The shape of DNA.
The shape of RNA
What is a double helix?
What is a single helix?
The central dogma of life.
What is DNA-> RNA -> Protein?
Definition of a gene.
What is a section of DNA that codes for a protein.
The phases of the cell cycle; what are the phases of mitosis?
What is G1, S, G2, Mitosis, and cytokinesis?
Mitosis: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Four steps of DNA replication (in order)
1. Unwinding
2. Base pairing
3. Sealing strands together
4. Checking for errors
The backbone of DNA.
The "rungs" of the ladder.
What are the sugar and phosphate groups?
What are the nitrogen bases?
The steps (in order) of protein synthesis.
What is Transcription and Translation?
Using the letter "B" what would the genotype be for the following:
Heterozygous, homozygous recessive, homozygous dominant
Heterozygous: Bb
Homozygous R: bb
Homozygous D: BB
What is the difference between the parent and daughter cells in mitosis vs meiosis?
Mitosis: parent and daughter cells are genetically identical (somatic cells)
Meiosis: parent and daughter cells are genetically varied due to crossing over (gametic cells)
What is DNA Ligase's job in DNA replication?
Sealing parent and daughter strands of DNA together
The complementary base pairs for RNA
Adenine - Uracil
Thymine - Adenine
Guanine - Cytosine
The reason chromosomes are arranged in pairs.
You receive one chromosome from each parent (mom and dad)
What is the difference between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid: one set of chromosomes
What is DNA Helicase's job in DNA replication?
Unwinding the parent DNA strands
The complementary base pairs for DNA.
Adenine - Thymine ; Guanine - Cytosine
The location of translation in the cell.
What is the ribosome?
There are some disorders that occur on the X chromosome. If a parent is a carrier of the recessive allele, who will pass the gene onto the baby, mom or dad?
Mom because dad does not give the baby an X chromosome, only mom.
Males: XY
Females: XX
Definition of apoptosis.
1. Attaching base pairs to the new growing DNA strand
2. Checking for errors
Difference between pyrimidines and purines & which bases are which.
Pyrimidines are smaller with only 1 carbon ring (cytosine and thymine)
Purines are larger with 2 carbon rings (adenine and guanine)
Transcribe the following DNA code into mRNA, then translate it into protein using the codon chart:
TAC GTA ATG CCC AAG ATC
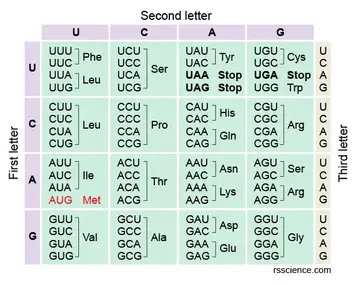
mRNA: AUG CAU UAC GGG UUC UAG
protein: Met - His - Tyr - Gly - Phe - Stop
Straight hair is dominant over curly hair. Use the letter "h" to represent the alleles.
Draw a punnett square; cross a homozygous recessive mom with a heterozygous dad.
What are the possible genotypes along with what phenotype that genotype would show.
h h
H Hh Hh
h hh hh
Genotypes: Hh - straight hair or hh - curly hair
Percentages: Hh - 50% hh - 50%
Why is it important that DNA is replicated PRIOR to mitosis?
So parent and daughter cells have a complete set of DNA after cell division
What are your 3 types of mutations?