The process that transports rocks, soil and sediments to a different location is called _________.

Erosion

Weathering of limestone by acid rain is an example of ____________________.

Chemical Weathering

This type of weathering is most often seen on ocean shores.

SALT CRYSTALLIZATION GROWTH

The removal of weathered rock and soil from its original location is called ________________.
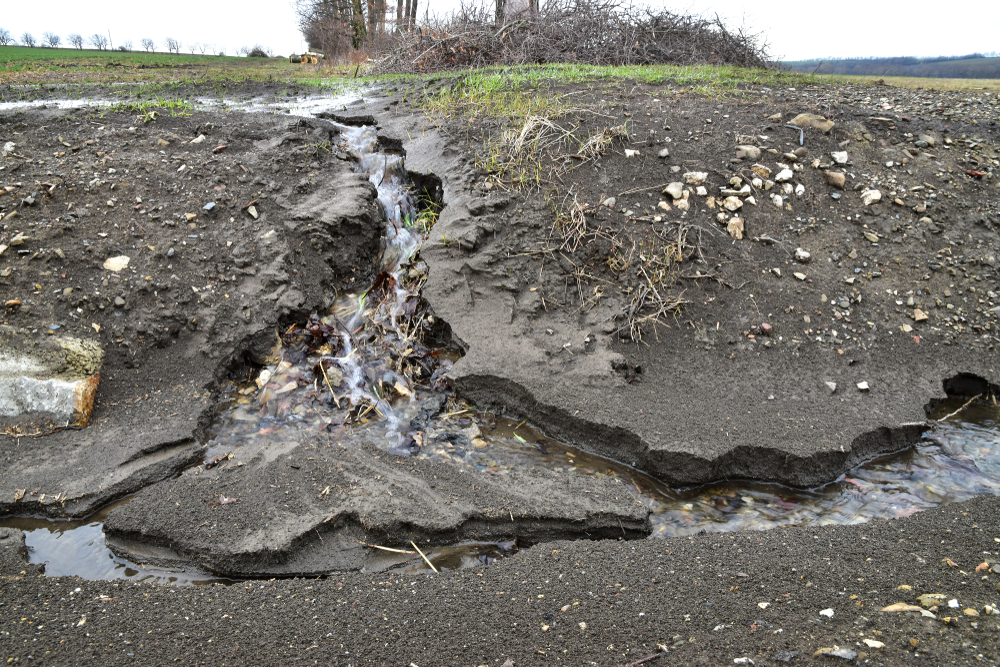

EROSION

Which number represents the O - Horizon
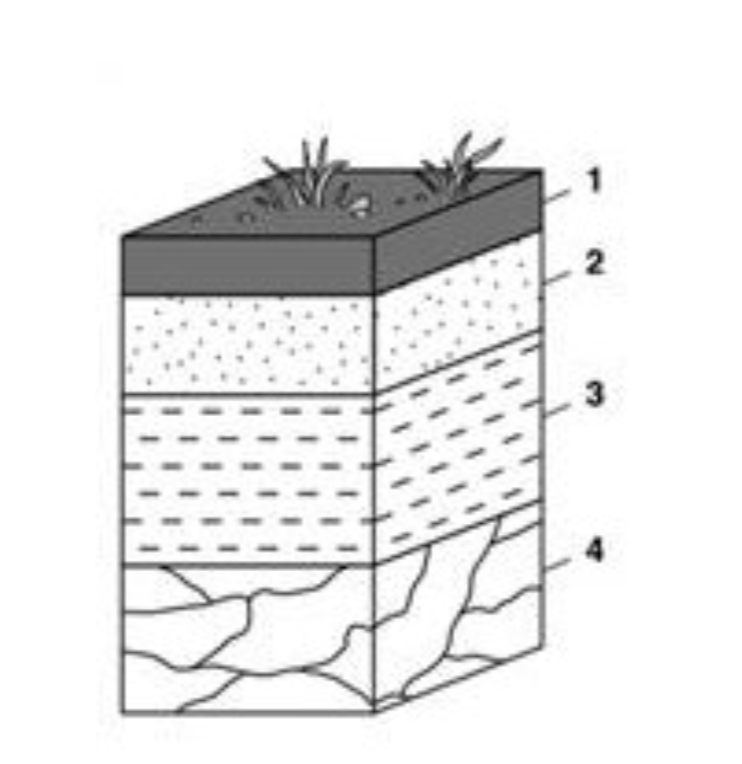
1
Fertility of soil relates to:
A. how the soil was formed over time
B. the amount of nutrients that allow plants to growth
C. the amount of water found in the soil
D. the amount of bacterias found in the soil
B. the amount of nutrients that allow plants to growth
Which layer of the soil profile would be affected the most by weathering and erosion?
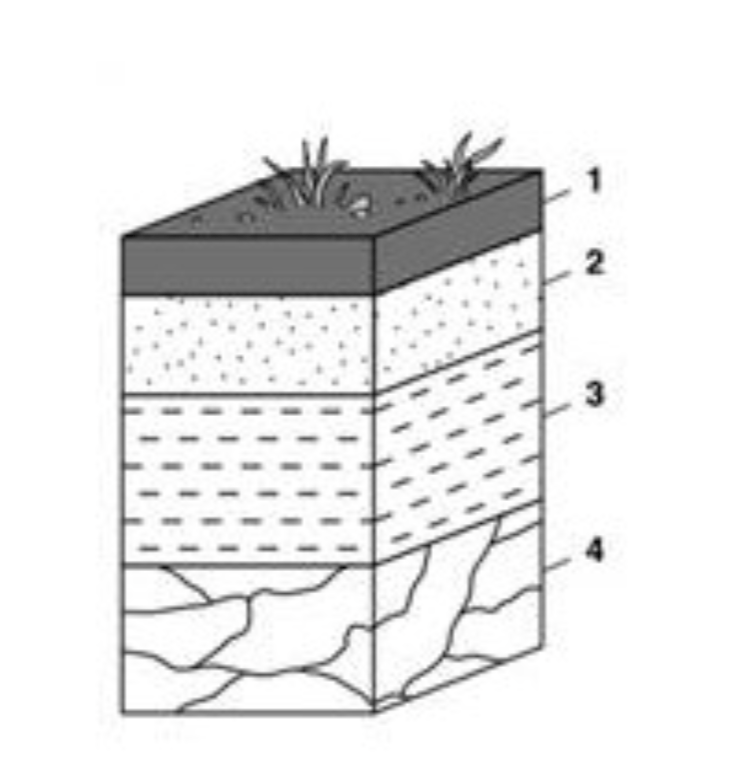
1

Ice expansion is an example of ___________________ weathering

Physical Weathering

___________ is by far the most important agent of chemical weathering.
WATER

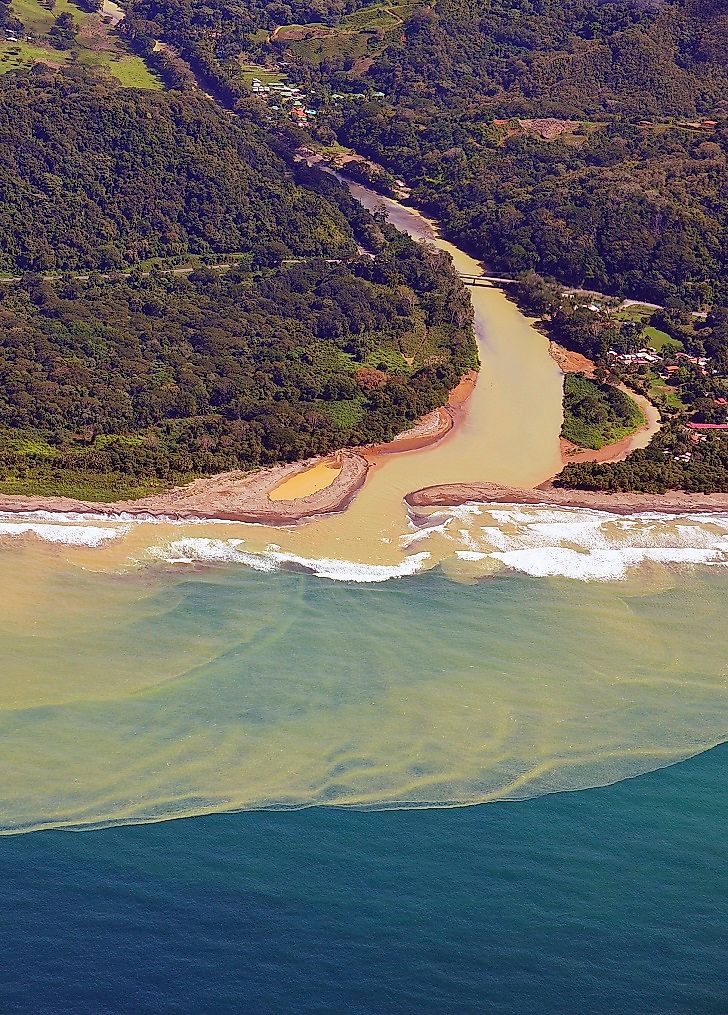
After the materials are transported, they are dropped in another location in a process known as ______________.

DEPOSITION

Which of the following best describes how most soil forms?
A- through the growth of trees
B- through the build up of snow
C- through the weathering of rock
D - through the cooling of lava
C- through the weathering of rock
Washing out of fine soil components from the E horizon is called _______________

ELUVIATION

Settling of soil that often occurs when water flow slows down or stops, and heavy particles can no longer be supported by the river turbulence.

DEPOSITION

Which type of weathering is illustrated:

Sheeting

Dominant type of weathering illustrated in the following image:
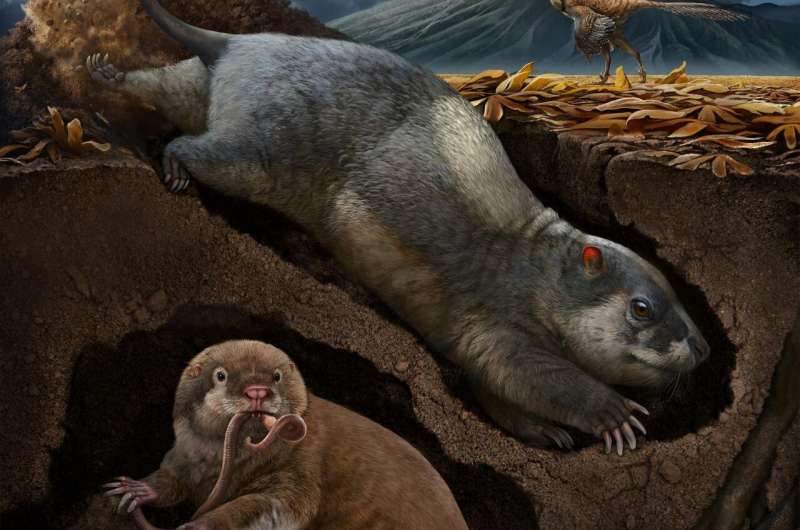

BIOLOGICAL WEAHERING

________ erosion develops when running water cuts small channels in the side of a slope.
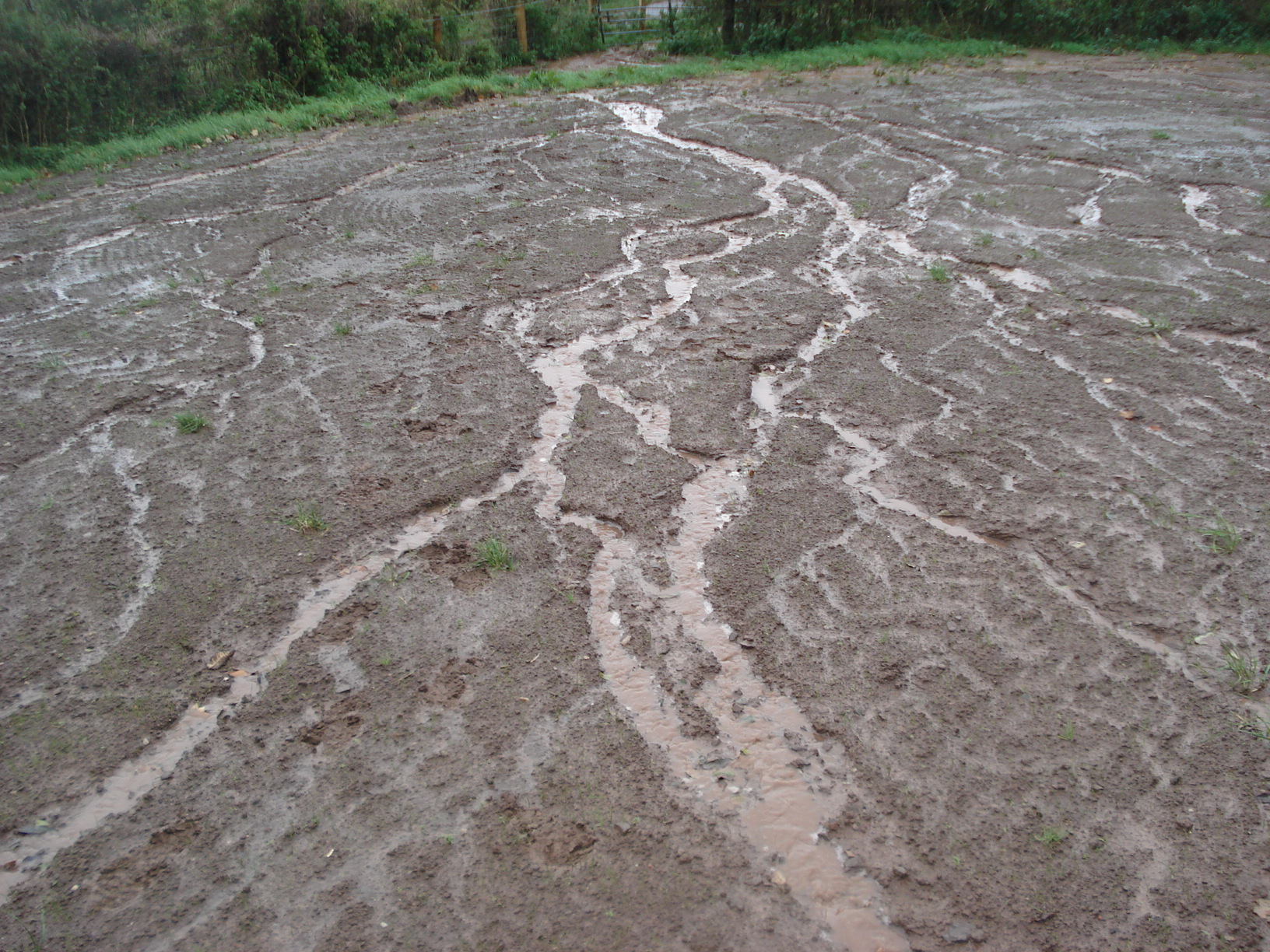

RILL EROSION

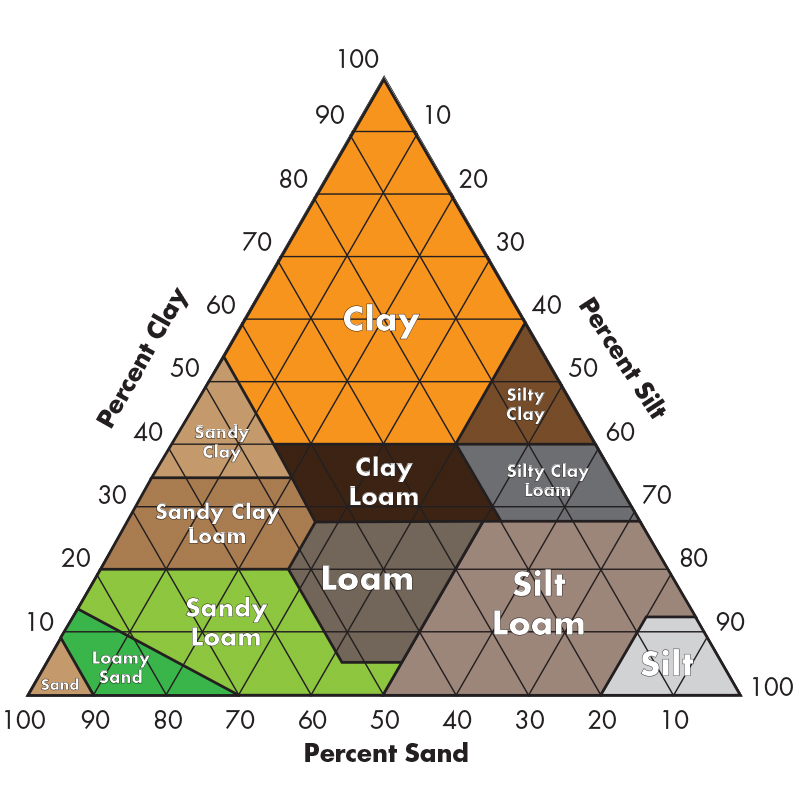 Soil that is 35% clay, 35% sand, and 30% silt is classified as ______________________
Soil that is 35% clay, 35% sand, and 30% silt is classified as ______________________
CLAY LOAM
 Soil that is 35% clay, 35% sand, and 30% silt is classified as ______________________
Soil that is 35% clay, 35% sand, and 30% silt is classified as ______________________
The measure of how fast the water enters the soils is called ________________________
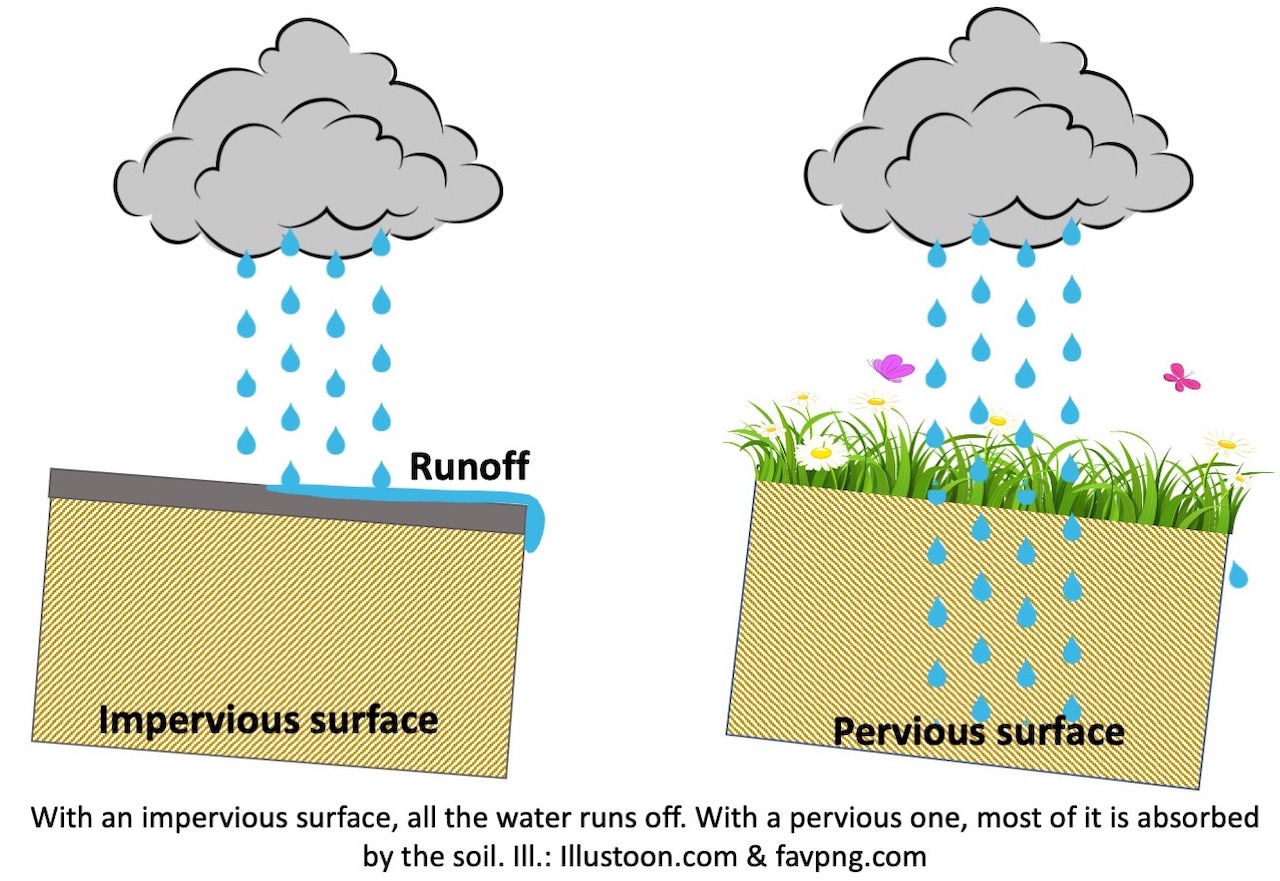
INFILTRATION

The process of breaking down rocks is called ______

Weathering

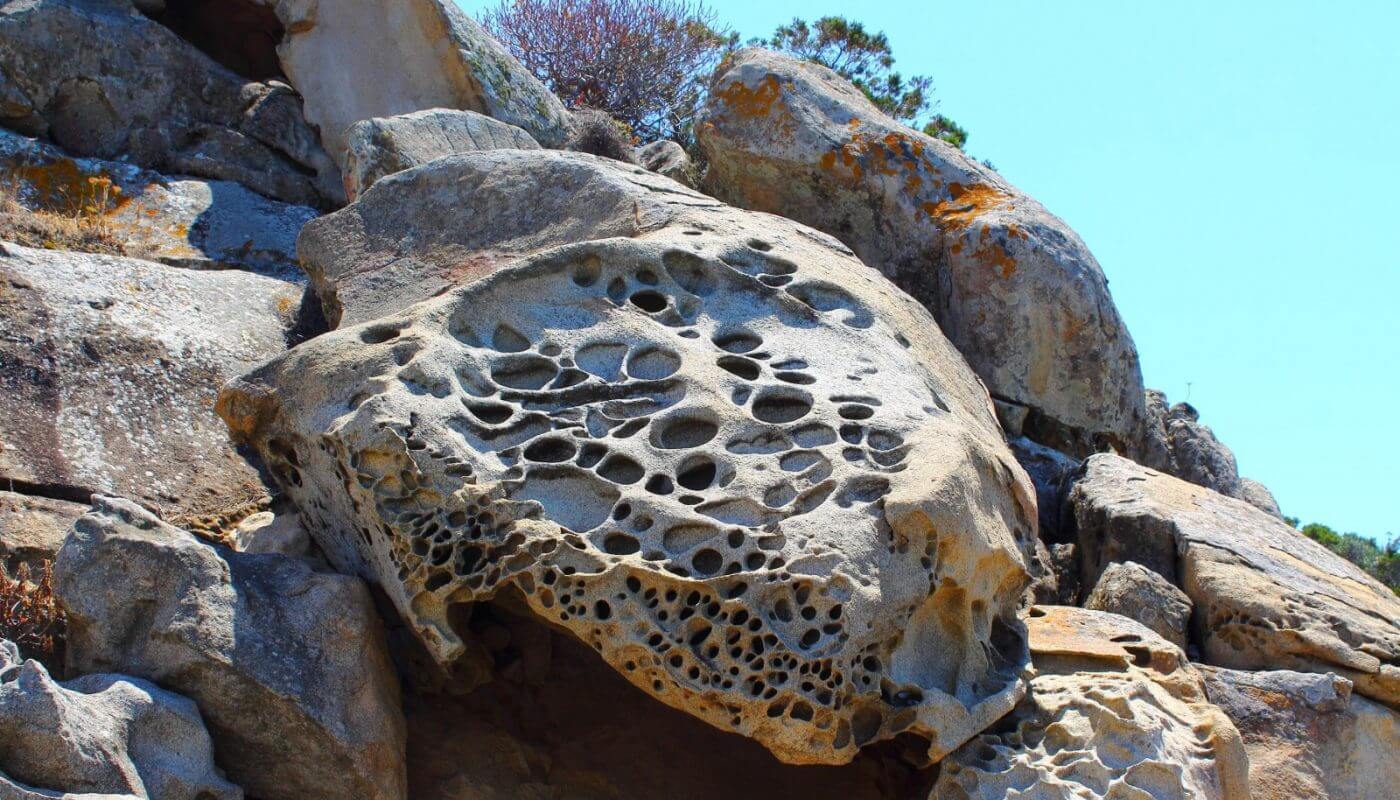
Type of weathering illustrated in the following image:

Biological Weathering
http://img.geocaching.com/cache/d4fb66d9-ebf4-4328-b116-507cd6ecf624.jpg
Red coloration in a sediment often indicates the presence of this element.

IRON

Erosion by _____________ often forms deep U shaped valleys like the one shown below.
GLACIAL
The layers of the soil are called ______________
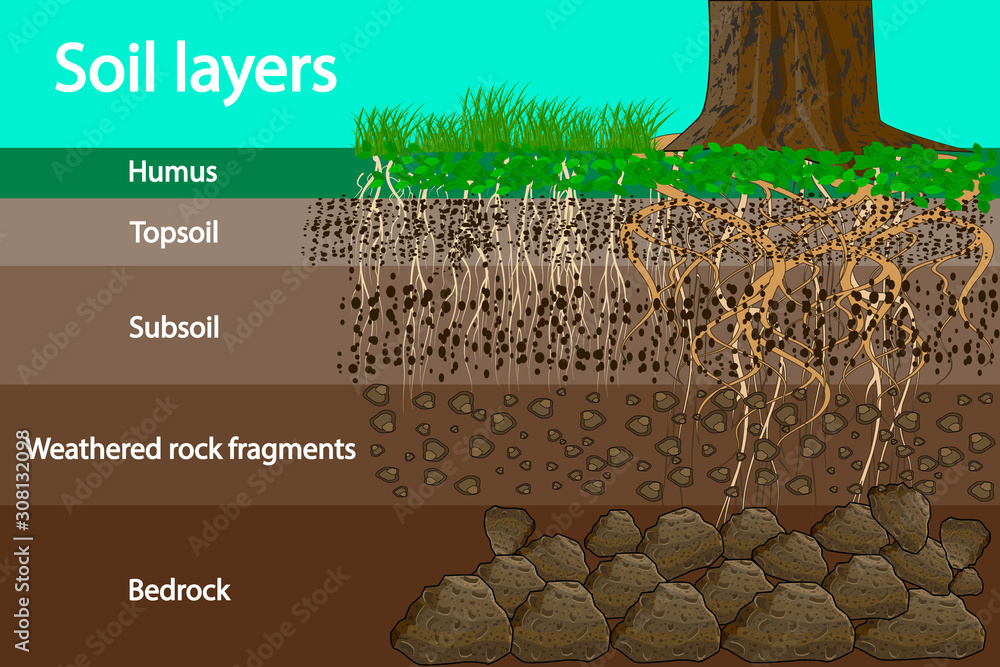
HORIZONS OR PROFILES

Transported soil is ______________________

SOIL THAT HAS BEEN CARRIED FROM ELSE WHERE

Which of the following aids in the weathering and erosion of rocks?
A. rain
B. water
C. wind
D. all are correct

D. all are correct
Chemical weathering involves a chemical transformation of rock into what?

Chemical transformation of rock into one or more new compounds.

Carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolved in water (H2O) forms _______________________
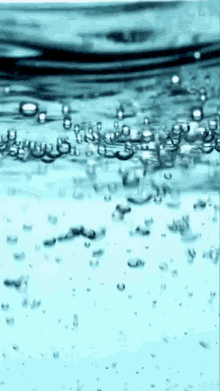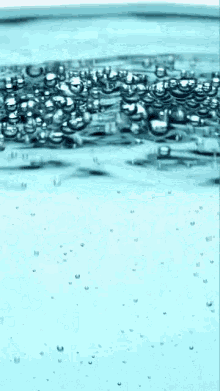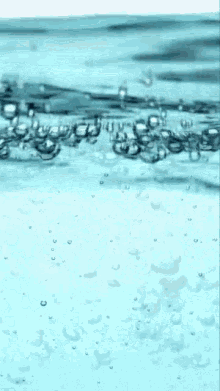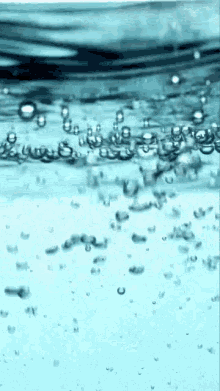
CARBONIC ACID

When a rill becomes deep and wide as a result of further erosion a _____________ is formed.

GULLY

Decayed plants and animals in the soil found predominately in the O (top) layer:

HUMUS

Choose the soil property illustrated:
A. Soil consistency
B. Soil moisture
C. Soil Temperature
D. Soil pH
B. Soil moisture
Weathering and erosion are called ______________ processes because they occur at or near Earth's surface.
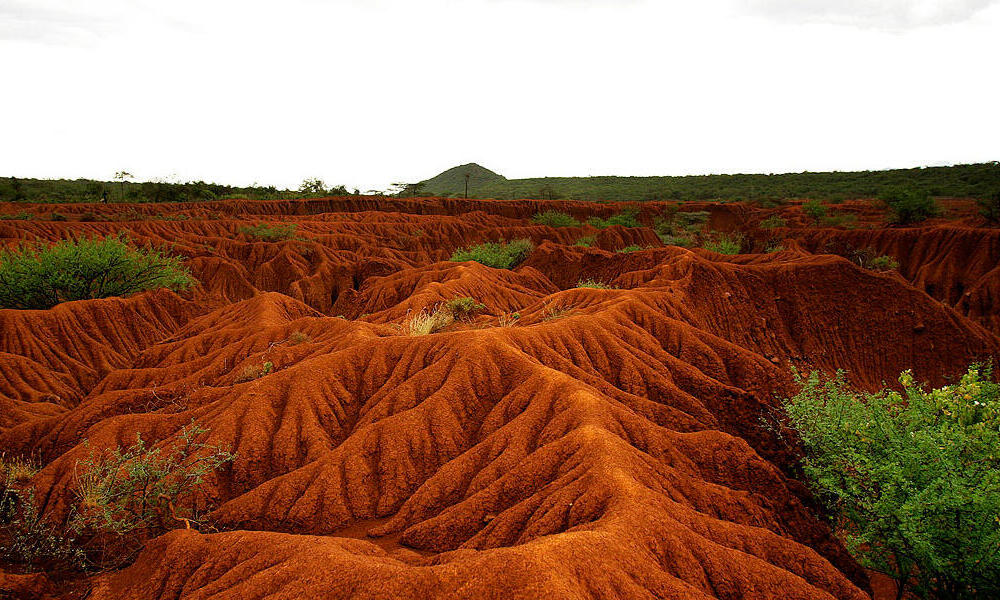

EXTERNAL PROCESSES

Which type of weathering is illustrated:

Physical
Illustration represents what type of weathering?
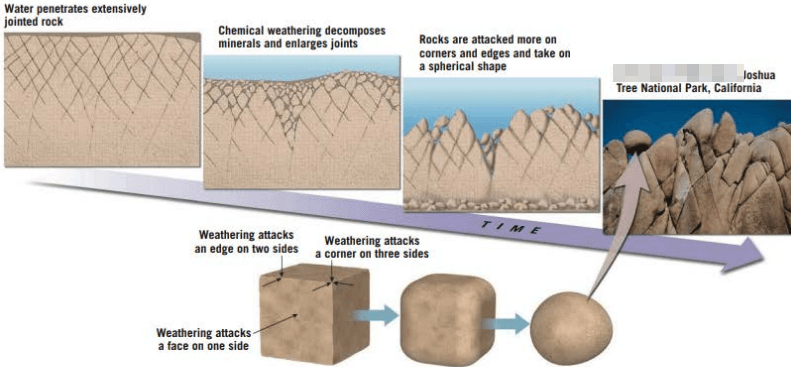
SPHEROIDAL WEATHERING

The inclusion of a barrier like the one shown below would be a good solution to prevent _________ erosion.

WIND EROSION

The solid layer of rock at the bottom of the soil profile is called ____________________

BEDROCK

Source of the weathered mineral matter from which soils develop is called the _____________ material

PARENT MATERIAL
