What are the fiscal policy tools?
Government expenditure (G) and Taxation (T)
Who controls the monetary policy in Australia?
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
This model shows the relationship between inflation and unemployment
Philips curve
What are the 6 macroeconomic objectives in Australia?
Sustainable economic growth, Price stability, Full employment, External stability, Sustainable development, Improved Living standards
Define the different types of indicators
Who controls the fiscal policy in Australia?
The Australian Government
What is a contractionary monetary policy?
Increasing the cash rate
In the long run, the Aggregate supply (AS) curve becomes this shape, reflecting full employment
Vertical
What are the measures of the internal balance objectives?
Sustainable economic growth = GDP growth
Price Staiblity = Inflation
Full employment = Unemployment rate
How would Gross Domestic Product (GDP) be moving if the economy is in a downturn?
The GDP would decrease in a downturn
What is an expansionary fiscal policy?
Decreasing taxes (T) and/or increasing government expenditures (G)
On the graph below, where is an evidence of an expansionary monetary decision?
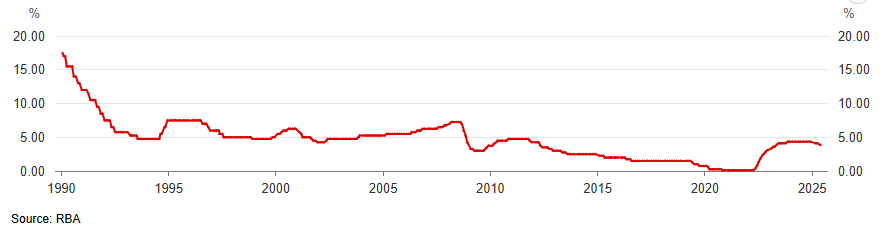
Eg. between 1990-94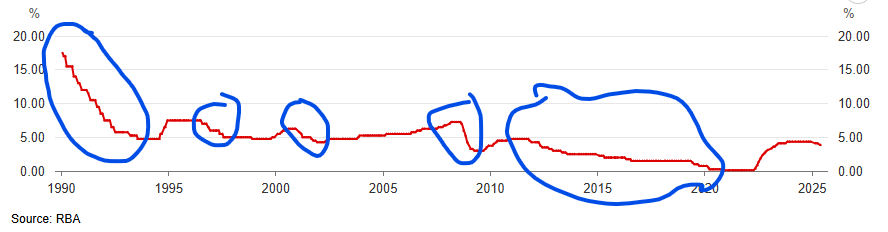
This model shows all combinations of good and services an economy can produce using all resources efficiently.
Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
This is a key objective of macroeconomic policy, aiming to increase national income over time
Sustainable economic growth
How would the Consumer Price Index (CPI)/Inflation be moving if the economy is in an upturn and why?
The CPI/inflation would increase as the AD increases, causing a demand-pull inflation if the supply-side (AS) can't keep up with the demand
According to the graph below, in which years was the federal budget in surplus?
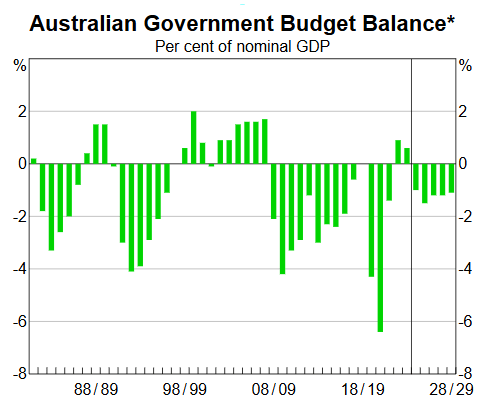
~2022,23, 2000-2007, 82-85
What is the dual mandate of the RBA?
The dual mandate involves maintaining price stability (inflation within 2-3%) and sustained full employment.
This model explains the movements of money, resources and goods between households and businesses.
Circular Flow of Income model
Describe the different types of unemployments
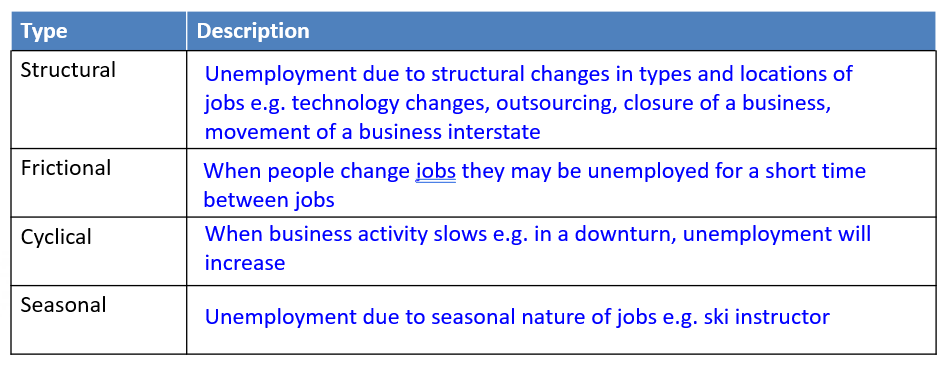
(+ long-term or discouraged unemployment = looking for a job unsuccessfully for over a year and now gave up)
Change in spending / change in income
% of Y they spend
According to the graph below, in which year did the government apply a contractionary fiscal policy?
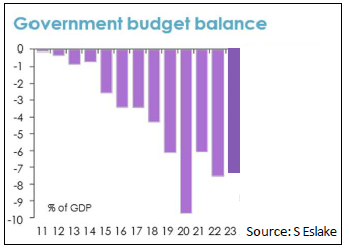
2021
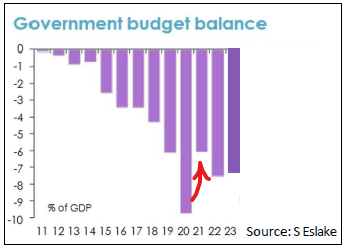
What monetary stance would the RBA take when the economy is overheating and why?
Contractionary, meaning increasing the cash rates to decrease inflation by dampening aggregate demand
This model shows the relationship between output and the general price level in the economy.
AD/AS model
Define the NAIRU
Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment = The lowest rate of unemployment that an economy can sustain without causing an acceleration in inflation
What is the multiplier? Explain it through an example.
An initial increase in injections can have a multiplied effect on the economy.