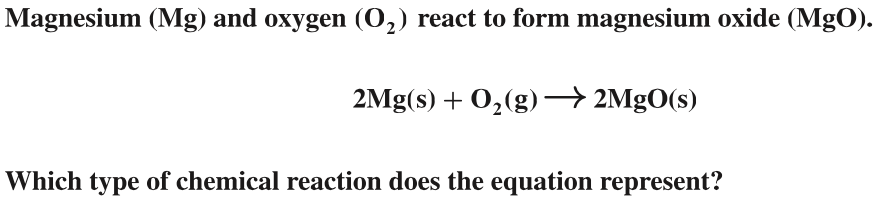A neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds.
A molecule
What is a covalent compound?
When electrons are shared between 2 nonmetals
What is an ionic compound?
A type of bond that results from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely-charged particles.
Which type of bond will dissolve in water and be conductive in water?
Ionic - contains a metal
Synthesis
The relative attraction an atom has for a pair of electrons in a bond; scale developed by Linus Pauling.
Electronegativity
What must be included in naming covalent compounds?
Prefixes
What is the formula for Aluminum Bromide?
AlBr3
Which type of bond is conductive as a solid?
Metallic - Metal-metal
What type of chemical reaction produces heat, carbon dioxide, and water?
Combustion
A type of bond in which a small number of electrons are shared by a large number of metal atoms; electrons become delocalized.
Metallic Bond
How many F's are in F4O7
4
What is the name of this compound: V2O5
Vanadium (V) Oxide
Which of the following molecules would have the lowest melting point?
Covalent Compounds - no metals, only non-metals
Balance this equation and identify the type.
4, 3, 2
A group of atoms bonded together covalently that have an overall electrical charge and act as a group. Used in nomenclature with metals.
Polyatomic Ion
What is the name of this compound: P2S5
What is the name of this compound: KNO3
Potassium Nitrate
Which of the following would fit the description: Will melt at low heat, dissolves in ethanol, and can not conduct electricity?
Covalent Compounds - no metals
What are the coefficients that will balance the skeleton equation below?
N2 + H2 --> NH3
1, 3, 2
The simplest ratio of elements that make up an ionic compound (MgO)
Formula Unit
What is the formula for: Tetrasilicon dichloride
Si4Cl2
What is the formula for Iron (III) Sulfide?
Fe2S3
Because the particles in ionic compounds are more strongly attracted than in molecular compounds, the melting points of ionic compounds are ____
Higher
Label Picture.
a-
b-
c-
d-
e-
f-
a- reactants
b-Coefficient
c-subscript
d-yield
e-products
f-state of matter