells.
If a frog sperm contains 15 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would the skin cell of a frog contain?
30
If a somatic cell has 2n=46 chromosomes, which means it's diploid. What will the daughter cells be?
2n=46 chromosomes (diploid)
With your knowledge of Meiosis, What vocabulary word have we discussed on why siblings don't look like each other. And during what phase does this occur?
Independent Assortment, Anaphase I
What type of cells are produced by mitosis?
Somatic Cells (Body cells) Identical to the parent
A mutation occurs during DNA replication before both mitosis and meiosis. In which process would this mutation be more likely passed to offspring, and why?
Meiosis
Why is cell division important for growth and repair?
It replaces damaged cells and allows organisms to grow.
The Cell will spend 90% of it's time in this phase of the cell cycle.
Interphase
Why are no two gametes identical?
Because of crossing over and independent assortment
Gametes
Mitosis ensures genetic continuity, while meiosis ensures variation. Describe one mechanism from each process that achieves these outcomes.
Mitosis → accurate DNA replication and equal chromosome distribution;
Meiosis → crossing over and independent assortment create variation.
Examine this picture. Assume that in anaphase II, one of the sister chromatids fails to separate evenly at the centromere. If meiosis leads to the formation of sperm, what mutation has occurred?

Nondisjunction
During which phase does the nuclear membrane reform around each set of chromosomes?
Telophase
What error in Meiosis does this image show? And during what phase will this occur? 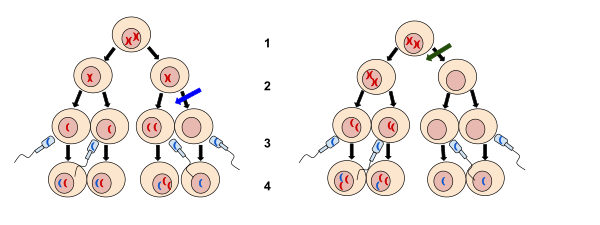
Nondisjunction, Anaphase, Anaphase I or II
If a dog’s diploid number is 1,068, what is its haploid number?
n=534
Why are both mitosis and meiosis important to life?
Mitosis allows growth and repair; Meiosis enables sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
How can understanding meiosis help explain genetic disorders?
Errors like nondisjunction during meiosis cause chromosomal abnormalities.