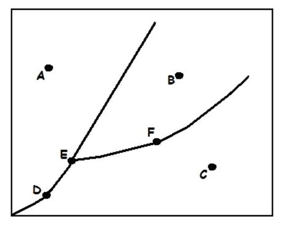
What letter is the triple point?
E

What state is this substance at line E?
gas
What state of matter has the strongest intermolecular forces?
Solids
What are the three types of intermolecular forces in order from strongest to weakest?
Hydrogen bonds, Dipole-Dipole interactions, London Dispersion forces
What type of solid is composed of metal and nonmetal atoms that form a lattice of alternating positive and negative ions held together by ionic bonds? What type of force must be overcome to melt this solid?
Ionic solids. ionic bonds

What phase is the substance at point A?
solid

What is happening at line B?
The substance is freezing or melting. It is in a mixed solid/liquid state.
Describe the particles movement in the three states of matter.
Solid: vibrate in place
Liquid: Farther apart and can slide past one another
Gas: Farthest apart, high energy, moving quickly.
What type of force must be broken when water boils?
Hydrogen bonds
If two covalently bonded atoms are identical, the bond must be (polar covalent, nonpolar covalent, ionic, or network covalent).
nonpolar covalent, same atoms have no difference in electronegativity.
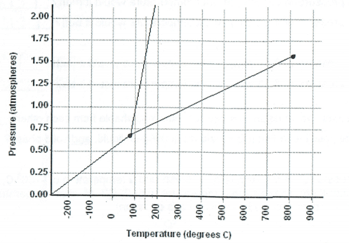
What is the normal boiling point of this substance?
350 C
What formula should be used to calculate the amount of energy used at line D?
q=mΔHvap
What happens to the boiling point of a liquid if the atmospheric pressure increases?
Boiling point increases. This is a direct relationship
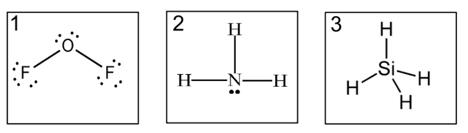
Which has the weakest intermolecular forces?
3, this is a non-polar molecule, which only contain dispersion forces.
1 is polar and has dipole-dipole forces.
2 is polar and has H-bonding.
What type of solid is composed of nonmetal atoms that are held together with intermolecular forces?
molecular covalent solids

What phase transition occurs if you go from 0.75 atm to 1.25 atm at 300 C?
gas to liquid = condensation
How many steps would the following problem be: How much energy is used to convert 10 grams of chloroform from -40 C to 70 C?
3 steps, one for C, D and E
What is the difference between boiling and evaporation?
In boiling, the heat source causes liquid to turn into gas bubbles starting at the bottom and throughout the liquid.
In evaporation, the heat source causes surface liquid to escape as gas.
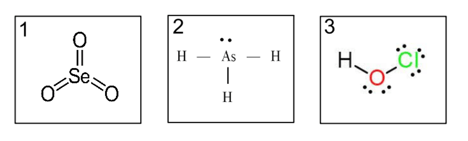
Which has the strongest intermolecular forces?
3. has H-bonding, the strongest intermolecular force which needs to be overcome in order to boil this substance.
2. has dipole-dipole forces
1. has LDFs
What type of solid is composed of nonmetal atoms that form a lattice held together with covalent bonds? Which forces must be overcome to melt this type of solid?
Network covalent solid, covalent bonds.

What phase transition occurs if you go from 0.5 atm at 100 C to -200 C?
gas to solid= deposition
Calculate the total amount of energy it takes to convert 10.0 g of water from -2.0 C to 105 C. (cs: 2.108 J/gC, Hfus: 334 J/g, cl: 4.184 J/gC, Hvap: 2330 J/g, cg: 1.996 J/gC)
qtotal=30,965.96= 31,000 J
1. q=(10)(2.108)(0-(-2))=42.16 J
2. q=(10)(334)=3340 J
3.q=(10)(4.184)(100-0)=4184 J
4. q=(10)(2330)=23300 J
5. q=(10)(1.996)(105-100)=99.8 J
NaCl is a solid at room temperature while water is liquid at room temperature, which has a lower enthalpy of fusion?
Water, it has weaker intermolecular forces which allow it to be in liquid form at room temperature.
NaCl has strong intermolecular forces which hold it together as a solid at room temperature.
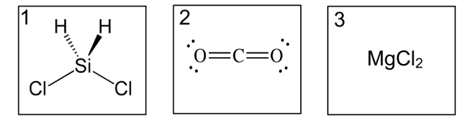
Put these structures in order from strongest to weakest intra/intermolecular forces.
3. MgCl2 has ionic bonds, this is stronger than the dipole dipole forces in 1 and the LDFs in 2. This means it takes more energy to break the ionic bonds to melt the solid=highest heat of fusion.
Which atom would the dipole point towards in a molecule of H-Cl?
Chlorine, it is more electronegative.
