the attractive force between objects; the force that moves objects downhill
Gravity
a period of the year that is distinguished by special climate conditions; due to the Earth's tilted axis; different parts of the Earth receive the Sun's most direct rays
Seasons
the periodic rise and fall of the level of water in the ocean
Tides
the partial or total blocking of one object in space by another
Eclipse
the amount of matter in an object
Mass
the scientific law that states that every object in the universe attracts every other object
The Law of Universal Gravitation
the spinning motion of a planet on its axis
Rotation
What causes tides?
The moon's gravitational pull
the movement of an object around another object
Revolution
Describe weight
a measure of the force of gravity acting on an object
What causes planets to orbit the Sun rather than the Sun to orbit the planets?
The Sun has a greater mass than the planets.
What causes seasons?
The tilted axis
the tide with the least difference between consecutive low and high tides
Neap Tide
Draw a Lunar Eclipse

What is the difference between mass and weigh?
Weight varies depending on where the object is in the solar system
What are the variables of gravity?
distance and mass
What season is the northern hemisphere.
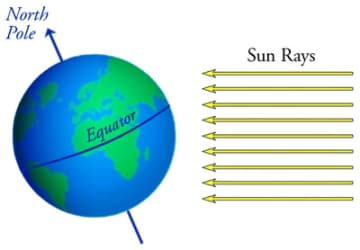
Winter
That is a Spring tide?
the tide with the greatest difference between consecutive low and high tides
Draw a Solar Eclipse.

Weight _________ depending on where the object is in the Solar System.
Fill in the blank
varies
Both the Sun and the Moon affect Earth's tides, but the Moon's affect is greater than the Sun's. Why?
The Sun has more mass than the Moon, but the Moon is much closer to Earth than the Sun, so its gravitational force on Earth is greater.