In a solution, what is the solute?
The thing that is dissolved
Movement down a concentration gradient is called
Passive transport
The process by which biological systems maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment despite changing external conditions is called what?
Homeostasis
Where does a cell spend 90% of it's time
Interphase
What is uncontrolled growth called
Cancer
When a cell has a higher concentration of solute than the surrounding solution, the solution is called what?
Hypotonic
What is the name for the movement of water?
Is this an example of positive or negative feedback:
A baby suckling at the breast stimulates sensory receptors, which cause the release of oxytocin, causing further milk ejection and signaling continued milk production.
Positive
What happens in S phase?
The DNA replicates
What does the checkpoint at the end of G1 check for?
Proper cell growth

Hypertonic
Large or charged molecules are unable to cross directly through the cell membrane and instead use channel proteins. This type of cell transport is called what?
Facilitated diffusion
Is this a positive or negative feedback example: 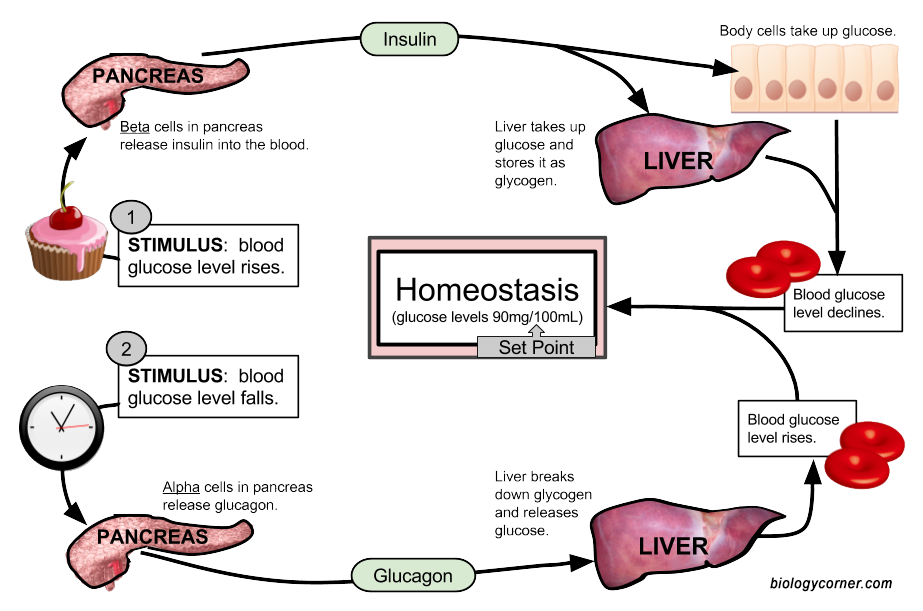
Negative
 What is this phase called?
What is this phase called?
Metaphase
If cells are in bad condition, where will they enter to stop dividing?
G0

Water will leave the cell and the cell will shrink
Active transport uses what molecule?
ATP
Describe gravitropism
Movement in response to gravity
 What phase is this?
What phase is this?
Anaphase
What is apoptosis?
Programmed cell death
How is the cell membrane arranged and why
Phospholipid bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing out to interact with the water both inside of and outside of the cell
Utilizing a vesicle to move particles out of a cell is called
Exocytosis
What part of a plant displays negative gravitropism
The shoots
What is the difference between cytokinesis in plant cells and in animal cells?
Plant cells: cell plate forms
Animal cells: have a cleavage furrow where cells pinch in to split
What is checked in the M phase
That spindles are attached to the chromatids