Two major types of mutations.
What are point and frameshift?
The driving force of artificial selection.
The process that creates new species.
What is speciation?
The study of fossils.
What is paleontology?
Something a cladogram cannot tell you.
What is time?
When a mutation causes no change in the protein.
What is silent?
The measure of an organism's survivability.
What is fitness?
Two methods of speciation.
What are behavioral and geographic isolation?
Structures that are build the same but have different functions.
What are homologous structures?
Something a cladogram does tell you.
What are evolutionary relationships?
When a mutation causes change but continues.
What is missense?
The driving force of natural selection.
What is survival of the fittest?
The result of behavioral or geographic isolation.
Structures that are built different but have the same function.
What are analogous structures?
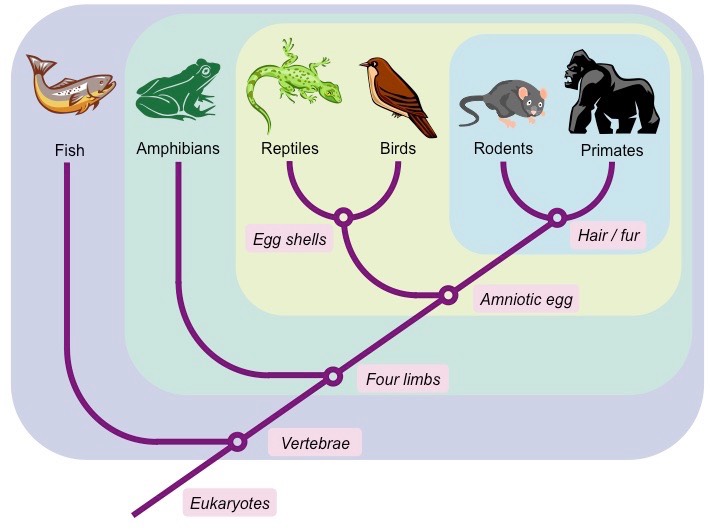
The oldest organism on this chart.
What are fish?
Initial: AATTGG
New: TATTGG
What is point substitution?
The majority of the future population of our butterflies.
What are blended?
A new river flows through a colony of rabbits. This results in new rabbit species.
What is geographic isolation?
Leftover structures that used to be helpful but no longer serve a function.
What are vestigial structures?
The most closely related group to reptiles.
What are birds?
Initial: AATTGG
New: ATTGG
What is frameshift deletion?
The four principles of natural selection.
What are variation, competition, extra offspring, and fitness?
Birds from the same area sing different songs and do not mate together.
What is behavioral isolation?
The study of embryos.
What is embryology?

The youngest group(s) on this chart.
What are rodents and primates?