Genetics
the study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics.
segregation
separate 
phenotype
the physical and psychological characteristics of an organism from both genetics and environment
Codominance
a relationship between two versions of a gene.
zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
trait
a trait or character is a feature of an organism.
gamete
the cells used during sexual reproduction to produce a new individual organism or zygote.
genotype
Genotype is the collection of genes responsible for the various genetic traits of a given organism. 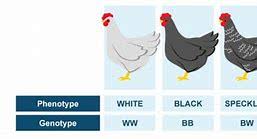
multiple alleles
Three or more alternative forms of a gene (alleles) that can occupy the same locus.
offspring
offspring are the young born of living organisms, produced either by a single organism or, in the case of sexual reproduction, two organisms.
hybrid
a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction.
probability
theoretical probability can be used to calculate the likelihood that offspring will be a certain sex, or that offspring will inherit a certain trait or disease if all outcomes are equally possible.
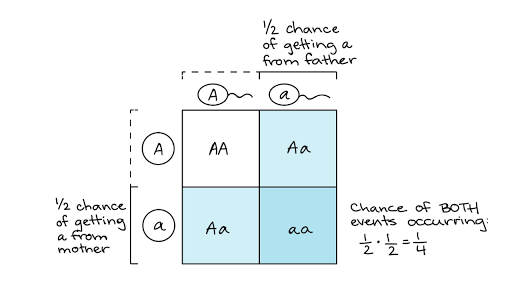
punnett square
The Punnett square is a square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment 
polygenic trait
one whose phenotype is influenced by more than one gene.
blood type
A, B, AB, and O. Blood types are based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells.
Gene
A gene is the fundamental, physical, and functional unit of heredity.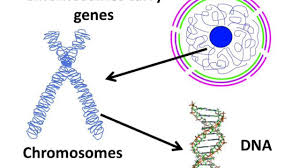
Homozygous
homozygous dominant, if it carries two copies of the same dominant allele, or homozygous recessive, if it carries two copies of the same recessive allele.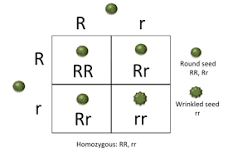
Independent
Assortment
formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis 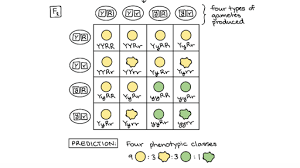
Homologous
Chromosomes
a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis.
Meiosis
In biology, meiosis is the process by which one diploid eukaryotic cell divides to generate four haploid cells often called gametes.
Allele
An allele is one of the possible forms of a gene. Most genes have two alleles, a dominant allele and a recessive allele. 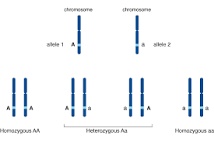
Heterozygous
In diploid organisms, heterozygous refers to an individual having two different alleles for a specific trait. 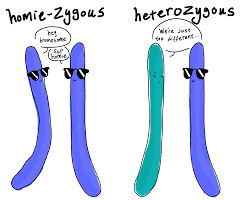
Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete dominance is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. 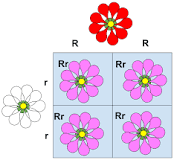
diploid
(of a cell or nucleus) containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
empty
empty