What is biomass energy? Be able to give examples of solid biomass fuel sources. Understand benefits/disadvantages of each.
What type of carbon is released when biomass is burned?
- Biological material that has mass --> a large class of fuel types that include: wood, charcoal, animal products/manure, plant remains, solid waste, & biofuels. Inexpensive & abundant. Makes up 40% of renewable energy in U.S.
1. Wood: derived from woody materials (trees). Relatively inexpensive form of heating/cooking. Potentially renewable if trees are not overharvested.
2. Charcoal: woody material that’s been heated in the absence of oxygen so that water & VOCs are driven off. Relatively inexpensive form of heating/cooking. Potentially renewable if trees are not overharvested. People in developing worlds use wood to make charcoal because it's lighter, it contains 2x as much energy as wood, the fires produce less smoke & the fires don’t need to be constantly tended. BOTH WOOD & CHARCOAL --> Produce major air pollutants when burned like particulates, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and carbon dioxide.
3. Manure: waste products from animals. Cost effective when wood/charcoal is not available. Produces air pollution when burned.
- Modern carbon: Carbon in biomass that was recently in the atmosphere & captured thru photosynthesis. Burned & returned to the atmosphere and then taken up by replacement vegetation. No net increase in CO2 concentrations over long periods of time (carbon neutral; in theory).
What is solar energy? Where in the United States is the most solar energy produced? Where in the world is the most solar energy produced?
- Produced by the Sun every day (fusion). Amount of solar energy depends on cloudiness, time of day, season, & geography/topography.
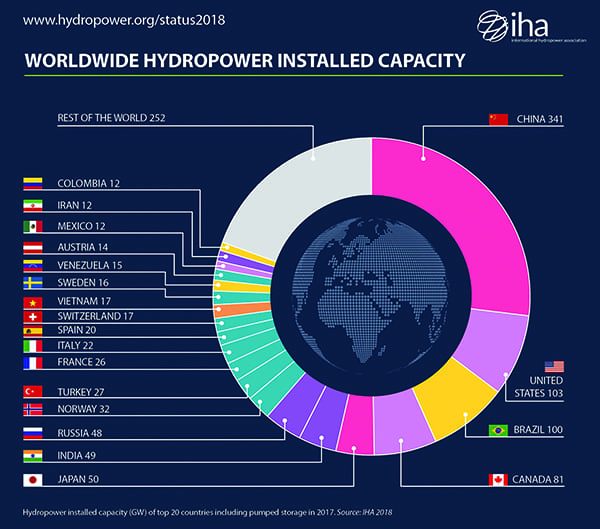
What is hydroelectric energy? How does it work?
Where in the United States is the most hydroelectric power produced?
Where in the world is the most hydroelectric power produced?
- Electricity generated by the kinetic energy of moving water. 2nd most used form of renewable energy (after biomass).
- Moving water has kinetic energy. Water turns turbine → turns generator → generates electricity. Electricity generation is based on flow rate of water & vertical distance water falls (higher flow rate = more kinetic energy = more electricity; greater distance = more potential energy = more electricity).
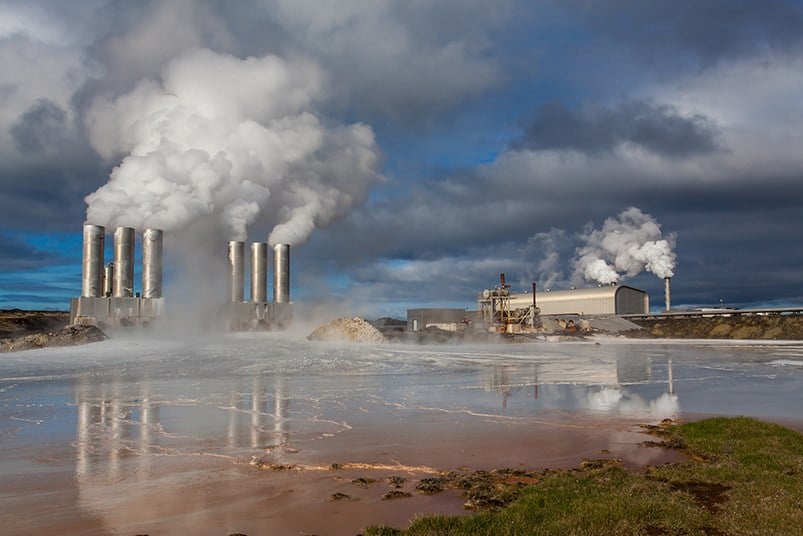
What is geothermal energy? How can it be used to produce electricity?
Who produces the most geothermal energy? In what part of the country?
Where is geothermal energy produced?
- Geothermal energy - heat energy that comes from the natural radioactive decay of elements within Earth
- Electricity: Produced as convection currents bring magma toward surface. Magma heats groundwater → driven to surface by pressure or by drilling. Can heat water directly (as Magma moves towards the surface) or indirectly (cold water is pumped down, heated, & pumped back up). Water is heated --> creates steam --> turns a turbine --> turns a generator --> generates electricity.
- Globally:
Location: Along plate boundaries!
What is energy conservation? What are some ways you can conserve energy throughout your daily life? How can governments help with energy conservation?
What are phantom loads?
- Energy Conservation: using less energy to do the same activities. Some energy is always lost as unusable heat. Must consider losses to fully account for energy conservation savings (Amount of energy saved = Sum of energy not used + energy that would have been lost during conversion).
- Governments: Can implement measures that encourage or require strategies to use less energy. Includes increasing efficiency of appliances/vehicles , improving availability of public transport, increasing taxes on fossil fuels, & offering rebates/tax credits for using less energy, energy efficient options, & renewables.
- Phantom Loads: Electrical demand by a device that draws electrical current, even when it is turned off. AKA vampire power.
What are biofuels? Know the differences between and benefits/disadvantages of ethanol & biodiesel.
- Biofuels: liquid fuel created from processed or refined biomass
1. Ethanol: Alcohol made by converting starches & sugars from plant material into alcohol and CO2. Added to traditional gasoline. Comes from corn, sugarcane, and switchgrass. Produced using fossil fuels. Periodically related to food shortages. Less efficient than traditional gasoline (lower gas mileage --> more fuel to go same distance).
2. Biodiesel: A diesel substitute produced by extracting & chemically altering oil from plants. Direct substitute for petroleum-based diesel. Comes from (land-intensive) soybean oil (vegetable oils), animal fat, or greases. Can only be used in diesel engines (harder on engines than traditional diesel).
3. Cellulosic ethanol: a biofuel produced from non-food plant materials like grasses, wood chips, and agricultural waste. Lower carbon footprint than traditional ethanol. Includes fuels made from algae.
What is the difference between passive and active solar energy? Know examples of both.
What are the benefits/disadvantages of solar energy?
- Passive: A use of energy from the Sun that takes advantage of solar radiation without active technology. Energy cannot be stored. Ex: Solar ovens --> concentrates sunlight/absorbs solar energy. Used for boiling water, cooking, etc. Other examples include type of material used for construction, direction of windows, use of dark/light colors for sunlight absorption.
- Active: A use of technology that captures & stores the energy of sunlight with electrical equipment & devices. Include small-scale solar water heaters, photovoltaic solar cells, & large-scale concentrating solar thermal systems.
Pros: No CO2 production. No air/water pollution during operation. Used during peak demand. Economically feasible (pays for itself eventually). Subsidization can lower costs.
Cons: PV cells = $$$ to manufacture/install, require toxic metals which must be mined, & require industrial chemicals. High start-up costs & long time to pay back (5-20 years). Environmental costs associated with manufacture, disposal, & recycling of batteries. Energy lost during charging, storage, & recovery of electricity in batteries.
What are water impoundment systems? What is a reservoir?
What dam produces the most hydroelectric power in the U.S.? What dam produces the most hydroelectric power in the world?
What are some pros/cons of water impoundment systems?
What are some benefits of dam removal?
- The storage of water in a reservoir (artificial lake where water is stored) behind a dam. Most common method. Allows for generation on demand.
- Most Hydro Power in U.S.: Grand Coulee Dam, WA
- Most Hydro Power in the World: Three Gorges Dam, China
- Pros: Large amounts of electricity produced with no air pollution. Cheaper electricity & higher net energy yield. Provides downstream flood control. Provides recreational & economic opportunities ($$$).
- Cons: Large land disruption (habitat loss) due to flooding. Leads to loss of agricultural land & aesthetic/archaeological sites. Alter dynamics of river ecosystem downstream --> affect species whose life cycles depend on seasonal variations in water flow & kills fish. Displacement of people. Release of greenhouse gases as CO2 (production of cement) & methane (decomposition of dead plants/organic material). Leads to standing water → mosquito breeding grounds. Construction = $$$. Accumulation of sediment. Dam failure --> flooding.
- Dam Removal: Removal leads to Habitat restoration, Less danger of failing structures (consider $$ of repair), & Restores fish populations & migration routes.
- Pros: Renewable & sustainable energy source. Consistent and reliable power source, especially close to tectonic plate boundaries. Less environmental impact than fossil fuels.
- Cons: Less potential for growth (not easily accessible everywhere, requires drilling wells to reach heated groundwater, is expensive, & requires access to groundwater, which can be depleted). Fossil fuels generated during construction. Hazardous gases & steam are produced during electrical production (i.e. - hydrogen sulfide --> rotten egg smell & methane --> potent greenhouse gas).

What is peak demand? What factors affect peak demand?
What is the difference between a brownout and a blackout?
What is variable pricing?
- Peak Demand: The greatest quantity of energy used at any one time. Depends on time of day, season, & weather. Inability to meet peak demand can lead to brownouts and blackouts.
- Brownout: partial power outage
- Blackout: total power outage
- Variable Pricing: A way to encourage less electricity use during hours of peak demand. Customers pay less to use electricity when demand is low (nights/weekends) & more when demand is high.
What are hydrogen fuel cells? What chemical reaction takes place?
- An electrical-chemical device that converts fuel, such as hydrogen, into an electrical current. Can continue to produce electricity for as long as fuel is added.
- Electricity generated by reaction of hydrogen & oxygen into water & energy. Forces protons & electrons in different directions → electrical current. Only waste products = water & energy.
How do solar water heating systems work?
Allows heat energy from the Sun to be transferred directly to water/liquid → hot water heating system.
Can be driven by a pump (active) or by convection (passive) as cold water is heated by a solar collector.
Can include use of nontoxic antifreeze.
Know examples of ways that fish move around water impoundment systems.
- Fish Ladders: A structure that allows migrating fish passage over or around an obstacle on a river.
- Fish Passages:
- Salmon Cannons: Made to transport salmon between bodies of water to restore migratory patterns.
What are ground source heating pumps? How do they work?
- A technology that transfers heat from the ground to a building (below ground temps fairly constant year-round (50-60℉)). Cycles fluid thru pipes buried underground. Technically a form of solar energy because the ground retains heat from Sun. Can be used anywhere & are energy efficient.
- In winter: fluid absorbs heat & is compressed → increases temps. Heat is distributed through house. As fluid expands → cools → completes cycle again.
- In summer: Underground temps are lower than air. Fluid cooled underground & pulls heat from house as it circulates.
What is sustainable design? What are some examples of sustainable design?
- Sustainable Design: Designing objects, the environment, & services to comply with the principles of ecological sustainability while improving the health/comfort of occupants. Includes good community planning (building homes close to where residents work), passive solar heating in home design, green roofs, & using recycled building materials.
What are the pros and cons of hydrogen fuel cell technology?
Where is this technology predominantly used?
- Pros: Hydrogen = energy carrier. The production of electricity for electrolysis with wind/solar/geothermal → sustainable energy carrier. Hydrogen gas → used to generate more efficient electricity.
- Cons: Requires supply & transportation of hydrogen. Free hydrogen = rare because it bonds with other molecules → water, methane, etc. Hydrogen must be separated using heat/electricity (fossil fuels). Hydrogen gas = explosive. Storage of hydrogen gas in vehicles requires large tank under high pressure. Possibility of leaks/ruptures. Electrolysis (The application of an electric current to water molecules to split them into oxygen & hydrogen) requires electricity. Electricity can be generated with renewables but is generally generated using fossil fuels.
- Used predominantly for transportation (I.e. - fuel cell vehicles)!
How do photovoltaic systems work? What materials are used?
What are the pros & cons of PV systems?
- A use of energy from the Sun as light, not heat, & converting it directly into electricity. Certain (silicon) semiconductors (thin, ultra-clean layers of material) generate low-voltage electrical current when exposed to direct sunlight. Can be used to charge batteries (for future use) or to power appliances/lights far from electrical grids.
- Pros: No emissions during operation. Can produce electricity during peak demand. Economically feasible (5-20 years payback then basically free). Use of net metering allows you to store & receive credits for solar energy produced.
- Cons: Expensive to manufacture & install. Manufacturing requires mining & the use of energy/water → can release toxic metals & chemicals. Limited by availability of Sun. System must be modified when sunny days are few. Affected by weather & season --> more power in spring/fall (cold, sunny, windy days) & less power during hottest parts of year (more water vapor).
What are run-of-the-river systems? Know some pros/cons.
- Hydroelectric generation in which water is retained behind a low, small dam (or no dam). Water passes through a channel with submerged turbine. Requires no storage in a reservoir.
- Pros: Little flooding & Less disruption to flow of river.
- Cons: Smaller & unpredictable electrical generation. No storage of runoff from rain/snowmelt. Cannot generate when water is low.
What is wind energy? How is wind used to generate electricity? How does the size of the turbine & tower affect electricity generation?
Where is wind energy generated in the U.S.?
- Wind Energy: energy generated from kinetic energy of moving air. Created by Sun --> Solar radiation → ground surface heating patterns → air moving from areas of high to low pressure. Fastest growing source of electricity globally.
- Electricity Generation: Use of wind turbines. Wind turns turbine --> turns generator --> generates electricity. Turbines can be on land or near-shore.
- Size: Longer turbine + longer tower = more electricity generation.
- U.S.:
What does our existing electrical infrastructure look like? How many electrical grids exist?
- Existing: Requires significant upgrades (in power plants, storage capacity, & distribution). Not originally designed to move electricity long distances.
- Grids: Eastern Grid, Western Grid, & Texas Grid.
What are renewable energy sources? What types exist?
- Sources of energy that are infinite
1. Potentially renewable: can be regenerated indefinitely as long as it’s not overharvested
2. Nondepletable: an energy sources that can’t be used up
How and where does concentrated solar thermal (CST) electricity generation work?
What are some of the drawbacks to CST systems?
- Large-scale application of solar energy → electricity. Uses mirrors/lenses used to focus sunlight into small beam. Operate like thermal power plants (sun evaporates water → steam --> steam turns turbine → turns generator → electricity).
- Best constructed in desert areas with consistent sunshine & wide open spaces
- Can lower primary productivity of desert floor. Impact temperatures & humidity → impacts both plant/animal species. Require large amounts of land, large amounts of water, & cannot generate electricity at night.
What is tidal energy? Understand why it's not a major source of energy and where it comes from.
- Tidal Energy: energy that comes from the movement of water driven by gravitational pull of the Moon. Use of gates & turbines in estuaries, rivers, & bays. Not a major energy source (Not enough difference in high/low tides & Transmission lines on/near coastline → negatively impacts coastal ecology & aesthetics).
- CAUSED BY THE MOON
- Pros: Non-depletable, clean, & free energy source. High energy yield. No CO2 emissions (but fossil fuels required to travel to wind farms for construction/maintenance). Easy to manufacture & install. Can share land with other uses.
- Cons: Birds & bats killed by collisions. Visual & noise pollution. Requires a back-up & batteries to store electricity. Can be difficult to dispose of & recycle.
What is the smart grid? Know examples of benefits.
- Smart Grid: An efficient, self-regulating electricity distribution network that accepts any source of electricity & distributes it to end users.
- Benefits: Programs inform electric generators when there is a surplus of energy. Appliances programmed to run during hours of surplus. Can address energy storage concerns.