This geologic principle states that: In undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are found on the bottom."
What is the Geologic Principle of Superposition?
This is a definition for Absolute Age Dating.
Answers will vary, but should be similar to: "What is the numerical age, in years, of a rock or object?"
This type of fossil happens when minerals fill the spaces between an organisms tissues. Then the tissues decay and leave the minerals behind.
What is a Mineral Replacement? (aka permineralization/petrification)
These are the preserved remains or evidence of ancient living things.
What is a fossil?
This is the largest division of Geologic Time.
What is an EON?
This geologic principle states that: "Rocks that contain a section of another rock were deposited after the rocks that are found inside of them."
What is the Principle of Inclusions?
This is a definition for Relative Age Dating.
Answers will vary, but should be similar to: "What is the age of rocks and geologic features compared with other rocks and features nearby."
This type of fossil is created when an organism becomes completely encased by a substance like tar or ice, that keeps the organism from decaying.
What are Preserved Remains?
These are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
What are Isotopes?
This is the smallest division of geologic time, excluding "Ages."
What is an Epoch?
This geologic principle states that: "Features that pass through or across other layers of rock were formed after the layers of rock that they transverse."
What is the Principle of Cross Cutting Relationships?
How much of a radioactive isotope is remaining after two half-lives?
What is 25%, or 1/4?
This type of fossil forms when gases and liquids are squeezed out of the organism by heat and pressure. It leaves only the Carbon Atoms behind.
What is a Carbon Film?
This is the time required for half of an unstable parent isotope to decay into a stable daughter isotope.
What is a half-life?
This geologic division of time is larger than an Epoch, but smaller than an Era.
What is an Period?
This geologic principle states that: "Layers of sedimentary rock are first formed in flat layers going side to side."
What is "Original Horizontality?"
Use the diagram of the rock wall to tell how the "Star" fossil relates to the "Lightning" fossil.
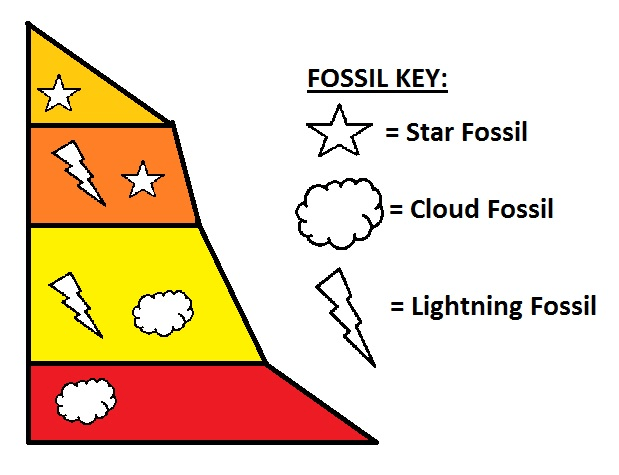
What is the "Star" Fossil is younger than the "Lightning" fossil, but they both existed at the same time?
This type of fossil is made when a mold gets filled in.
What is a Cast?
These are species that existed on Earth for a short length of time, were abundant, and inhabited many locations.
What are Index Fossils?
This geologic Division of Time is larger than a Period, but is smaller than an Eon.
What is an Era?
This geologic principle states that: "Layers of rock initially extend out in all directions (side to side). Similar layers that are separated by an erosional feature are the same layer."
What is Lateral Continuity?
Using the Half-Life Graph of Uranium 238 predict how old a sample is that contains 12.5% of the parent isotope.
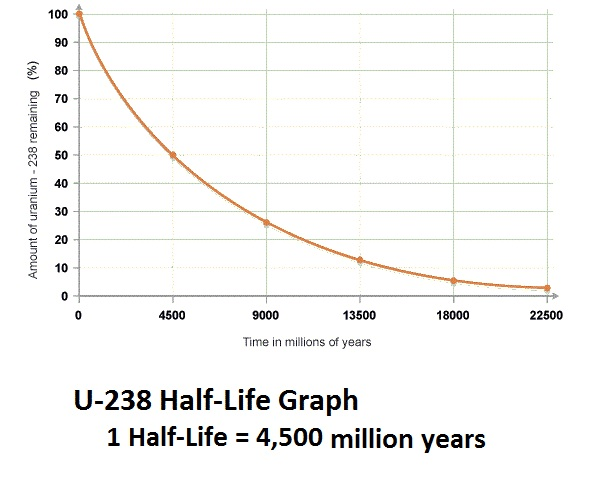
What is 13,500 million years, or 13.5 billion years old?
This type of fossil does not contain the actual living thing. It is evidence that the living thing existed.
What is a Trace Fossil?
This is the process of an unstable element naturally changing into another element that is stable.
What is Radioactive Decay?
This is how scientists decided where to place divisions in geologic time.
What are major changes to the fossil record?