With this compromise, ___________ would enter as a free state and _______________ would enter as a slave state.
Maine, Missouri
_____________ was a phrase describing the belief that America was to expand and settle the entire continent
Manifest Destiny
After the Mexican War, this issue became the most persistent question dividing Americans as new territories were added to the United States.
whether slavery would spread across the United States
California was admitted to the Union as a free state, the New Mexico and Utah territories were organized using popular sovereignty, the slave trade was abolished in Washington, DC, and a new and more effective fugitive slave law was enacted under which compromise?
Compromise of 1850
In this 1857 case, the Supreme Court ruled that enslaved people were property, not citizens, intensifying tensions between North and South
Dred Scott v. Sandford
Slavery would be prohibited north of the _______________ except for Missouri
36°30” Line
What was it called when the people of New Mexico and Utah could vote to allow or ban slavery?
Popular Sovereignty
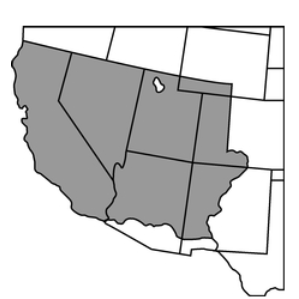 The shaded territory was gained at the close of which of the following conflicts?
The shaded territory was gained at the close of which of the following conflicts?
The Mexican-American War
During the Compromise of 1850, A stronger __________________ was created that allowed Southerners to recapture slaves in the North
Fugitive Slave Law
After Abraham Lincoln’s victory in this 1860 event, Southern states—fearing he would abolish slavery—began to secede from the Union
Election of 1860
This 1820 agreement tried to keep the peace by maintaining an equal number of free and slave states in Congress.
Missouri Compromise
In the years before the Civil War, this growing sense of loyalty to one’s own region rather than the nation deepened the divide between North and South.
sectionalism
Signed in 1848, this treaty ended the Mexican-American War, ceded vast territories to the United States, and included a $15 million payment to Mexico.
Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo
The Compromise of 1850 ended the ______________ in Washington, DC.
Slave Trade
This 1854 act let settlers in Kansas and Nebraska decide on slavery for themselves, angering Northerners who believed it violated the Missouri Compromise.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Known as a champion of Manifest Destiny, this president oversaw U.S. expansion through the Oregon Territory and the Mexican Cession
James K. Polk
the territories the United States gained after the Mexican-American War (1848)
California, New Mexico, and Utah
This 1850 agreement admitted California as a free state, strengthened the Fugitive Slave Law, and tried—unsuccessfully—to ease tensions between North and South
Compromise of 1850
This abolitionist’s 1859 raid on Harpers Ferry made him a hero in the North and a feared villain in the South, deepening the divide between the two regions.
John Brown
In 1855, pro-slavery Missourians crossed the border to vote illegally in Kansas's first territorial election, leading to violent clashes between pro-slavery and anti-slavery settlers
Bleeding Kanas