These organisms get their energy and food from others.
What is HETEROTROPHS?
The approximate percentage of energy passed from one trophic level to the next.
What is TEN PERCENT?
The three states that water exists in on Earth.
What is SOLID, LIQUID and GAS?
A carbon-based fuel source used by factories.
What is FOSSIL FUELS?
The nitrogen cycle relies on types of these microscopic organisms.
What is BACTERIA?
A plant or animal that plays a unique and crucial role in the way an ecosystem functions.
What is a KEYSTONE SPECIES?
This is the process that makes the solar energy a usable source of energy for an ecosystem.
What is PHOTOSYNTHESIS?
This is a type of pyramid to that is based on the total dry mass of the organisms at each level. One is pictured below.
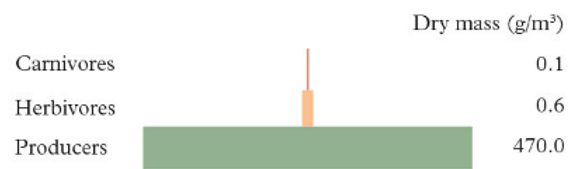
What is BIOMASS PYRAMID?
When water is warmed in the oceans, it goes through this process.
What is EVAPORATION?
Carbon's place in the Photosynthesis equation.
(i.e. product or reactant)

What is REACTANT?
This farming product increases the nitrogen in soil.
The role and space that an organisms fills in an ecosystem, including all its interactions with the biotic and abiotic factors of its environment.
What is ECOLOGICAL NICHE?
The amount of organic matter in a system, often measured in terms of weight or volume.
What is BIOMASS?
In a pyramid of numbers for a tree ecosystem the bottom part of the pyramid will appear this way.
What is SMALL?
Once water condenses and cools it then enters this process of the water cycle.
What is PRECIPITATION?
Carbon's place in the Respiration equation.
(i.e. product or reactant)

What is PRODUCT?
This is the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to nitrite by bacteria and cyanobacteria.
What is NITROGEN FIXATION?
A subset of the fundamental niche where an organism can maintain a stable species population.
What is REALISED NICHE?
This is the highest consumer in a food web with four levels.
What is TERTIARY CONSUMER?
Energy loss from consumers can occur from respiration (as heat), egestion and this process.
What is EXCRETION?
A small component of a biogeochemical cycle with active exchange of matter between organisms and the environment. There can be more than one of these and they can also be referred to as the exchange pool.
What is THE CYCLING POOL?
This is a way animals add Carbon to the earth?
What is by DEATH or DECAY?
These convert nitrogen into ammonia. Some of these have a symbiotic relationship with legumes and live in root nodules.
What is NITROGEN-FIXING BACTERIA?
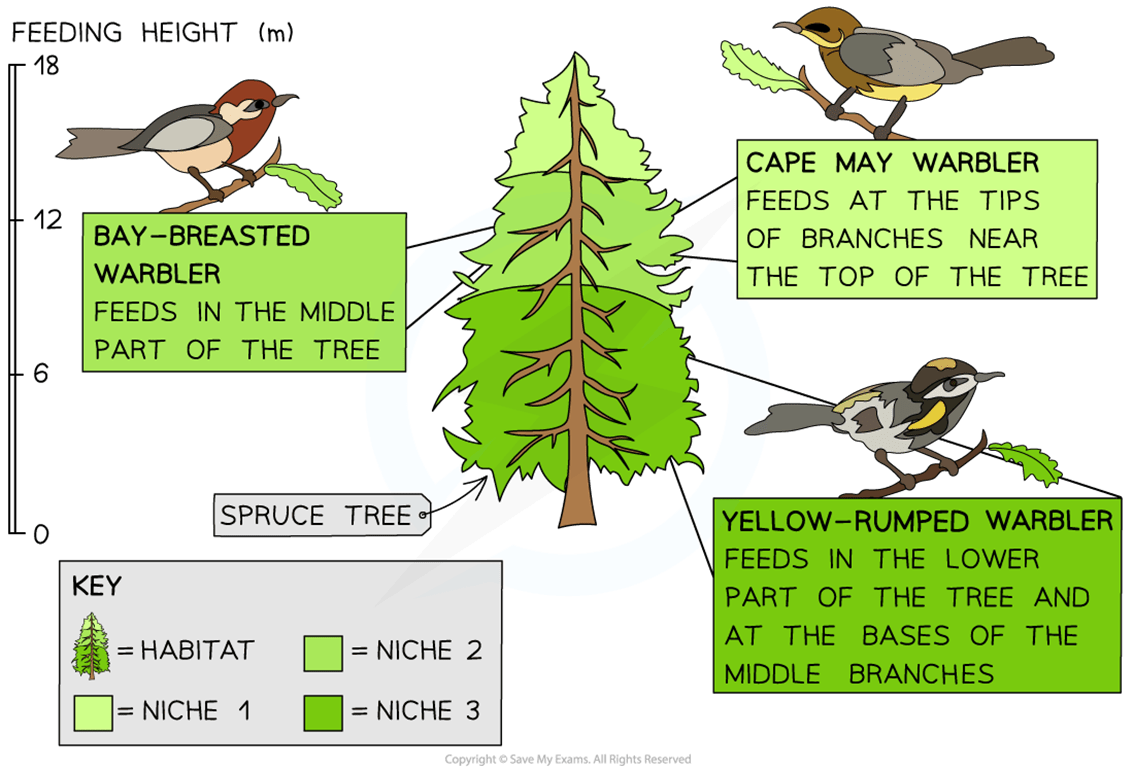
In the example above which type of niche are all three birds living in separately?
What is REALISED NICHE?
From the diagram below, this is the amount of energy that is passed on from secondary consumers to tertiary consumers.
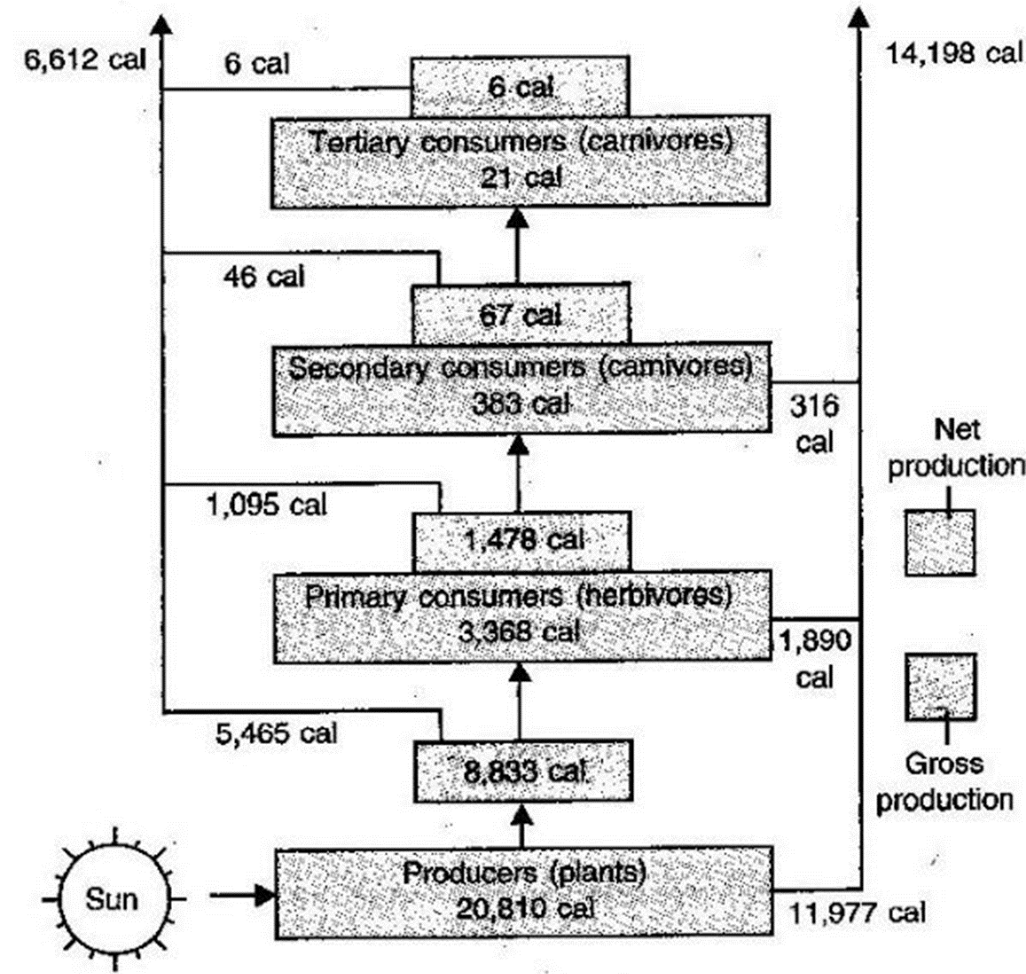
What is 67 CALORIES?
The amount of energy available for herbivores in an ecosystem.
What is NET PRIMARY PRODUCTION?
A large abiotic component of a biogeochemical cycle in which matter is slowly exchanged with organisms.
What is THE RESERVOIR POOL?
The area below the surface of the Earth where carbon is most plentiful.
What is the LOWER MANTLE?
The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic conversion of gaseous nitrogen into nitrites and these compounds.
What is NITRATES?
Usually defined as a state in which two species competing for the same resources cannot stably coexist if other ecological factors are constant. Also called Gause's principle.
What is COMPETITIVE EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE?