Actin and myosin are attached to each other at a ______________.
Z-line
What attaches muscles to bone?
Tendons
Name the following muscle:

Biceps brachii
Name the following muscle:

Quadriceps group
What causes muscles to burn? What does the burning sensation signal?
Muscles burn due to lack of oxygen; burning sensation is a sign to stop exercising in order to prevent muscular injury
Actin and myosin interact to pull the muscle fiber towards the ______________, shortening the muscle fiber.
M-line
What is the cellular membrane that surrounds each muscle fiber?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (sarcolemma)
Name the following muscle:
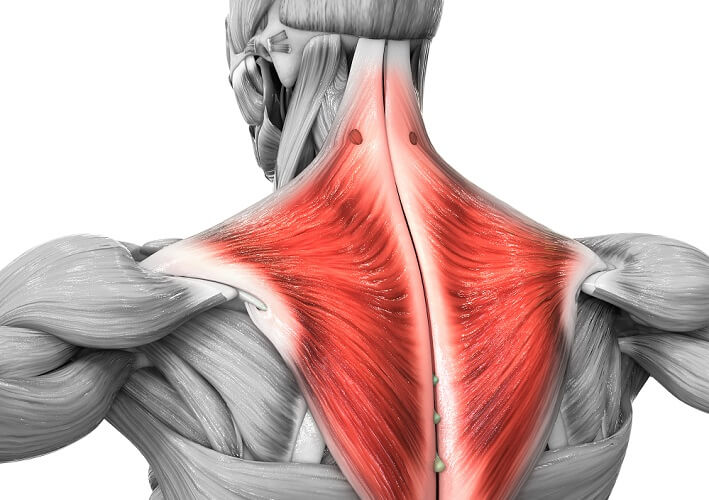
Trapezius
Name the following muscle:

Deltoid
What is the middle of the muscle called?
The belly
How much ATP is used in each myosin/actin cross-bridge cycle?
1 ATP molecule
List and describe the 3 different types of muscle tissue
Skeletal: striated; voluntary-attached to bones
Cardiac; striated; involuntary- found in the heart
Smooth; non-striated; involuntary- lines most internal organs
Name the following muscle:
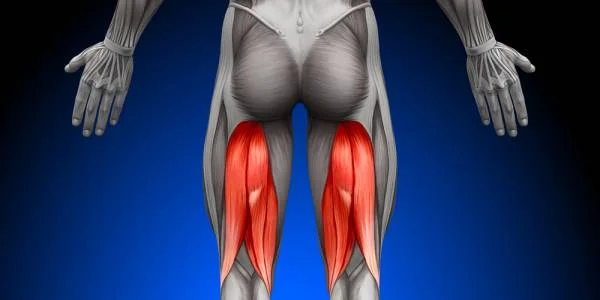
Hamstrings
Name the following muscle:
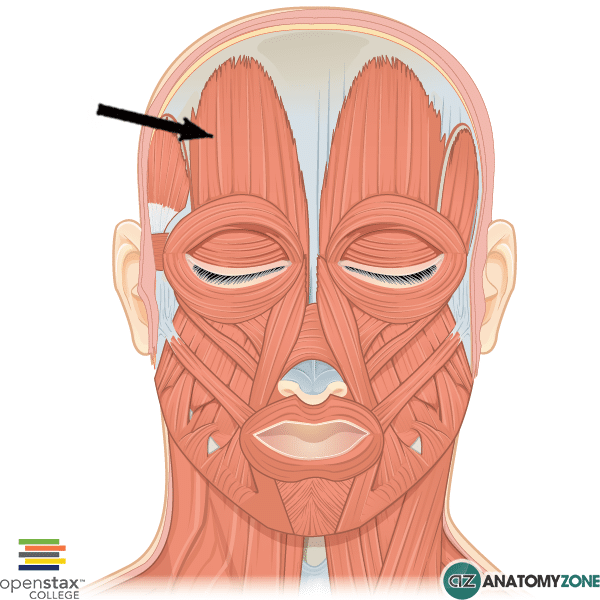
Frontalis
Define prime mover & antagonist.
The prime mover is the muscle that is contracting (doing all of the work) and the antagonist is the muscle that is relaxing
What is oxygen debt?
A difference occurs between the amount of oxygen available and the amount required (You become out of breath)
What are the major tasks of the muscular system?
-Movement
-Heat production
-Maintaining posture
Name the following muscle:
Pectoralis major
Name the following muscle:

Gastrocnemius
List the characteristics of muscle tissue
Elasticity
Contractability
Extensibility
Excitability
What is required to move myosin heads? What type of ions move to allow the myosin heads to attach to the active site?
ATP
Calcium ions
List the levels of organization of a muscle from largest to smallest (Hint: start with Epimysium --> muscle)
Epimysium
Muscle
Perimysium
Fascicle
Endomysium
Muscle fiber
Myofibril
Myofilaments (Actin & Myosin)
Name the following muscle:
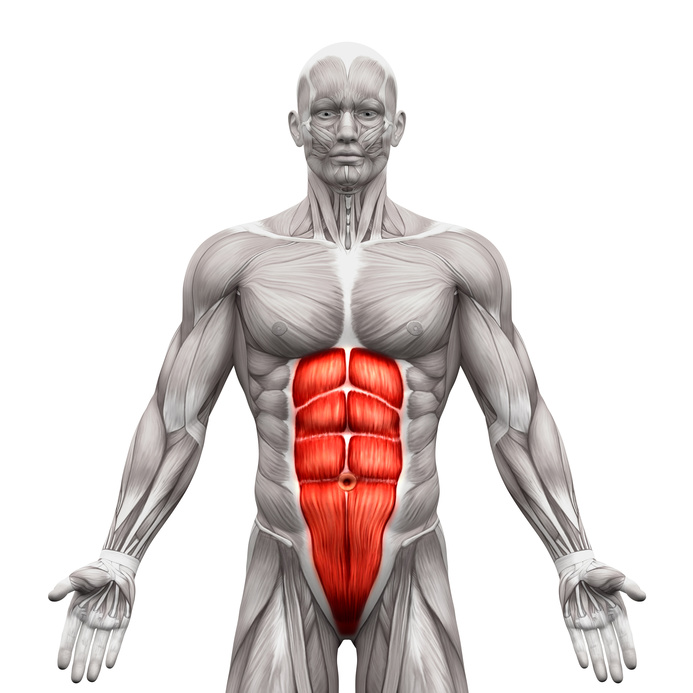
Rectus abdominus
Name the following muscle:

Latissimus dorsi
Define origin and insertion and give an example.
The origin is the part of the muscle that attaches to the stationary bone and the insertion is the part of the muscle that attaches to the movable bone.
Example: Biceps attach to scapula (origin) and radius (insertion)
