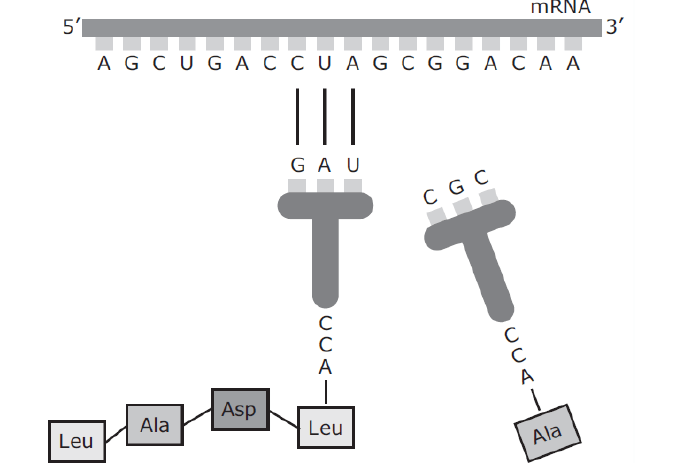
What is the purpose of this process?
-To replicate the DNA of an organism before cell division
-To assemble nucleotides in an mRNA chain along a DNA template
-To synthesize amino acids used to unzip strands of DNA and copy the genetic code
-To translate the genetic code into a specific sequence of amino acids
-To translate the genetic code into a specific sequence of amino acids
Nitrogenous bases are located on both strands of the DNA double helix. What is the significance of the nitrogenous bases?
-The number of adenines and cytosines determines the type of RNA that will be produced.
-The order of nitrogenous bases determines the order of amino acids in the proteins synthesized.
-The amount of thymine and guanine in the DNA molecules determines the length of the genes.
-The type of hydrogen bonding between the nitrogenous bases determines which amino acid will be added to the peptide chain.
-The order of nitrogenous bases determines the order of amino acids in the proteins synthesized.
A mutation in the DNA sequence might have which of the following consequences?
-A different trait being seen
-Change in the mRNA produced
-Change in the shape the mitochondria
-Change in the type of protein produced
-The cell membrane collapses inward
-A different trait being seen
-Change in the mRNA produced
-Change in the type of protein produced
Organisms can be classified based on homology, which is shared characteristics inherited from a common ancestor. In the past, homologies were based on studies of anatomical structures and patterns of embryonic development. In more recent years, the use of molecular biology techniques has allowed homologies to be compared at the level of nucleotide sequences.
Nucleotide sequence comparisons are possible because all organisms share which of the following?
-DNA bases
-Cellular organelles
-Division of the nuclear chromosomes
-Types of proteins needed for cellular functions
-DNA bases
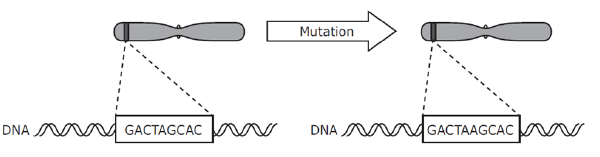
Which statement(s) describes the mutation in the diagram?
-A silent mutation results in the insertion of a different amino acid.
-A nucleotide, with adenine, is inserted into one strand of the DNA.
-A deletion of a cytosine base occurs.
-A substitution occurs between the thymine and cytosine.
-A nucleotide, with adenine, is inserted into one strand of the DNA.
Which of the following mutations would have the potential to affect future generations of a species?
-A frame shift mutation in the X chromosome of a cheek cell
-A point mutation in the Y chromosome of a kidney cell
-A insertion mutation in the first chromosome of a sperm cell
-A substitution mutation in the third chromosome of a uterus cell
-A insertion mutation in the first chromosome of a sperm cell
There are several theories about the origin of the DNA. Which of the following is NOT one of those theories?
-DNA and RNA were formed at the same time.
-There was a molecule that had characteristics of both DNA and RNA and later developed into two separate molecules.
-DNA formed from RNA.
-DNA arose from a carbohydrate combining with nitrogen-containing compounds.
-DNA arose from a carbohydrate combining with nitrogen-containing compounds.
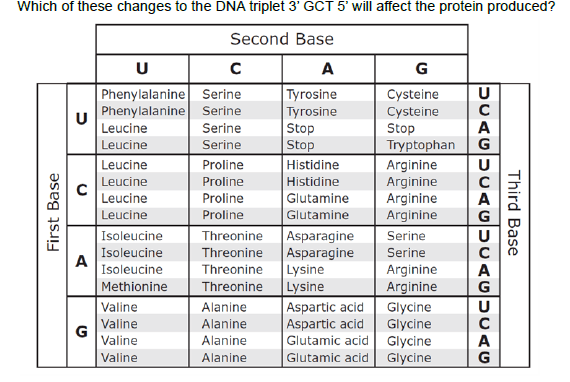
-GTT
-TCT
-TCC
-GCA
-GTT
Chromosomes are composed of two types of biomolecules. One of the biomolecules inchromosomes is called DNA, which functions as the genetic code. The other biomolecules inchromosomes are called histones, which bind the DNA tightly for cell division. Genes in DNAhave the code for making histones.
Based on the information above, which types of biomolecules are in chromosomes?
-Carbohydrates and lipids
-Proteins and nucleic acids
-Proteins and carbohydrates
-Nucleic acids and carbohydrates
-Proteins and nucleic acids
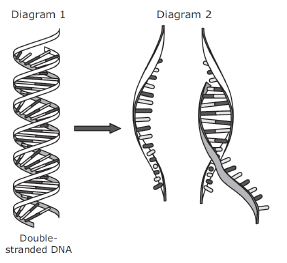
The initial steps in gene expression are modeled in the two diagrams on the left. Double-stranded DNA first unwinds into two strands. Which process and product are represented in Diagram 2?
-Process: transcription; product: mRNA
-Process: translation; product: protein
-Process: replication; product: tRNA
-Process: recombination; product: polymerase
-Process: transcription; product: mRNA
Which of these is the direct result of an error in the transcription of a DNA nucleotide?
-The nuclear membrane is ruptured.
-Amino acids do not bond to tRNA.
-A codon sequence is incorrect.
-Transportation of mRNA does not occur.
-A codon sequence is incorrect.
Which of the following processes involves the synthesis of a complementary RNA strand from a DNA template?
-Mutation
-Replication
-Translation
-Transcription
-Transcription

What type of mutation is depicted in this sequence?
-Substitution
-Insertion
-Deletion
-Frameshift
-Substitution
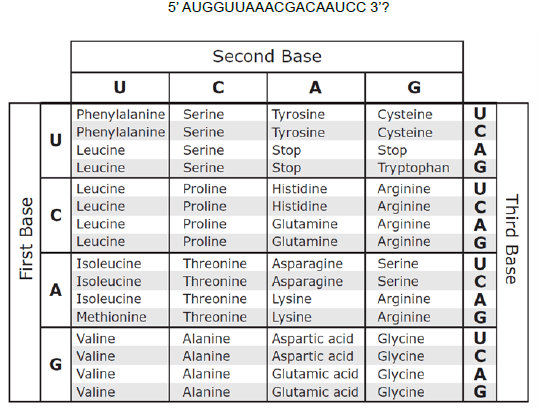
Identify the polypeptide that is coded for by the mRNA sequence:
Methionine - Valine - Lysine - Arginine - Glutamine - Serine
Differences in traits such as hair texture are determined by differences in -
-the location of sugar groups in DNA
-the sequence of nucleotides in DNA
-the number of nitrogenous bases in DNA
-the molecules attached to the phosphate in DNA
-the sequence of nucleotides in DNA
Which of the following best describes a frameshift mutation?
-A mutation that results in a premature stop codon
-A mutation that inserts or deletes a base, altering the reading frame
-A mutation that substitutes one base for another
-A mutation that duplicates a segment of DNA
-A mutation that inserts or deletes a base, altering the reading frame
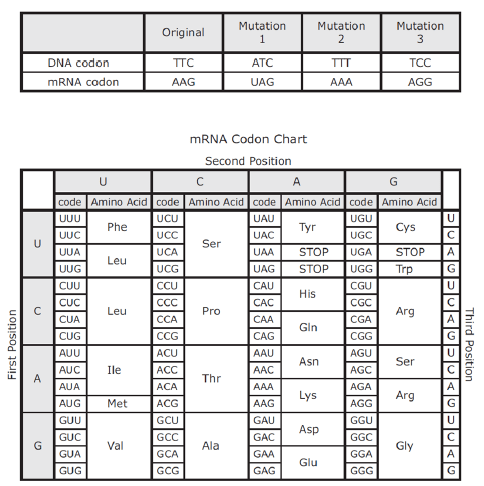
Which mutation will cause translation to stop?
-Mutations 1 and 3 only
-Mutation 1 only
-Mutation 2 only
-Mutations 1, 2, and 3
-Mutation 1 only
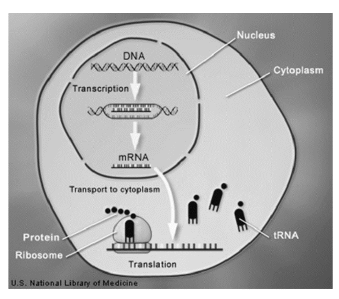
Observe the illustration of the protein synthesis process. What statement correctly describes part of the process in the diagram above?
-The growing protein has the amino acids in the sequence coded by cytoplasm.
-The two subunits of the ribosome translate the DNA code into mRNA codons.
-DNA is transcribed into ribosomes to form proteins in the cytoplasm.
-Anticodons on tRNA pair with mRNA codons to join amino acids to form proteins.
-Anticodons on tRNA pair with mRNA codons to join amino acids to form proteins.
The following are some steps that take place when protein synthesis occurs in the cell.
A. A specific anti-codon on transfer RNA bonds to a specific codon on messenger RNA.
B. Amino acids bond together to form a polypeptide chain.
C. Messenger RNA is produced using DNA as a template.
D. Messenger RNA attaches to the ribosome.
C,D,A,B
Are the statements below true or false:
Transcription is the process by which genetic information from DNA is copied into a complementary RNA molecule.
Translation is the process by which the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA is used to build a protein.
DNA → RNA (Transcription) → Protein (Translation)
True
Think of transcription and translation like writing and reading a book.
1. Transcription: Copying the book's text (DNA) into a draft (RNA).
2. Translation: Reading the draft (RNA) and building the book's meaning (protein).