_______ are non reactive because they have a full octet/duet of valence electrons.
noble gases
Which of the following elements is the most reactive: Sr, Y, V
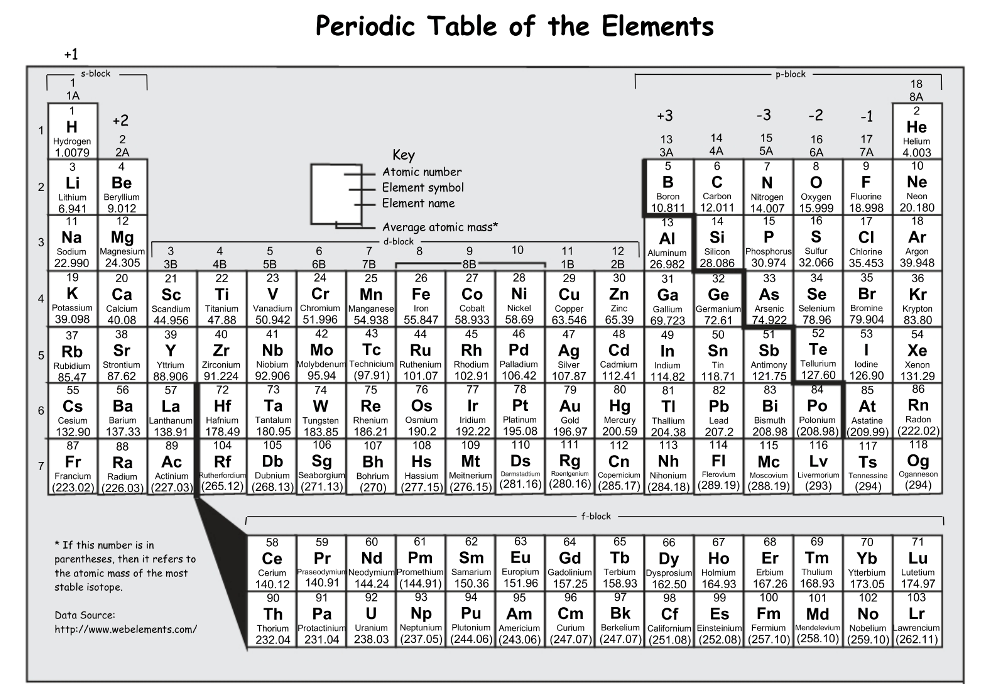
Sr, it would have the highest reactivity of the metals listed because it is the closest to Fr
Describe hydrogen
diatomic, combustible, can lose, gain, or share its electron, extreme circumstances creates metallic properties, can create a hydrogen bond
Sort the following into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids: Br, Na, B, Mn, Te, O
Metal: Na & Mn
Nonmetal: Br & O
Metalloid: B & Te
Does this show a periodic trend?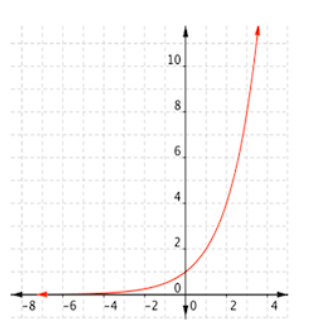
No (there is no discernible repeating pattern)
The nuclear charge of sulfur is ________.
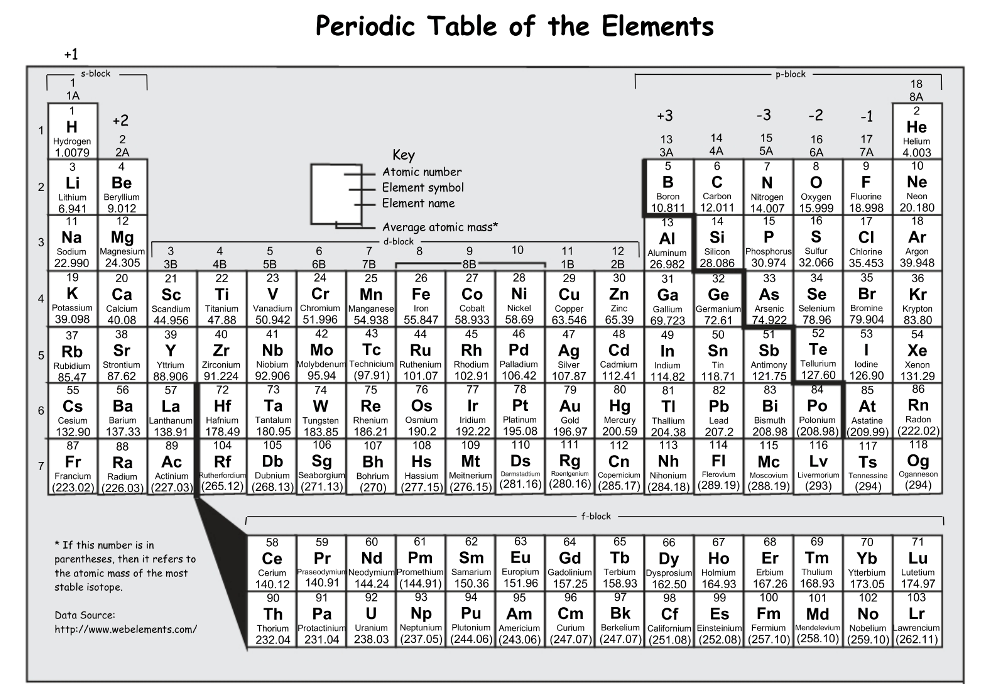
16 (there are 16 protons)
Which has a larger atomic radius: Ti or Y
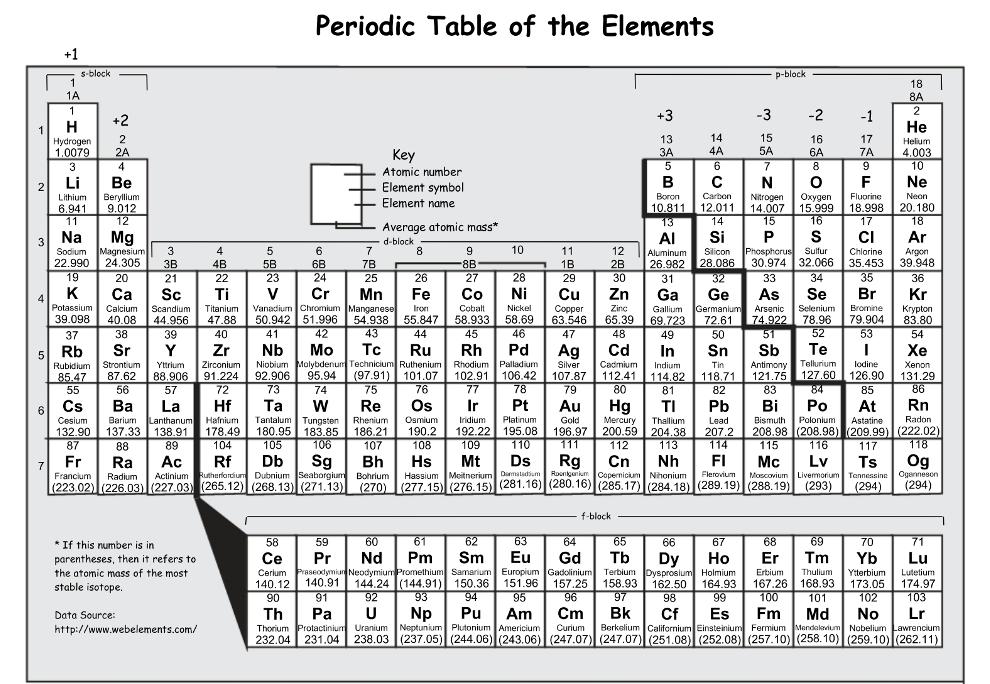
Y: atomic radius increases down a group and decreases across a period, we also know that helium has the smallest radius so the further an element is to He the larger it will be
Describe polonium.
Discovered by Pierre and Marie Curie. High toxic and radioactive. Can be found in pitchblende and tobacco.
Do the following elements have similar properties: P, Bi, Sb
Yes (all elements are in group 15, elements in the same group tend to have similar chemical and physical properties)
Does the graph below represent a periodic trend?
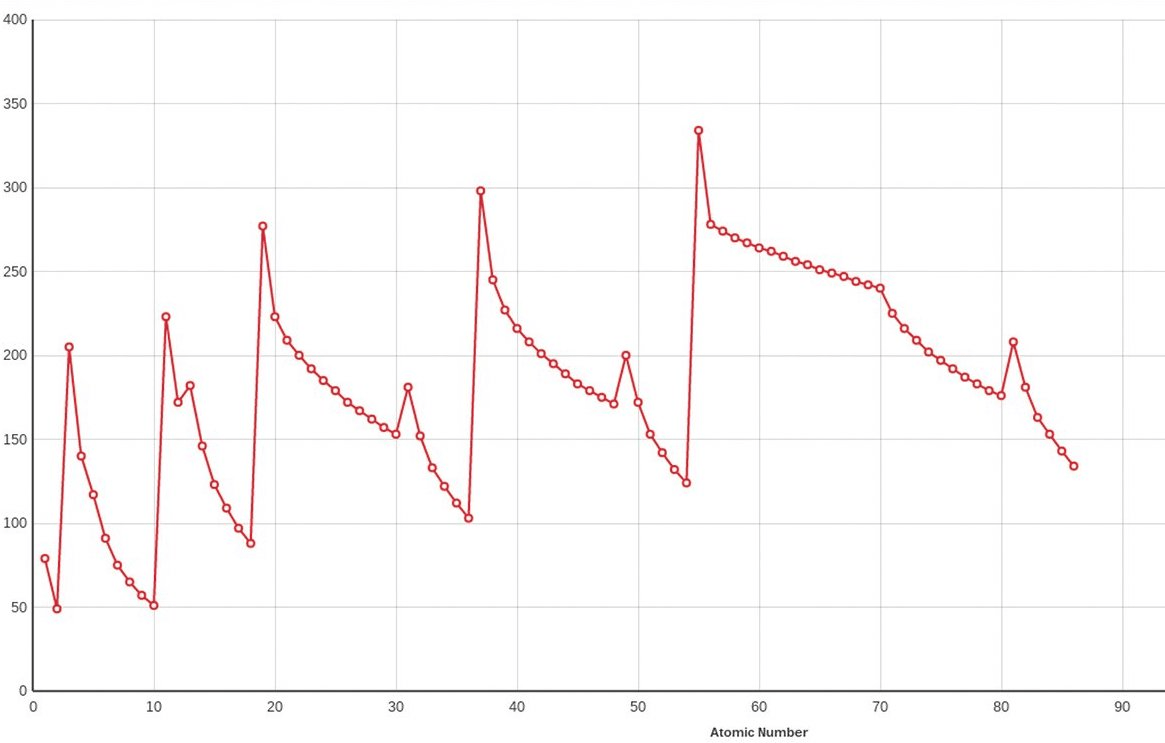
Yes (repeating pattern)
The number of valence electrons in an atom of As?
As has 5 valence electrons (in group 15 or 5A)
[Ar]4s²3d104p³
Which has a larger atomic radius: Ti or Y
Y: atomic radius increases down a group and decreases across a period, we also know that helium has the smallest radius so the further an element is to He the larger it will be
Describe carbon
basis for all life, found in starts and the atmospheres of most planets, 3 allotropes (amorphous, graphite, and diamond), also buckminsterfullerene (C60)
Where are the representative (main group) elements located?
s & p blocks
TRUE or FALSE When moving left to right across a group effective nuclear charge is increasing thus causing the atomic radius of an atom to decrease and ionization energy in increase.
TRUE
The effective nuclear charge of sulfur is _________.
16-10 = 6
(atomic number - inner electrons = effective nuclear charge)
Which element has a lower ionization energy?
S or Si
Si: ionization energy increases across a period, both elements are in period 3 so the element further to the left would have a lower ionization energy (also Si is further from He)
Describe nitrogen
needed in the form of nitrates and nitrite for plant growth, used in hydrazine which is rocket fuel, Oswald process used to make nitric acid
Do the following elements have similar properties: W, Pt, Au, Hg
No (they are all in period 6, but not a part of the same group)
What are the other terms used for columns and what are the other terms used for groups on the periodic table?
Columns are also known as groups and families.
Rows are also known as periods.
In what energy level are the valence electrons of zirconium and how many does it contain.
[Kr]5s24d2
2 valence electrons, 5th energy level
What element has the higher electronegativity?
N or P
N (nitrogen), electronegativity tends to decrease down a group
(the closer an atom is to fluorine on the periodic table the more electronegative the atom is)
What are chemical and physical properties of metals?
What are chemical and physical properties of nonmetals?
What are chemical and physical properties of metalloids?
Metals: mostly solid at room temperature, malleable, shiny, ductile, good conductors
Nonmetals: mostly gases at room temperature, brittle, dull, poor conductors
Metalloids: properties depend on the conditions that the element is under
Which group of transition metals are considered coinage metals because they are non-reactive/stable
Group 11 (Cu, Ag, Au)
Periodic means _________.
Repeating
The number of valence electrons contained by the noble gases.
8, except He which has 2
Which of the following elements is the most reactive:
P, Ar, Br
Br, it would have the highest reactivity of the nonmetals listed because it is the closest to F after recognizing the Ar is automatically the lease reactive since it is a noble gas
Which two elements do not follow the metal, nonmetal, metalloid patterns of the periodic table?
Hydrogen is a nonmetal
Aluminum is a metal
State the properties, valence electrons, and most likely charge for:
alkali metals, alkaline earth, chalcogens, halogens, and noble gases
alkali metals (group 1): soft, shiny, very reactive, 1 valence electron, forms +1 charge
alkaline earth metals (group 2): shiny, silvery-white color, low melting points, 2 valence electrons, forms +2 charge
chalcogens (group 16): name refers to ores of copper (that contain oxides and sulfides and trace amounts of selenium and tellurium), 6 valence electrons, tend to form -2 ions
halogens (group 17): high electronegativities, are diatomic elements, highly reactive, 7 valence electrons, tend to form -1 charge
noble gases (group 18): non-reactive, odorless, colorless gas, 8 valence electrons, do not form ions (due to stable electron configurations)
Where are the s,p,d,f blocks?
Where are the metals, metalloids, and nonmetals located?
Where are the representative, transition, and inner transition elements located?
s block (columns 1-2), p block (columns 12-18), d block (columns 3-12), f block (bottom two rows)
metals (left of the stairs), metalloids (touching the stairs), nonmetals (right of the stairs)
representative (s and p blocks), transition (d block), inner transition (f block)