What process is happening in the image?
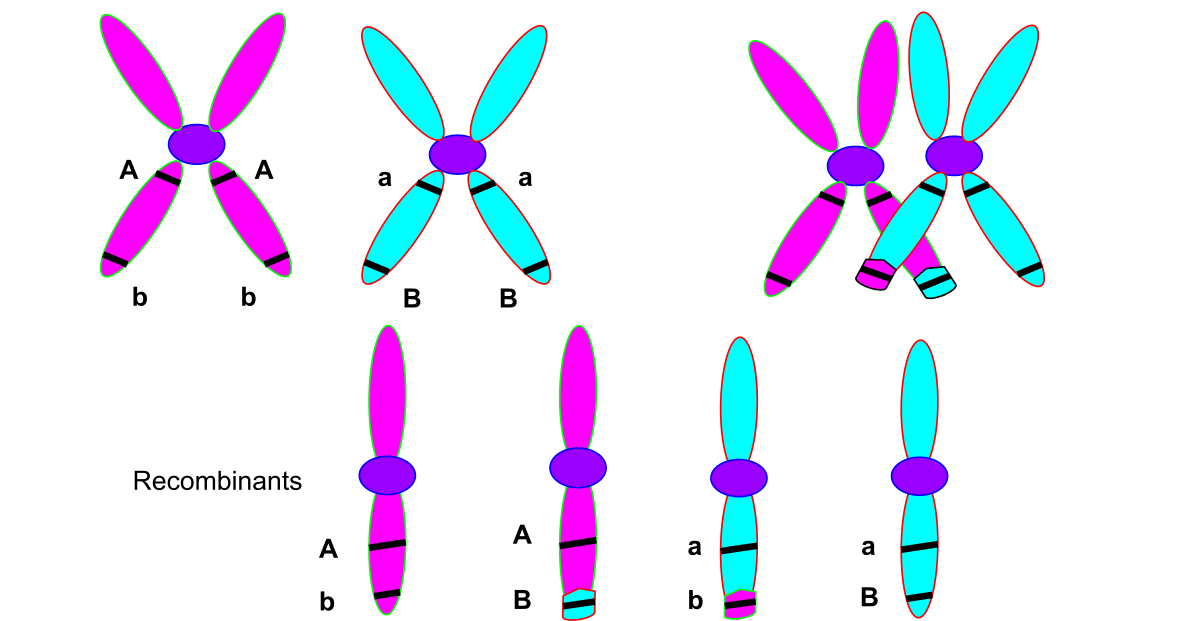
Crossing over
What cellular process forms egg and sperm cells?
Meiosis
What occurs during S phase of the cell cycle?
DNA is replicated
What happens when a cell can no longer control their rate of growth?
Cancer forms
Somatic cells of Asian elephants contained 56 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would its gametes contain?
28
How does sexual cellular reproduction affect genetic variation?
Sexual cellular reproduction produces genetically new individuals, increasing genetic variation.
What type of cell division is depicted below?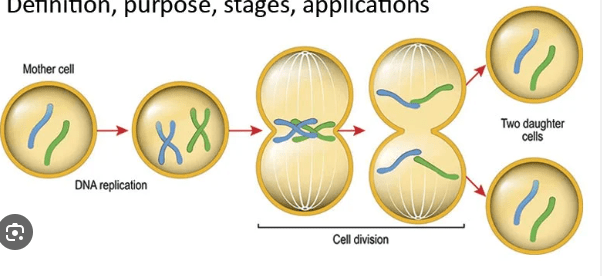
Mitosis
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in plants. If a plant with 48 chromosomes reproduces asexually, how many chromosomes will the new individual contain?
48
What stage of mitosis is depicted in the image below?
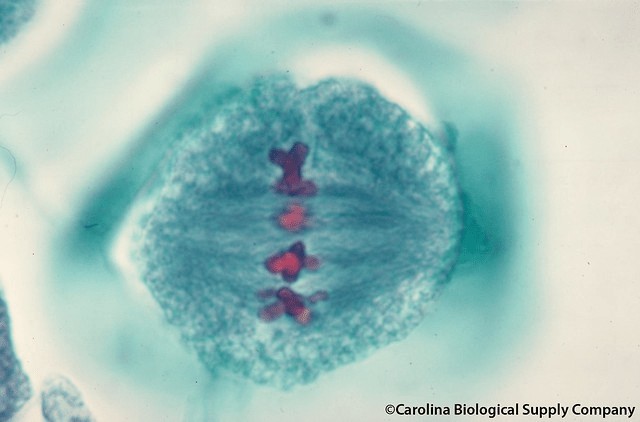
Metaphase
How does meiosis contribute to genetic variation?
crossing over
Identify process 1 and 2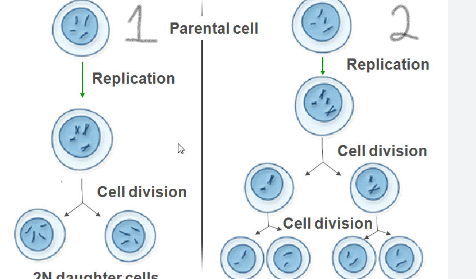
1 mitosis
2 meiosis
What cellular process allows an embryo to grow?
Mitosis
Where does cell division take place? (A, B, C, or D)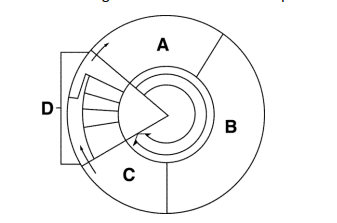
Section D
What structure separates the sister chromatids and isolates them to opposite poles of the cell?
spindle fibers
Describe the cells produced by meiosis.
(# of cells produced, haploid/diploid & genetic variation)
Four haploid daughter cells that are genetically unique
Which process produces genetically identical daughter cells?
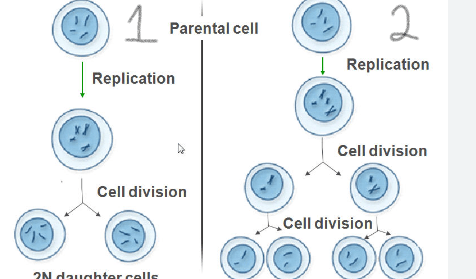
1
In what cells does binary fission take place?
Prokaryotic
Which phase of the cell cycle directly prepares for cell division? (Name 1 specific phase)
G2
Describe the cells produced by mitosis.
(# of cells produced, haploid/diploid & genetic variation)
2 diploid daughter cells that are genetically identical
Which meiotic process creates different combinations of genes within the egg and sperm cell?
Crossing Over
Describe how metaphase is different in Meiosis and Mitosis.
In metaphase 1 of meiosis, homologous chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate and then separate.
This does not happen in mitosis.
Describe the product of binary fission.
(# of cells produced, haploid/diploid & genetic variation)
2 diploid cells that are genetically identical