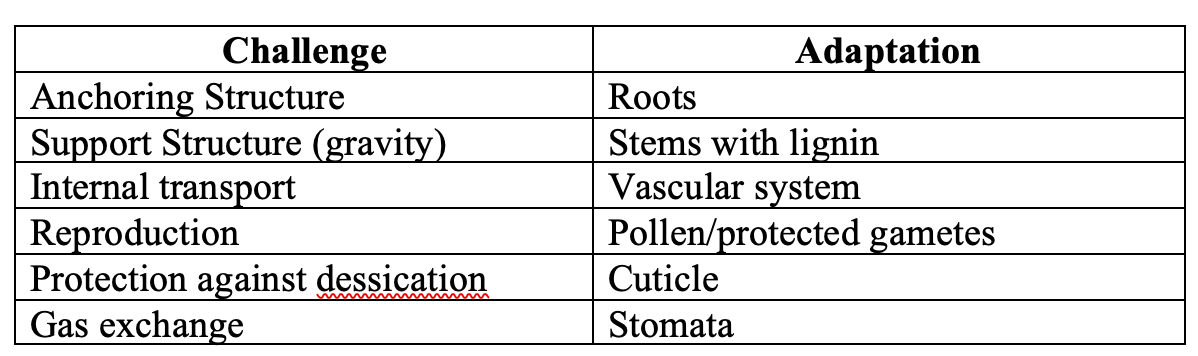
Fill out the adaptations necessary for plants to move to land?
____ used for defense are secondary metabolic compounds that are not directly involved in normal growth, development or reproduction. These are a few examples.
Chemical defenses
- Toxins: cyanide, caffeine, nicotine
- Juvenile hormones
- Digestion inhibitors: tannins
Repellants: menthol oil, sage or citrus oils
1. Self-incompatibility is the ability of a seed plant to reject its own pollen and sometimes the pollen of closely related individuals to prevent fertilization of an egg; this is why its beneficial____
It favors cross-pollination since self-pollination leads to inbreeding depression.
Sporophytic (fertilization blocked by products of alleles in tissues of stigma of sporophyte that bind to the pollen grain wall and prevent germination of the pollen grain)
Gametophytic (fertilization blocked by allele in the pollen’s genome which cause production of enzymes in the style of the sporophyte that destroy the RNA of the pollen tube after the pollen tube has started to germinate)
_____ conducts food, hormones, amino acids, and other substances for plant growth and development
Phloem
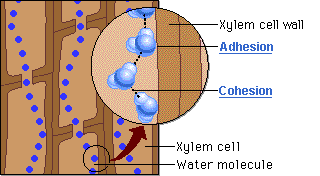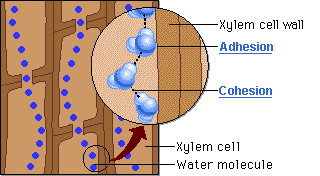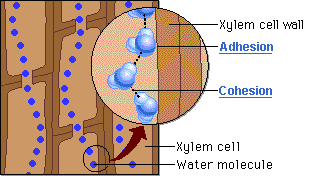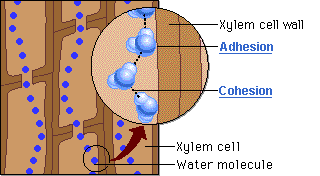
The word for the tendency of water molecules to cling to the walls of the xylem.
Adhesion
Plants have this type of life cycle.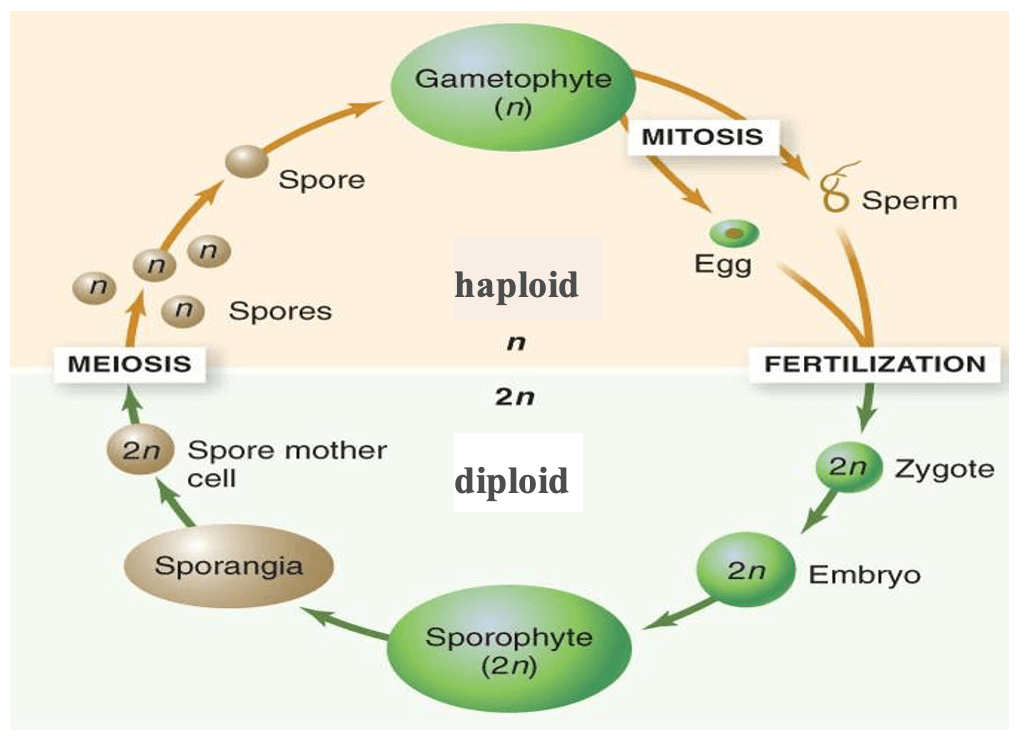
haplodiplontic
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, when we discuss the diffusion of water it's called __A__ and it occurs through these structures __B__ in plants.
A. Osmosis , B. Aquaporins
This group of nonvascular seedless plants are the closest living descendants of the first land plants, their reproduction is tied to water, they have flagellated sperm, and lack roots
Bryophytes
A blastula is a hollow ball of cells formed early in development. In mammals, this hollow ball of cells is a bit different as it has outer cells, the __A__, which facilitate implantation in the uterus and formation of the placenta as well as an inner cell mass, the __B__, which give rise to the mammalian embryo, and so it is called a C.
A-trophoblast
B-embryoblast
C-blastocyst
This is the organ that releases insulin, which lowers blood glucose level and glucagon, which raises blood glucose level
Pancreas

Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell that has small granules. These granules contain proteins. The specific types of granulocytes are____,______,_____. These are each of their their functions
Neutrophils (Phagocytosis, Most abundant, First to appear), eosinophils (Release enzymes, Allergic diseases & parasitic infections), and basophils (Histamines).
Imagine that you are out for a jog in the park one brisk winter morning. As you run, you spot a patch of slick ice on the path ahead. Your visual system perceives the icy patch and relays this information to your brain. Your brain then sends signals to engage your muscles to take action and walk around the ice. What kind of system is this response part of? Once you get around it you realize that your heart rate has increased, what nervous system is this response apart of.
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
About 40% of all sharks are ___, meaning the egg is fertilized in the womb then an egg sac is laid. You may have seen these sacs on the beach, sometimes they are called mermaids purses.

Oviparous
Sharks are also ovoviviparous (producing young by means of eggs which are hatched within the body of the parent) and viviparous (live birth)
These are the three types of mechanisms for regulation of homeostatic regulation, what they mean, and an example of each (ex. morphological, etc.)
Morphological – physical characteristics that aid in homeostasis; ex. Fur
Physiological – physical mechanisms that are used to maintain homeostasis; ex. Sweating, “antifreeze” chemical production
Behavioral – behavioral mechanism used to regulate homeostasis; ex. Sunbathing; beetle that holds abdomen up at an angle to gather moisture
This is something that Crocodiles, birds, and mammals have in common.
Four chambered heart
This is the difference between Clorophytes and Charophytes?
Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group of green algae living predominantly in marine water while Charophyta is a taxonomic group of green algae thriving mainly in freshwater. Both are major clades of green algae, but chlorophytes never made it to land while charophytes gave rise to land plants.
This the ability of plants occurs when a membrane receptor protein absorbs blue light and results in the stem bending in a that direction.
Permanent form change in response to mechanical stresses such as constant wind, raindrops, or rubbing by passing animals_____, caused by the directional growth of a plant in response to contact, called____.
Phototropism
Thigmomorphogenesis, Thigmotropism
Two strategies plants use to promote outcrossing is separation of male/female structures in space, especially helpful for_____ plants or in time, which is helpful for _____ plants.
dioecious, monoecious
This is the stem cross section of a _____ angiosperm.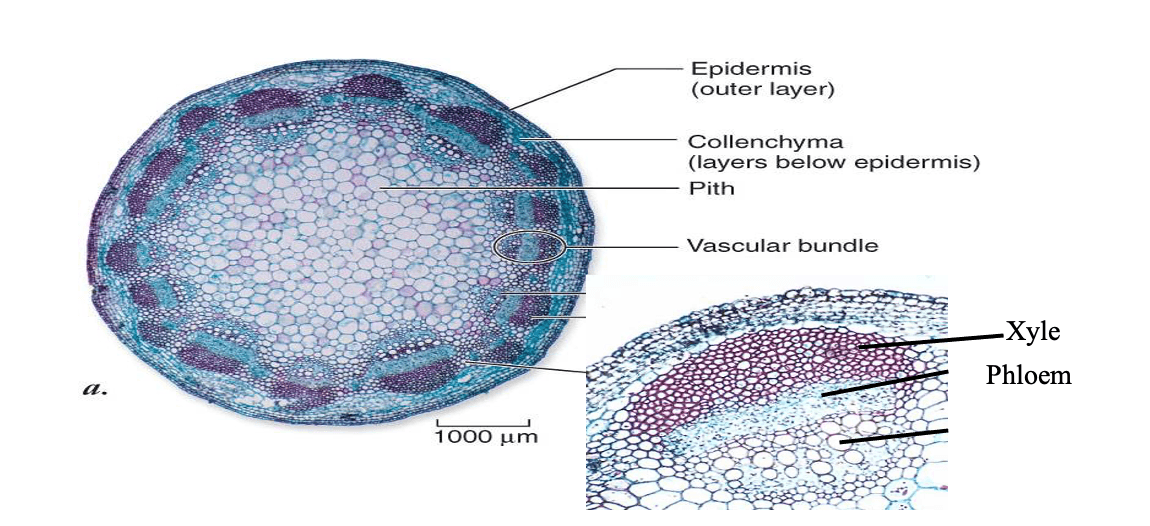
Dicot (you can tell because its vascular tissue is arranged in ring)
This is a symbiont of plants that fix nitrogen, produce hormones that stimulate plant growth, produce antibiotics that protect roots from disease, absorb toxic metals or make nutrients available to roots
Rhizobacteria
Arrangement of leaves on a plant stem. Sequential leaves tend to be placed 137.5° apart. This angle relates to the golden mean, a mathematical ratio found in nature, and in plants it is thought that it optimizes exposure of leaves to the sun.
Phyllotaxy
This is the reason for the evolution of carnivorous plants. Carnivorous plants are an example of this type of evolution.

They developed as a way for plants to obtain nitrogen in low-nutrient environments, convergent
___ are the most varied gymnosperms. The world’s oldest trees are the 5,000-year-old bristlecone pines (Pinus longaeva) of desert mountains in California and Nevada. The largest trees are the giant sequoias (Sequoiadendron giganteum) of the Sierra Nevada of California, reaching heights of more than 95 metres (312 feet).
Conifers
Pharyngeal arches account for the complexity of our head as different ones are responsible for giving rise to different structures & nerves in our head. This is what they each give rise to in humans.

The first arch gives rise to the upper and lower jaws plus incus and malleus bones in the ear.
The Second produces the stapes and many face muscles.
The third and fourth give rise to our hyoid, thymus, larynx as well as muscles and nerves in our throat as well as thyroid and epiglottic cartilage.
This is the mechanisms by which adrenaline works and its function.
Raises blood glucose, blood flow, blood pressure, heart rate, increases metabolism, constricts certain blood vessels as an alarm or stress response to fight-or-flight efforts
The bone marrow produces the body's blood cells (including T and B lymphocytes). What might it mean if your lymphocytes are high?
High lymphocyte blood levels indicate your body is dealing with an infection or other inflammatory condition. Remember, lymphocytes are white blood cells!
This part of your ear allows the ‘popping’ that happens when you fly,
While this part of your ear makes you feel dizzy when you get off the t-cup ride at an amusement.
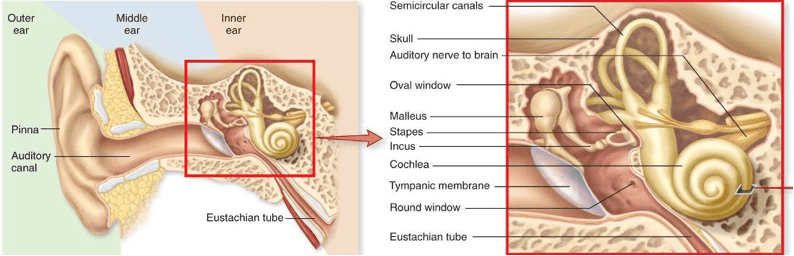
Eustachian tube. This tube connects the middle ear to the back of your nose and it allows for drainage of fluid and for pressure to be released. It is small however and can become narrowed or blocked by the swelling of soft tissues locally. The resulting buildup in pressure, either in an aircraft or if infection is present, can be extremely painful. Popping in your ears is when the pressure inside the middle ear is balanced with the pressure outside it, which often gives great relief and improves hearing. This is different from when water is trapped in the outer ear after swimming, although the effect can be similar.
Fluid moving in the semicircular canals causes you to feel dizzy after you stop spinning.
Developmental modularity is where a few genes contribute to significant morphological characteristics. These master regulatory genes are called _____ and direct the formation of the overall body plan and limb development. In mammals, these are called ____.
homeotic genes, hox genes
This is a list of the three forms of nitrogenous waste in order of their toxicity from most to least with examples of the sorts of organisms that produce each type
Ammonia – bony fish and aquatic inverts, least energetically expensive but most toxic – requires lots of water to flush away toxicity, which makes sense in an aquatic environment
Urea – mammals, amphibians, and cartilaginous fish, less toxic and water soluable
Uric acid – reptiles, birds and insects, most energetically expensive but also saves the most water, least toxic
This is the oxygen carrying molecule in mollusks and aquatic arthropods.
This is the oxygen carrying molecule in mammals.
Aquatic arthropods and mollusks have hemocyanin which uses copper; mammals have hemoglobin which uses iron.
Dormancy of deciduous trees and shrubs is due to changes in temperature, water and light. Color change occurs as chlorophyll is broken down and ____ are synthesized to facilitate nutrient recovery.
anthocyanins
__A__ is the response of a plant to the gravitational field of the earth. Gravity is perceived by __B__ found in amyloplasts. Plants respond through upward growth of stems by accumulation of __C__ on the lower side of cells and elongation of roots downward.
A-gravitrophism
B-statoliths
C-auxin
In double fertilization one sperm fertilizes the polar nuclei and initiates development of a __A__ endosperm whose function is __B__ , the other sperm fertilizes the egg to produce a __C__ zygote. They both occur after fertilization.
A-triploid
B-provides nutrients for the embryo
C-diploid
These are the three primary apical meristems and what they each give rise to.
Protoderm – epidermal cells
Procambium – primary vascular tissues
Ground meristem - ground tissue
____ transport through transport proteins involves gives the greatest amount of control over what leaves and enters cells.
____ transport occurs between cells
____ transport occurs through the continuum of cytoplasm via plasmodesmata
Transmembrane transport
Apopolastic movement
Symplastic movement

A single layer of cells impregnated with bands of suberin that comprises the endodermis of roots and blocks transport between cells.
Casparian Strip
Below are four macronutrients (other than Carbon, Oxygen, and Hydrogen) that are required by plants, what are their functions
Nitrogen
Potassium
Magnesium
Phosphorus
Nitrogen – critical for production of amino acids (dNa), proteins, and cholorphyll
Potassium – used for protein synthesis and opening/closing of stomata
Magnesium – component of chlorophyll (central molecule) and activates many enzymes
Phosphorus – component of ADP, nucleic acids, phospholipids and several enzymes
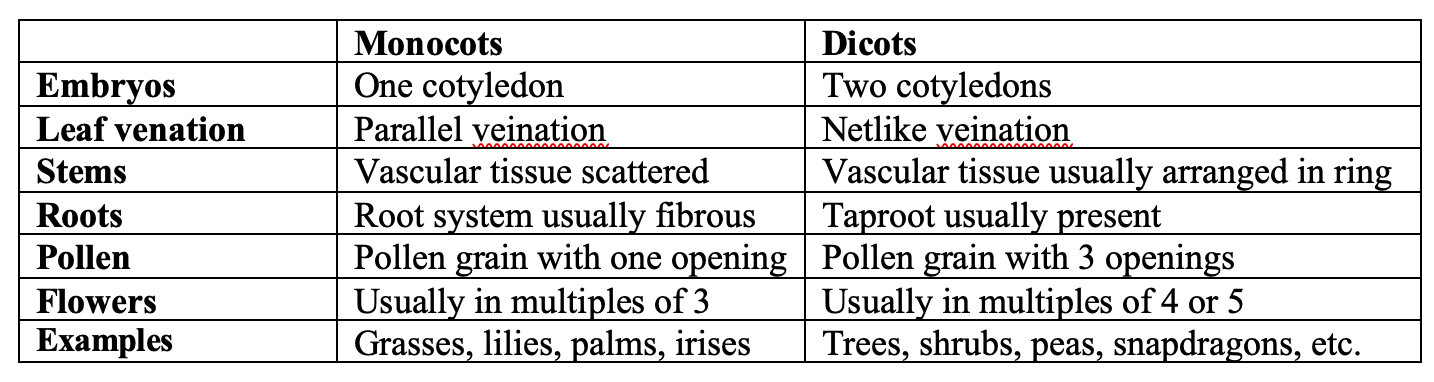
These are some characteristics of dicots.
Give an example of the types of organisms that have each of these types of skeletons
Hydrostatic – a fluid-filled cavity is surrounded by 2 sets of muscles (circular and longitudinal) that are used for support and movement
Exoskeletons – composed of chitin and must be shed in order for the animal to grow; protect from dessication and provide sites for muscle attachment
Endoskeletons – rigid internal skeletons made of bones and/or cartilage – offers surfaces for muscle attachment and protection of internal organs
Hydrostatic – a fluid-filled cavity is surrounded by 2 sets of muscles (circular and longitudinal) that are used for support and movement (earthworms, aquatic inverts)
Exoskeletons – composed of chitin and must be shed in order for the animal to grow; protect from dessication and provide sites for muscle attachment (arthropods)
Endoskeletons – rigid internal skeletons made of bones and/or cartilage – offers surfaces for muscle attachment and protection of internal organs (vertebrates)
______ Pituitary releases hormones made in the hypothalamus including oxytocin, which is involved in human bonding and ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) which promotes retention of water by kidneys.
While the ______ Pituitary releases growth hormones, prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and the melanocyte stimulating hormone. Explain the function of at least two of these hormones.
Posterior Pituitary
Anterior Pituitary
Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell that has small granules. These granules contain proteins. The specific types of granulocytes are____,______,_____. These are each of their their functions
neutrophils (Phagocytosis, Most abundant, First to appear), eosinophils (Release enzymes, Allergic diseases & parasitic infections), and basophils (Histamines).
These are the three ways in which neurotransmitters are terminated.
Rapid enzymatic cleavage, e.g. acetylcholinesterase degrades acetylcholine
Re-uptake by transporter proteins in the presynaptic nerve
Uptake by adjacent neuroglial cells
These are two disadvantages and two advantages of sexual reproduction.
Disadvantages
Less fecund & greater costs (requires more time and energy, more complicated, higher female investment, puts females at competitive disadvantage to males)
Advantages
Greater genetic diversity & more resilient (immunity, morphology, physiology, behavior)
Salmon are osmoregulators, do they have to deal with a hypotonic or a hypertonic environment?
Whats an example of an osmoconformer?

Saltwater-hypertonic
Fresh-hypotonic
Osmoconformers include marine inverts

Name two types of involuntary muscle types, what they do, and where they are found.
Smooth:Walls of blood vessels, stomach, and intestines-> Powers rhythmic contractions to move substances through vessels
Cardiac: Walls of heart-> Interconnected cells promote rapid spread of signal initiating contraction of heart