This is what is left over from the supernova of a supermassive star if it is so large the core collapses and creates a singularity that not even light can escape.
What is a black hole?
The hottest part of our sun, where all of the heat and light is generated.
What is the core?
This type of telescope collects radio waves using a dish and redirects them to a receiver.
What is a radio telescope?
This is the the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different locations. We can use this to estimate the distance of stars.
What is parallax?
The diagonal band that runs from the upper left to the lower right of a HR diagram and is referred to this.
What is the main sequence?
When a star runs out of hydrogen and stars to fuse helium or heavier elements, it transitions into this stage.
What is a red giant/supergiant?
This is the primary state of matter of the elements in/on the sun.
What is plasma?
This type of telescope uses a series of mirrors to collect light in order to view deep space objects
What is a reflector telescope?
This is the variable that controls the color of a star.
What is temperature?
These stars are extremely hot but very dim.
What are white dwarfs?
This is the primary stage of a stars life cycle, with ~90% of all stars at this stage currently.
What is main sequence?
This is the primary "fuel" for main sequence stars
What is hydrogen?
This type of telescope bends light using a series of lenses to collect light and increase magnification. It is commonly used in terrestrial telescopes.
What is a refracting telescope?
This is the name of the process which stars use to turn hydrogen into helium.
What is nuclear fusion?
This star has a luminosity of one and a relative mass of one on the H-R Diagram.
What is the Sun?
When a red supergiant star goes supernova and does not become a black hole, this is what is left behind.
What is a neutron star.
These features found on the surface of the sun are visible from earth and can be used to predict solar storms.
What are sun spots?
This type of telescope does not give a clear image of an object, but rather separates the light it receives into its different wavelengths so that it can be analyzed.
What is a spectroscope?
This type of rapidly spinning, highly magnetized neutron star is known for its regular pulses of electromagnetic radiation.
What is a pulsar?
This is color of low-mass, but long-lived stars.
What is red?
This type of "star" is thought to occur after the dead core of a star cools down over trillions of years
What is a black dwarf?
This is the "surface" of the sun, which we can see features such as granules and sunspots on.
What is the photosphere?
This is an optical distortion found in telescopes with lenses where the bending of the light separates out the wavelengths, causing a rainbow effect to appear on the object being viewed.
This light curve represents this type of star:
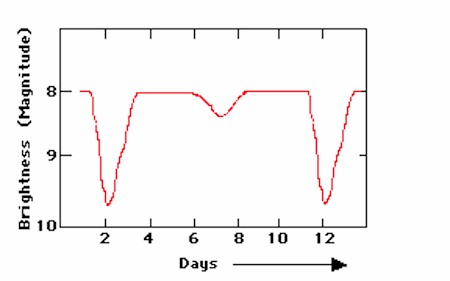
What is a binary star system?