The process by which indivudals explain the causes of behaviors and events?
What is Attribution
The belief that people get what they deserve and deserve what they get
What is just-world phenomenon
When an individual is influenced by superficial cues rather than the actual content of the message (celebrity)
Peripheral persuasion
A individual's unique and relatively stable patterns of thought, emotion, and behavior
Personality
Psychoanalysis is associated with which psychologist
Freud
The tendency to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition
What is Fundamental Attribution Error
The belief that one’s own culture or ethnic group is superior to other.
What is Ethnocentrism
Making a small request first increasing tolarger request
Foot in the door
Psychoanalytic theory proposed that childhood sexuality and unconscious motivations influence personality.
Who is Sigmund Freud
Pleasure principle demands immediate gratification → largely unconscious reservoir of psychic energy that strives to satisfy basic drives to reproduce, survive and aggressive drives
Id
The tendency to attribute positive outcomes to internal factors and negative outcomes to external factors (I win the game is “I played well”; I lose the game is “the judges are unfair”)
What is Self-serving bias
When a belief persists even if evidence suggests it is not accurate. The tendency of believing only information that confirms your beliefs and ignore those against your ideal.
What is Belief perseverance?
The tendency of individuals to align their beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors with those of a group or majority standard.
Conformity
Theory focusing on understanding individuals inner capacities and growth as a whole, unique beings with inherent worth and potential for self-fulfillment and growth.
What is Humanistic
The view of human behavior as a dynamic interaction between the conscious mind and unconscious mind.
Psychodynamic theories of personality
When people are exposed to a stimulus repeatedly over time, which causes them to like the stimulus more
What is Mere exposure effect
 The mental discomfort that occurs when actions or attitudes are in conflict.
The mental discomfort that occurs when actions or attitudes are in conflict.
Cognitive dissonance
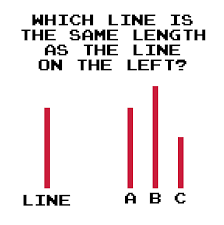
This conformity is associated with whom?
Solomon Asch
The process of realizing and fulfilling one’s potential and capabilitie
Self-actualizing
The theory that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts, as well as, the associated treatment techniques to expose and interpret these unconscious tensions.
Freud’s psychoanalysis
When people behave in ways that elicit behaviors from others that confirm their beliefs or perceptions about themselves or others
What is Self-fulfilling prophecy
Students tend to befriend students that are more like them than they do with people they dont relate to.
ingroup bias
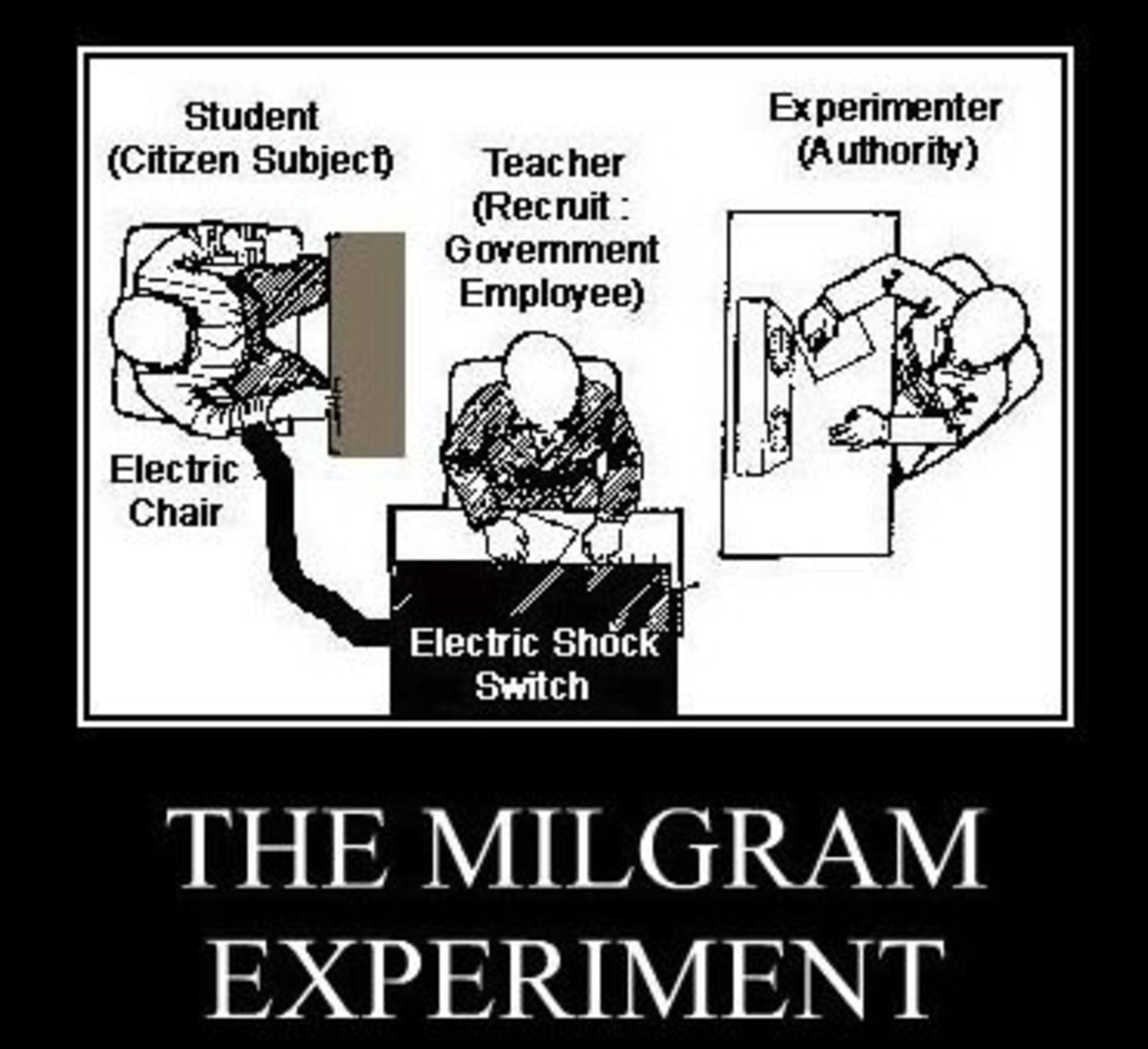 This famousexperiment studied?
This famousexperiment studied?
obedience
Accepting and valuing a person without conditions or limitations
Unconditional regard
The ______ focuses on morality principals, how we ought to behave. It strives for perfection, judging actions and producing positive feelings of pride or negative feelings of guilt. Someone with an exceptionally strong _____ may be virtuous yet guilt ridden; another with a weak _____ may be outrageously self-indulgent and remorseless.
Superego
Belief that internal qualities of others make them successful (e.g. intelligence, personality, motivation and hard working habits)
What is Dispositional attributions
The branch of psychology concerned with the way individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by others.
Social psychology
A psychological phenomenon that occurs when the desire for harmony and conformity in a group leads to irrational or dysfunctional decision-making
Groupthink
Exploring the interaction between people’s traits (including their thinking) and their social context.
Social-cognitive theories
Operating on the reality principle, seeks to gratify the id’s impulses in realistic ways that will bring long-term pleasure. Contains our partly conscious perceptions, thoughts, judgments, and memories.
Around age 4 or 5, Freud theorized, children recognizes the demands of the newly emerging superego, the voice of our moral compass (conscience) that forces the __ to consider not only the real but also the ideal.
Ego